The first stable release of openSUSE for ARM has just been announced. openSUSE 12.2 for ARM is officially available for the Beagleboard, Beagleboard xM, Pandaboard, Pandaboard ES, Versatile Express (QEMU) and the rootfs can be mounted with chroot, but “best effort’ ports have been made for Calxeda Highbank server, i.MX53 Loco development board, CuBox computer, Origen Board and Efika MX smart top. Work is also apparently being done on a Raspberry Pi port which should be available for the next release. openSUSE developers explains that almost all of openSUSE builds runs on these platforms (about 5000 packages). Visit “OpenSUSE on your ARM board” for download links and instructions for a specific ARM board. More details are available on the wiki page. openSUSE has limited resources for ARM development, so If you’d like to help with development (e.g. fixing builds), visit ARM distribution howto page to find out how to get […]
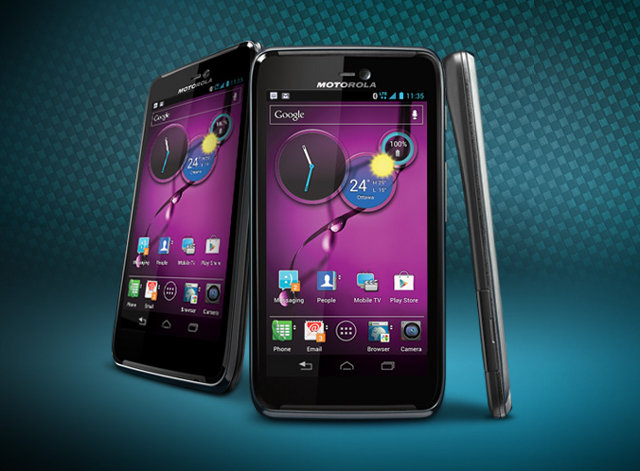
Motorola Announces ATRIX HD Smartphone Developer Edition
After 5 months after Motorola ATRIX HD hit the market, Motorola announced it would make a developer edition of the core Qualcomm MSM8960 Snapdragon based smartphone that comes with unlockable bootloader so that developers can play around and install their own firmware. Apparently the ability to unlock the bootloader is the only extra “feature” you get with this phone. You’ll then need to use a tool to unlock the device, lose your warranty, and start creating and flashing custom ROM to your phone. There is no plan to allow this on the “standard” edition of the phone however, and efforts by the XDA developer community to unlock the bootloader do not appear to have been successful to date, except for some some Atrix HD bought from Ebay which already came unlocked. Motorola ATRIX HD developer edition will be available soon for an undisclosed price, and only in the US. If […]
Getting Started with 64-bit ARM Development: Hello World and Linux on ARMv8 Fast Models
At the end of last year, ARM announced ARMv8, the first ARM 64-bit ARM archtecture, and last week at ARM Techcon 2012, ARM announced the first ARMv8 cores: Cortex A53 and A57. But since there’s no silicon at the moment, what if you wanted to develop code running on ARMv8 before the hardware is available? The answer is: Fast Models, a Virtual Platform (VP) to accelerate software development. This is especially important for ARMv8 since hardware is not expected to be available for another year. In this post, I’ll first show how to run “Hello World!” in ARMv8 fast models, then we’ll run ARM Linux 64-Bit (Aarch64) in the virtual platform. ARMv8 Foundation Model In order allow the developer’s community to program for ARMv8 (Cortex A53/A57 cores), ARM has made ARMv8 Foundation Model, a virtual platform, available free of charge. This v8 Foundation model provides a basic ARMv8 platform environment […]
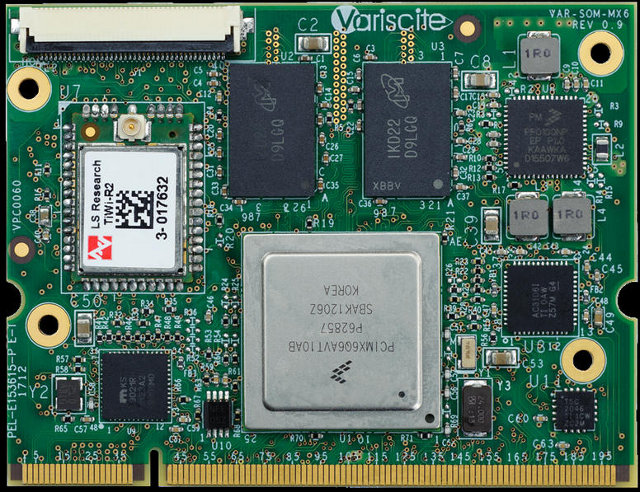
Variscite VAR-SOM-MX6 Freescale i.MX 6 Solo, Dual and Quad System on Modules Start at $59
Variscite has unveiled a new series of system on modules powered by Freescale i.MX6 Solo, Dual, DualLite and Quad processors with 512 to 2048 MB DDR3 RAM, and 128 to 1024MB SLC NAND Flash. Here are the modules key features: SoC – Freescale i.MX 6 series SoC (Single/Dual /Quad ARM® Cortex™-A9 Core, 1.2 Ghz) System Memory • Up to 16 Gb DDR3 RAM Storage – Up to 8 Gb NAND Flash for storage memory/boot Video Output: 2 x LVDS display interface HDMI V1.4 i nterface 1 x MIPI DSI Touch panel interface Camera – Parallel & serial camera interface (CSI) Connectivity On-board 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet PHY WLAN (802.11 b/g/n) Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR USB – 1 x USB 2.0 host, 1 x OTG Audio – Stereo line -In/out, digital & analog microphone, and S/PDIF In/Out Other interfaces: 2 x SD/MMC Serial interfaces ( SPI , I2C, UART, I2S,) 2x CAN […]
$100 Mele A1000G / A2000G Android Media Players with 1GB RAM and 8GB Flash
I’ve been asked by several people when there would be a Mele with 1GB RAM, well the time is now, with the Mele A1000G and Mele A2000G. Both appear to be based on the previous Mele A1000 and Mele A2000 set-top boxes, but feature 1 GB RAM and 8 GB Flash instead of 512 MB RAM and 4 GB Flash. Here are Mele A1000G & Mele A2000G Specifications: SoC – AllWinner A10 Cortex A8 processor @ 1GHz System Memory – 1 GB DDR3 Storage: 8GB NAND Flash SD card slot (up to 32 GB) Connectivity: Wi-Fi – 802.11 b/g 10/100 MB Ethernet USB – 3 USB Host ports SATA Interface for 2.5″ HDD Video Output – HDMI, composite and VGA. Audio Output – RCA stereo output and optical out (SPDIF) Audio Formats – MP3 / WMA / WAV / OGG / FLAC / MKA Video Formats – TS / M2TS […]
PengPod 700 & 1000 – Linux Tablets Based on AllWinner A10
There are plenty of tablet based on AllWinner A10 and A13 processors, but all of them run Android, and you are out of luck if you want to run Linux on your tablet, unless you hack this yourself. But this is about to change as PengPod will launch 2 tablets and 1 mini PC running Linux from NAND flash or micro SD card: PengPod 700 – 7″ tablet with Allwinner A10, 1GB RAM and 8GB Flash PengPod 1000 – 10″ tablet with AllWinner A10, 1GB RAM and 8GB Flash PengStick – AllWinner A10 mini PC with 1GB RAM and 4 GB Flash The table below gives more detailed specifications and comparison of the three devices. Device PengPod1000 PengPod700 PengStick Type Tablet Tablet TV Stick CPU Allwinner A10 AllWinner A10 AllWinner A10 Android 4 4 4 Linux 3.0.42 3.0.42 3.0.42 Screen 10” 7” External Resolution 1024×600 800×480 1080i Ram 1GB 1GB […]
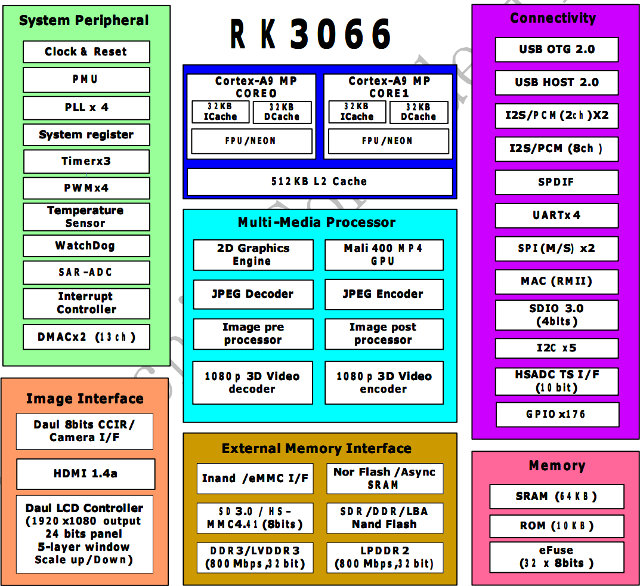
Rockchip RK3066/RK30xx Processors Documentation, Source Code and Tools
Rockchip RK3066 (part of RK30xx family) is a Chinese dual ARM Cortex A9 SoC targeting multimedia products such as tablets (e.g. Cube U30GT), mini PC (e.g UG802, MK808) and in theory set-top boxes, but I can’t find any products based on this Rockchip processor. It seems mini PCs/ HDMI TV sticks have taken over this market. RK3066 Processor The processor features two ARM Cortex A9 clocked at up to 1.6 Ghz with a quad core Mali-400MP GPU. It can support 1080p (3D) encoding/decoding, provides HDMI 1.4a, VGA, composite, component and LVDS video outputs (Dual display support), USB 2.0 Host and OTG ports, a MAC interface (Ethernet), and much more… Here are the key features of Rockchip RK3066 processor: Dual Core A9 + Quad Core Mali-400MP GPU 2 banks, 8/16 bit Nor flash / SRAM interface 8 banks, 8/16 bit async NAND flash, LBA NAND flash and 8-bit sync ONFI NAND […]
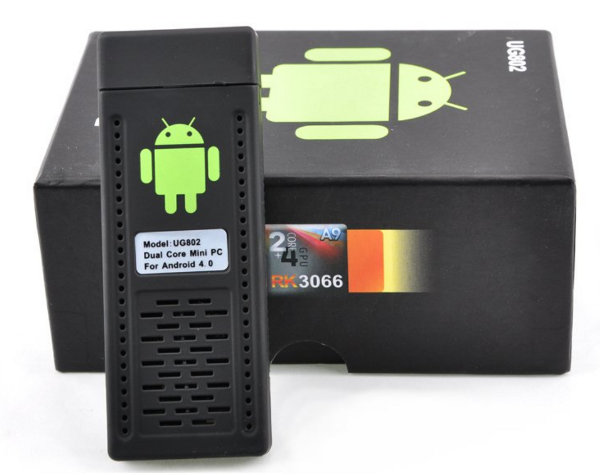
Rockchip RK3066 UG802 mini PC is Now Available for Just $46.50
Earlier today, a reader left a comment about a mini PC based on RK2908 sold for $40 including shipping on Ebay. No bad! But since I hadn’t checked mini PCs on Aliexpress for a few months, I decided to have a look for cheap devices. The cheapest sold by a company with decent feedback is the IP872 ($34 including shipping), but it’s based on an ARM11 chip (Infotmic IMAPX 200) and runs Android 2.3, so I don’t find it that interesting. There are also some AllWinner A10 mini PCs that cost just above $40 including shipping, but then I found one company selling UG802 for $46.50 including shipping via China Post. It’s quite shocking that the price halved within 3 months, and this makes single core mini PC that less attractive, unless you want to run Linux (Ubuntu, Debian…) which is not yet supported by RK3066. The device sold by […]