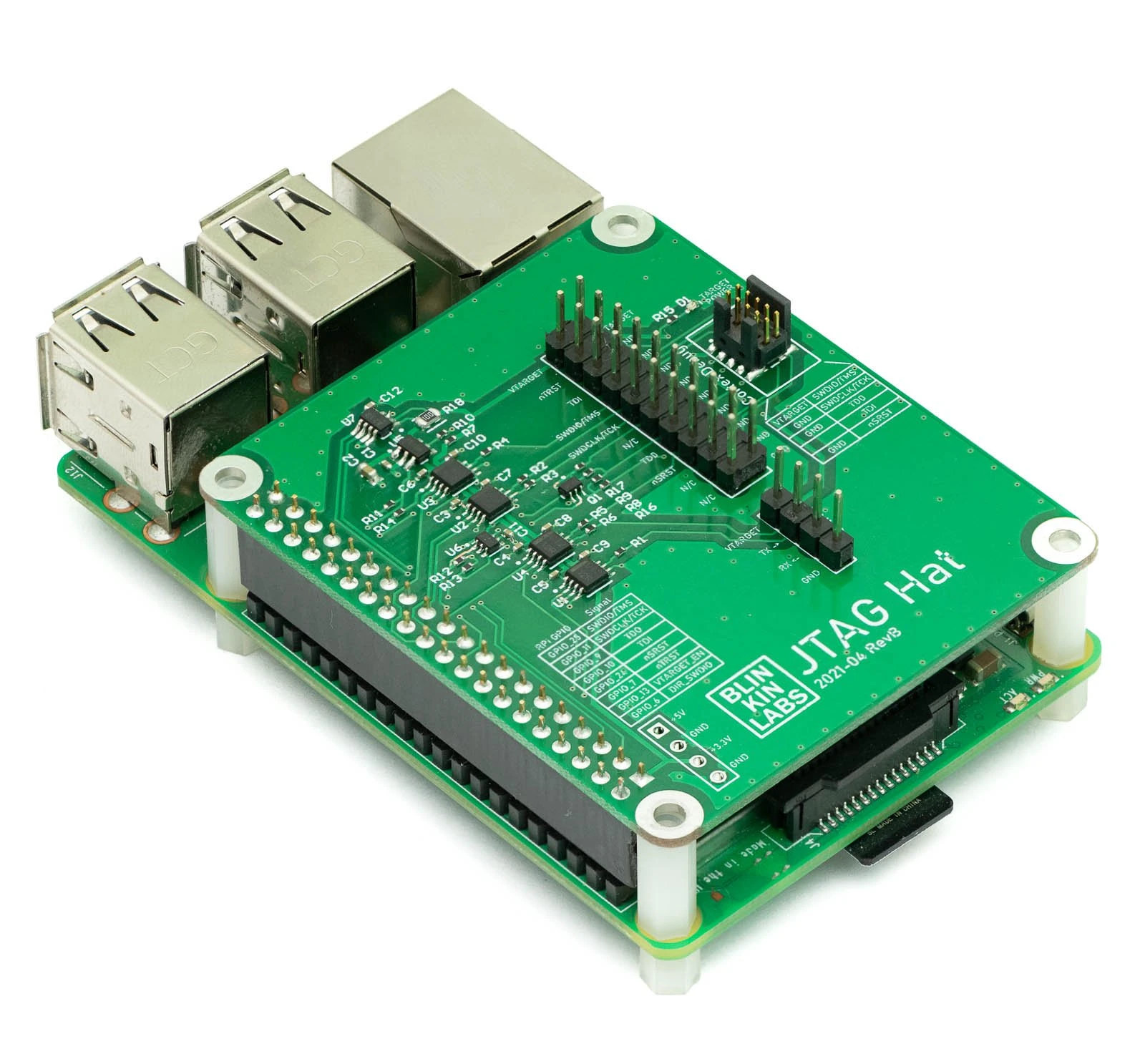
Low-level debugging can be performed with a JTAG debugger and OpenOCD open-source software, but since not everybody may have a JTAG debugger at home, some have reverted to using the Raspberry Pi as a JTAG debugger, and you’ll find instructions for cabling and installing the software on the Internet. Matt Mets of BlinkinLabs have been using the Raspberry Pi SBC and OpenOCD to debug Arm-based microcontroller boards for a while, but found it to be a pain to find jumper wires and look up the pin-outs manually each time. So he designed a JTAG Hat with properly labeled 20-pin .1″ and 1.27mm Cortex debug connectors to speed up the process. The expansion board also adds level-shifting buffers to interface with targets running at 1.8-5V, transistor-based power reset pins, a power switch for optionally supplying 3.3V to the target, a voltage/current sensor for measuring the target power consumption, and a buffered […]
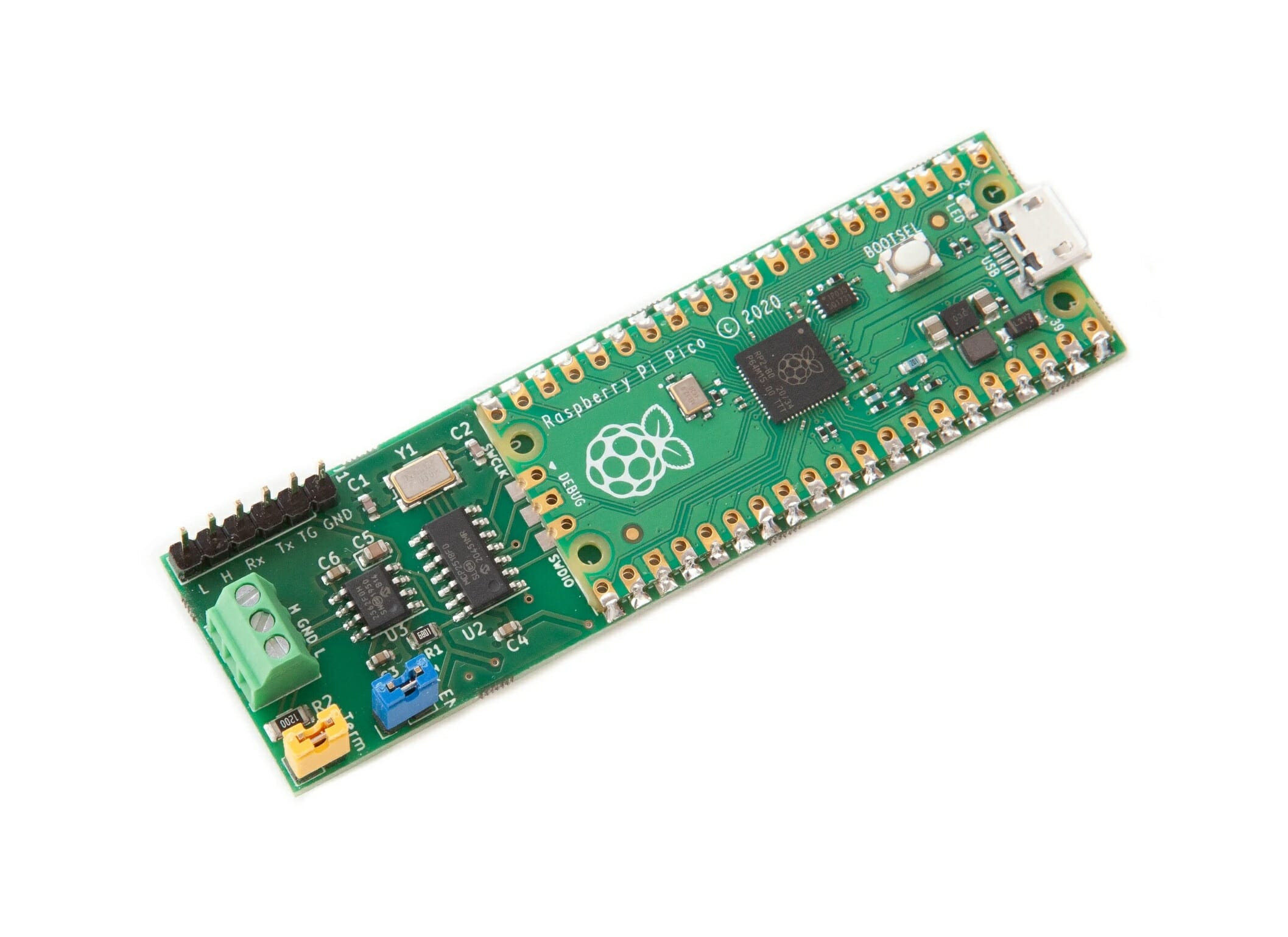
CANPico open-source board adds CAN Bus to Raspberry Pi Pico
Canis Labs’ CANPico board adds a CAN bus to the Raspberry Pi Pico. The open-source hardware board can then be used as a CAN adapter connected to a host computer The company also provides an open-source MicroPython SDK, as well as a pre-built firmware image to quickly make it started, making it possible to easily control or monitor the CAN bus using Python. CANPico specifications: MCU – Raspberry Pi Pico with RP2040 dual-core Cortex-M0+ microcontroller CAN interface through 3-pin terminal block implemented via: Microchip MCP2517/18FD (SPI) CAN controller with 2Kbyte buffer space Microchip MCP2562FD CAN transceiver. Misc Jumpers to connect a standard 120Ω CAN bus termination resistor and for disabling transmit access to the CAN bus 6-pin header for a logic analyzer or oscilloscope to see what’s happening on the bus Dimensions – Approx. 75 x 24mm The MicroPython SDK for CANPico contains two major APIs with CAN and CANHack. […]
First Armv9 cores unveiled – Cortex-A510, Cortex-A710, Cortex-X2
Armv9 architecture was announced in Q1 2021, building upon Armv8 but adding blocks and instructions for artificial intelligence, security, and “specialized compute”, i.e. hardware accelerators or instructions optimized for specific tasks. The company has now introduced the first three Armv9 cores with Cortex-X2, Cortex-A710, and Cortex-A510 cores, providing updates to respectively Cortex-X1, Cortex-A78, and Cortex-A55 cores. The company calls those new cores “Arm Total Compute solutions”. Arm Cortex-X2 flagship core is the company’s most powerful CPU so far with 30% performance improvements over Cortex-X1 and will be found in premium smartphones and laptops. Arm Cortex-A710 “big” CPU core provides a 30% energy efficiency gain and 10% uplift in performance compared to Cortex-A78, while Arm Cortex-A510, high efficiency “LITTLE” Armv9 core delivers up to 35% performance improvements and over 3x uplift in ML performance compared to Cortex-A55 announced four years ago, or about the same performance as the “big” Cortex-A73 cores […]
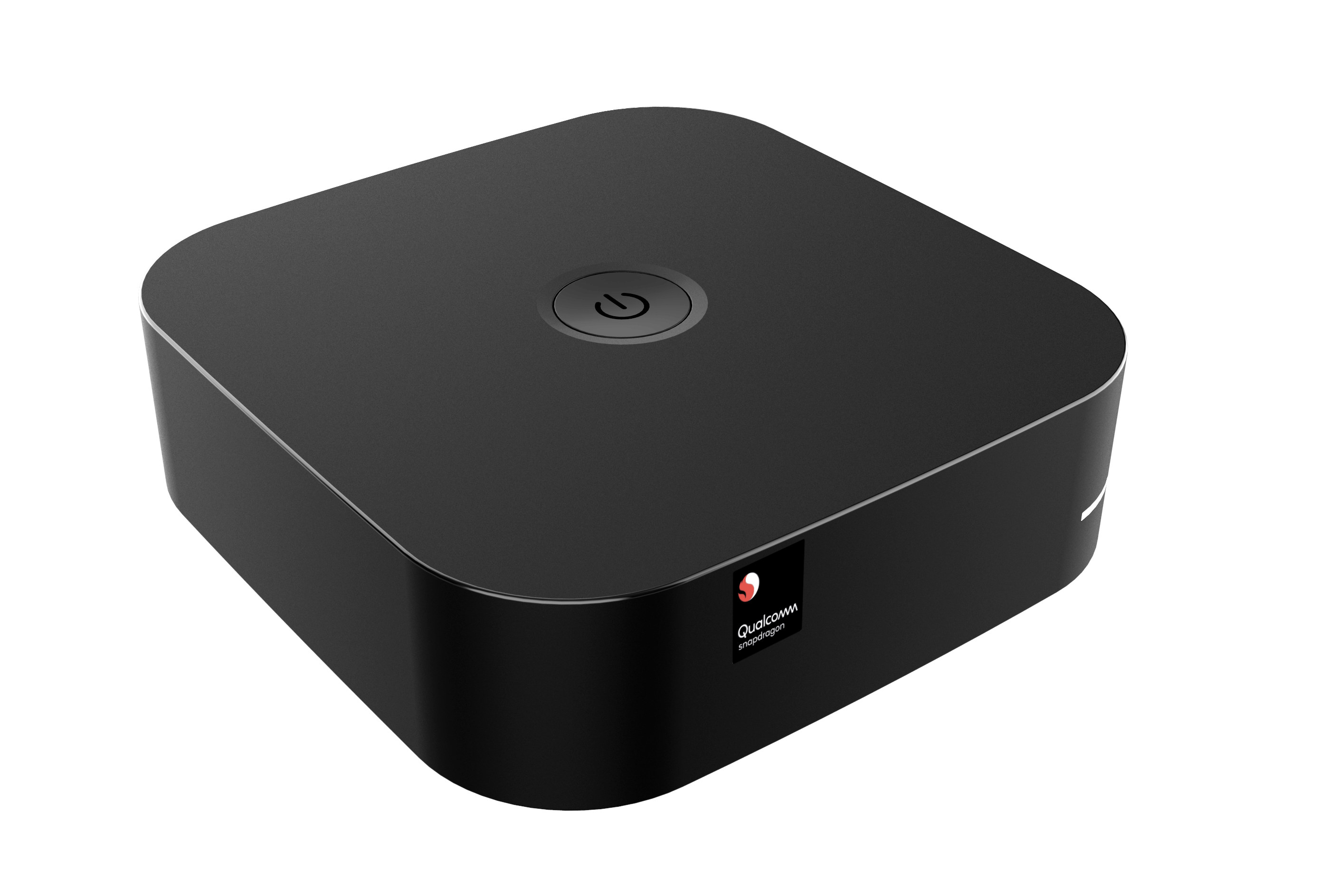
Snapdragon QC710 Developer Kit targets Windows 10 on Arm app development
In order to encourage developers to port their apps to Windows 10 on Arm, Qualcomm and Microsoft have announced the Snapdragon Developer Kit based on a Snapdragon Compute platform and aiming to provide a cost-efficient platform that will be less costly than a laptop. The development kit looks like a mini PC, and while the full specs have not been announced, it could well be powered by the just-announced Snapdragon 7c Gen 2 processor, itself a cheaper version of Snapdragon 7c. Qualcomm did not share photos of all the ports from the developer kit, but the photos we’ve got come with “QC710” file name, and reveal a power button on the top, an LED on one corner, two USB ports, a MicroSD card slot, and a SIM card socket. I’d assume at least one HDMI or DisplayPort at the back, and possibly an Ethernet port, but we just don’t know […]
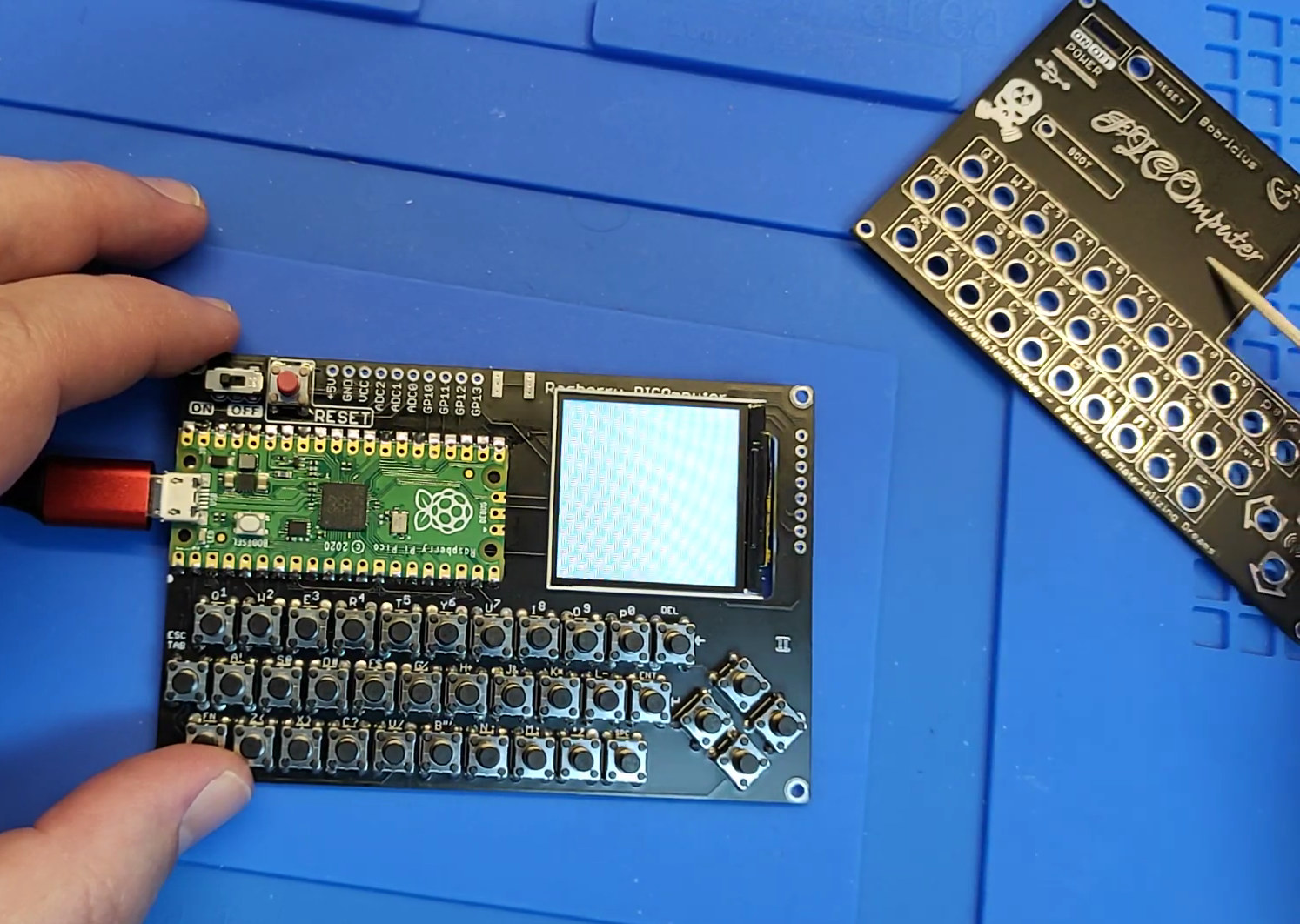
PICOmputer connects Raspberry Pi Pico to QWERTY keyboard, display, and optional LoRa module
Peter Misenko (aka Bobricius) has found an interesting use case for the Raspberry Pi Pico board with its PICOmputer, a compact terminal with a QWERTY keyboard, a small IPS display, and even footprint for an RFM95 LoRa module that would allow messaging/texting over LoRaWAN. Note the open-source hardware project is only offered as a kit with either the main board only, or the main board plus a gold or silver front panel, all without components, but fully assembled units are out of stock at this time. So read on, if you’re ready for some soldering and even some rework of the PCB, more on that latter. PICOmputer key features and specifications: Compatible with Raspberry Pi Pico board Storage – MicroSD card slot Display – Three types supported: 1.3-inch ST7789 IPS 240×240 display via 12-pin flex cable 1.54-inch ST7789 IPS 240×240 display via 12-pin flex cable ST7789 IPS 240×240 display via […]
Qualcomm unveils Snapdragon 7c Gen 2 SoC for laptops and Chromebooks
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 7c Gen 2 SoC for entry-level laptops and Chromebooks follows the steps of the Snapdragon 7c processor with a slightly higher frequency for the Kryo 468 cores, leading to a 6% performance improvements. As we’ll see below, most of the specifications are exactly the same, except the built-in Snapdragon X15 LTE modem is now listed as supporting LTE Cat 14 up to 600 Mbps, instead of LTE Cat 15 up to 800 Mbps, and UFS downgraded to UFS 2.1 from UFS 3.0. Snapdragon 7c Gen 2 specifications: CPU – Octa-core Kryo 468 (Cortex-A76) processor up to 2.55 GHz GPU – Unnamed Qualcomm Adreno GPU (Note: Snapdragon 7c had Qualcomm Adreno 618 GPU) DSP – Qualcomm Hexagon 692 DSP Memory – 2x 16-bit LPDDR4x-4266 Storage – eMMC 5.1, UFS 2.1 Display On-device display up to QXGA (2048 x 1536) @ 60 Hz External display up to QHD (2560×1440) @ […]
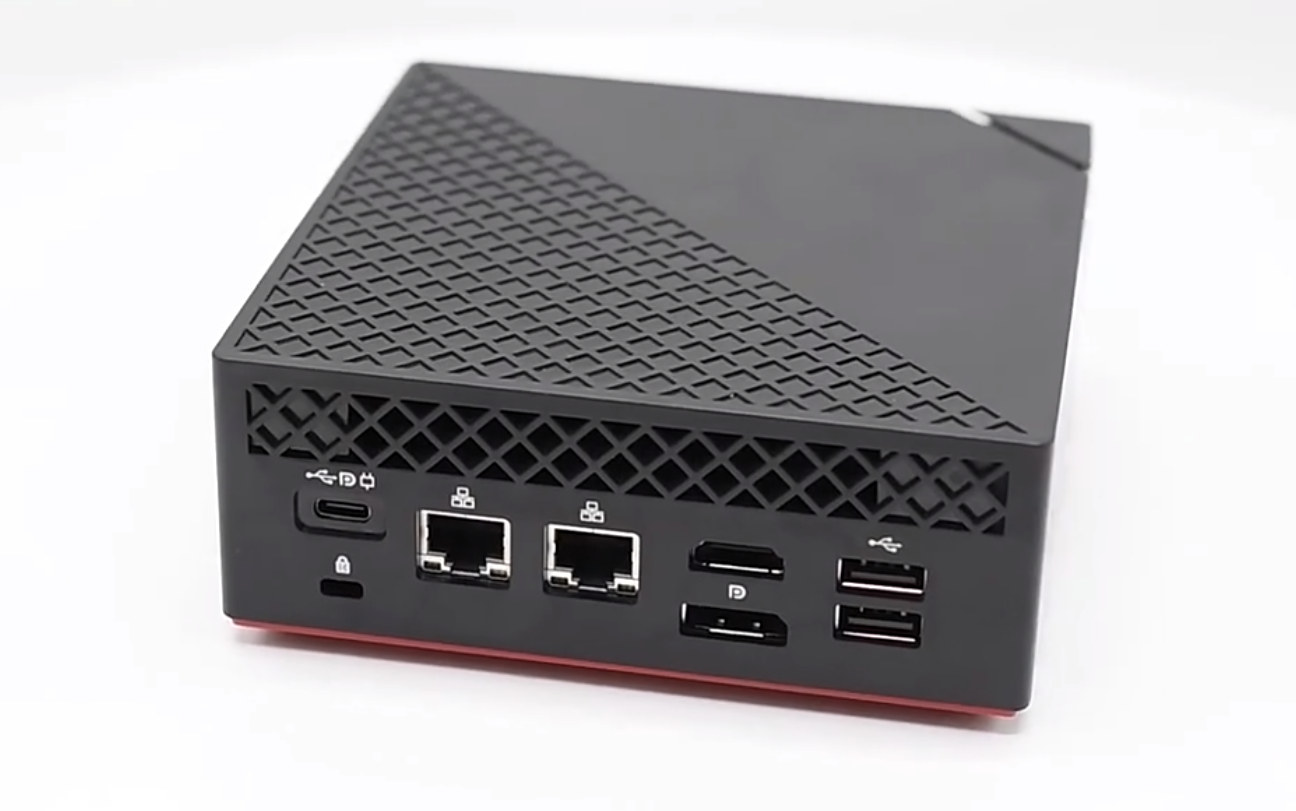
TOPTON D3 mini desktop features AMD Ryzen 5 4500U mobile processor
TOPTON D3 is an AMD Ryzen 5 4500U mini (desktop) PC that adds to the list of compact computers such as ASRock Mars 4000U or ASRock 4×4 BOX-4800U based on 15W AMD Ryzen 4000-series mobile processors. The mini PC offers two DDR4 SODIMM sockets, NVMe SSD storage, two Gigabit Ethernet ports, WiFI 6, as well as three 4K video outputs through HDMI, DisplayPort, and USB-C ports. TOPTON D3 (tentative) specifications: SoC – AMD Ryzen 5 4500U hexa-core/hexa-thread processor @ 2.3 GHz / 4.0 GHz (Turbo) with 11MB cache, Radeon Vega 6 Graphics ; 15W TDP System Memory – 2x SODIMM DDR4 sockets for up to 32GB RAM Storage – M.2 socket for up to to 1TB M.2 2280 NVMe SSD, 2.5-inch SATA bay for up to 2TB SATA HDD (as per default configuration options) Video Output HDMI 2.0 up to 4Kp60 DisplayPort up to 4Kp60 USB-C up to 4Kp60 using […]
Qualcomm 315 5G IoT modem announced for 5G IIoT applications
Qualcomm has announced the Qualcomm 315 5G IoT modem just a couple of days after the company’s introduction of Snapdragon 778G 5G SoC and M.2 5G card reference designs based on Snapdragon X65/62 modem. Qualcomm Technologies say it is their first purpose-built Internet of Things modem solution equipped with 5G connectivity and optimized for Industrial IoT (IIoT) applications. Qualcomm 315 5G IoT modem Qualcomm 315 5G IoT modem specifications: CPU – Cortex-A7 core running Linux Cellular connectivity 5G Technology – 3GPP Rel.15 5G NR Peak speeds – Download: 1.54 Gbps; upload: 330 Mbps Modes – SA (standalone), TDD & FDD RF – Adaptive antenna tuning, power tracking Sub-6 GHz Specs – 100 MHz bandwidth, 4×4 MIMO DL, 64 QAM DL/UL 4G LTE Technology – Rel.15 Cat.13 DL, Cat.5 UL Peak speeds – Download: 400 Mbps; upload: 75 Mbps LTE Modes – TDD & FDD LTE RF – 700 MHz to […]