I’ve started to test BFS 4KH Android TB box featuring HiSilicon HI3798M processor. I’m also the first things I normally do is to check for built-in screenshot support, and if not, I simply install a screenshot app like Screenshot Ultimate. This normally works pretty well, but the firmware is not rooted, and the usual root method for HiSilicon devices does not work, as it fails at the adb root stage with the message: “aabd cannot run as root in production builds”. So I was out of luck, and people who sent the sample for review do not seem to check / answer their email in a timely manner. ScreenShot Ultimate provides “No Capture Method Help“, but I found the instructions long, and it required me to install download and install something extra. So instead I check if I could do something with adb instead.
adb can connect via USB or Wi-Fi, and for most device you’ll have a USB OTG port to connect it to your computer. If developers options are not enabled in Android Settings, go to “About Device”, and click on the build number of 7 times. You should now be able to go to “Developers Options”, and enable USB debugging, something I had to do even though I had to use Wi-Fi since my box does not come with a USB OTG port.
You’ll also need to install adb. In Linux, at least Ubuntu / Debian, it’s easy to install, and I already had this:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install android-tools-adb |
For other OS, you may need to install the Android SDK.
If you are using USB, the setup is done. If you need to use Wi-Fi instead, you’ll need to find your Ethernet or Wi-Fi IP address. After enabling USB debugging, port 5555 should be open:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
sudo nmap -sS 192.168.0.107 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-01-06 12:19 ICT Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.107 Host is up (0.045s latency). Not shown: 988 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE 139/tcp open netbios-ssn 445/tcp open microsoft-ds 5555/tcp open freeciv 7100/tcp open font-service 7777/tcp open cbt 8888/tcp open sun-answerbook 10000/tcp open snet-sensor-mgmt 49152/tcp open unknown 49153/tcp open unknown 49154/tcp open unknown 49155/tcp open unknown 50006/tcp open unknown MAC Address: 00:11:22:36:45:C9 (Cimsys) Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 19.21 seconds |
and try to connection with adb.
|
1 |
adb connect ip_adress |
The rest of the instructions are the same whether you connect via USB or Wi-Fi, For a screenshot, I followed the instructions here to capture an image in a single command:
|
1 |
adb shell screencap -p | sed 's/\r$//' > screen.png |
The sed part is to get rid of the end of line character sent via adb. The image can be found in your PC as screen.png. In my case, the image capture and transfer over Wi-Fi is a little slow, as it usually take around 5 seconds. But at least it works, and it’s even more convenient than using a Screenshot app, at least for my use case.

While I was at it, I also checked about screen recording, and found some instructions on CNET which should work for Android 4.4 and greater.. Basically, you just have to run:
|
1 |
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/video.mp4 |
I have not tried to use the redirection as with screencap command line, because I believe it would have been too slow. So once you are done with recording, press Ctrl+C, get back the video to your PC and optionally delete it on the device to reclaim storage space.
|
1 2 |
adb pull /sdcard/video.mp4 adb shell rm /sdcard/video.mp4 |
That’s the result I got.
No too bad. At first, I thought “Hey, it might be possible to record online video that way!”, but a closer inspection of the file property quickly changed my mind.
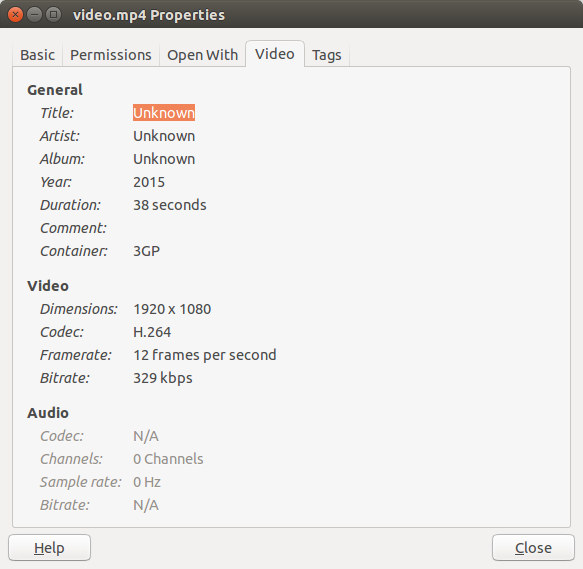
It recorded at 12 frames per second (maybe a limitation of the hardware), and more importantly there’s no audio, so even if you could record a video at a decent framerate, you’d still have to record audio separately, and mix video and audio at a latter stage, not the most convenient way….
More options for screenrecord command can be found on Android Developers’ ADB page, or by running:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
adb shell screenrecord --help Usage: screenrecord [options] <filename> Records the device's display to a .mp4 file. Options: --size WIDTHxHEIGHT Set the video size, e.g. "1280x720". Default is the device's main display resolution (if supported), 1280x720 if not. For best results, use a size supported by the AVC encoder. --bit-rate RATE Set the video bit rate, in megabits per second. Default 4Mbps. --time-limit TIME Set the maximum recording time, in seconds. Default / maximum is 180. --rotate Rotate the output 90 degrees. --verbose Display interesting information on stdout. --help Show this message. Recording continues until Ctrl-C is hit or the time limit is reached. |

Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011.
Support CNX Software! Donate via cryptocurrencies, become a Patron on Patreon, or purchase goods on Amazon or Aliexpress




