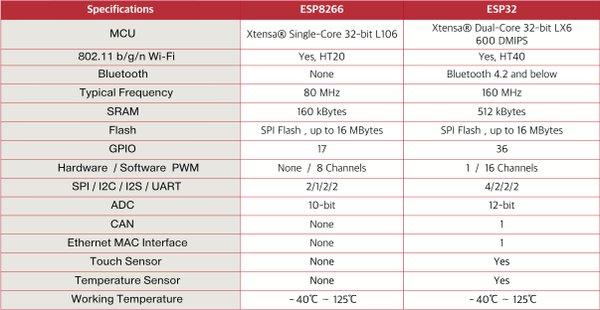
Espressif Systems ESP8266 is a very popular platform for IoT applications relying on WiFi, at least for hobbyists, while Espressif ESP32 is the new solution from the company that adds a CPU core, faster WiFi, Bluetooth 4.2, and various I/Os which should launch very soon. Amica.io released a table showing the main differences between the two processors which are expected to coexist in the market with ESP8266 used in the lower-cost segment, and ESP32 in applications requiring WiFi and Bluetooth, or some of the new interfaces.
Some of the features were clearly listed when ESP32 was first announced, but for example, I was not aware that an Ethernet MAC, and a temperature sensor were built into the new SoC. Other interesting features for the new ESP32 processor include a touch sensor, and hardware PWM both of which are missing in ESP8266.
The new dual-core processor also builds on existing features, as ESP32 provides more GPIO, additional software PWM channels, higher SRAM capacity, and an increased ADC resolution to 12-bit. The operating temperature range remains the same at -40°C to 125°C, as well as the maximum SPI flash capacity of 16 MB.

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress





Has the frequency really doubled? 160MHz is pretty fast for an MCU…
Most ESP32’s are 240mhz actually
This makes ESP32 look really exciting. ESP8266 wasn’t bad but this new one seems even better and it seems to have almost anything you could ask for.
And there are still things hidden in the ESP32 that haven’t been found yet. It is like an Easter Egg hunt!
Is there any data on energy consumption, both in idle when no data is being sent/received, when transmitting, and during periods of max consumption ?
Other than warnings that the ESP8266 demanded a high -power supply due to its high peak current consumption, I have seen little data published on ESP8266 energy consumption, or power management.
@paul
Well there is this, haha: https://mobile.twitter.com/qrs/status/706552734170935296
Is 512k correct? I thought it was closer to 400k and approx 200k free for user app.
@onebir
Esp8266 support already 160mhz cpu frequency so no change with esp32
esp8266 is 80MHz – 160MHz, esp32 is 160MHz – 240MHz. When the 8266 is clocked at 160MHz, wifi reliability goes down. Since the 32 is duel core, I suspect it doesn’t have the same drawback at higher clock speeds.
Any update on how many https sessions will be supported, 8266 is only 1.
what will be the price then, relative to ESP8266
@xxiao
I don’t think they have set the price exactly yet. But that have said “only a little more”.
@John Gentilin
Esp8266 can support multiple SSL if you customize the firmware but ram is limited. With close to 4x as much ram and hardware crypto engine esp32 should support many more. Of course still depends on the right SDK configurations.
Refer to above table,
if ESP8266 really has a second uart, so no need to switch uart from programming and run mode anymore!
“One Single Table” is redundant. But thanks for the post regardless 🙂
Temperature sensor will not be very accurate, since is influenced by the CPU activity. EspressIf also recommend to read temperature before starting the wifi, which also influence the value.
@onebir
Acctually isn’t too fast.. You can find ST and Renesas MCU up to 240 MHz..
Hi, dose the ESP 32 support OTA?
Both ESP8266 and ESP32 support OTA firmware update.
The 8266 does not have an I2C, and only 1 I2S device
What is the support model in US? Staff, locations, FAE?sales?
All of the big distributors in the US/EU carry Espressif now. They should have FAE support.