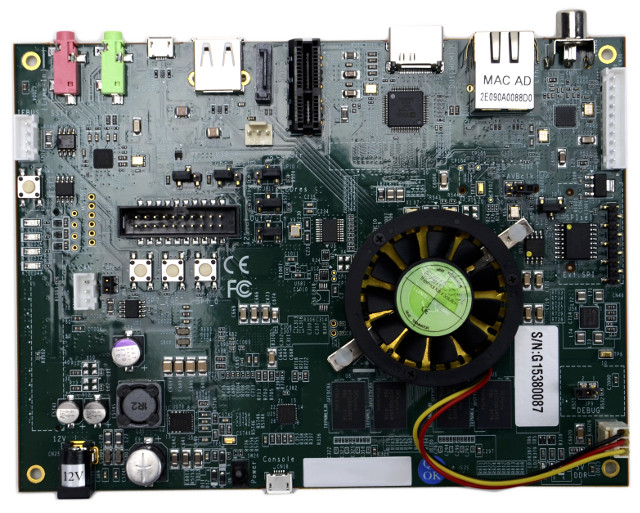
Another board has gotten initial mainline Linux support recently, with Renesas SK-RZG1M starter kit board based on Renesas RZ/G1M dual core ARM Cortex A15 SoC with 2GB RAM, a SATA interface, HDMI, LVDS, AV Ethernet bridge, and more. Renesas SK-RZG1M starter kit board actually has the exact same features as Renesas R-Car M2 Porter board except for the processor: SoC – Renesas RZ/G1M (R8A7743) dual core ARM Cortex-A15 processor @ 1.5GHz with PowerVR SGX544MP2 3D GPU, Renesas 2D graphics processor System Memory – Dual channel 2GB DDR3 Storage – On-board 4 MB SPI, and 64 MB SPI, 1x SATA rev 3.1 connector, 1x SD card slot, and 1x micro SD card slot Video Output / Display I/F – HDMI (via ADV7511), and LVDS + touchscreen Analog Video In – ADV7180 video decoder with RCA jack, NTSC/PAL/SECAM autodetection Audio codec – AK4643EN with 3.5mm jacks for Line In and Line Out Connectivity […]
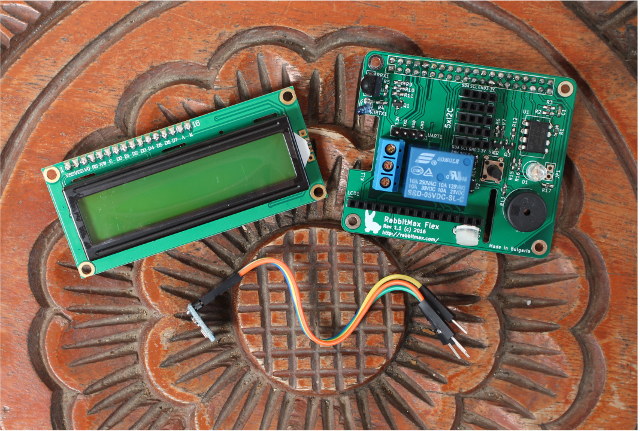
RabbitMax Flex IoT & Home Automation Board and Kit for Raspberry Pi
RabbitMax Flex is an add-on board for the Raspberry Pi boards with 40-pin headers, namely Raspberry Pi Model A+ and B+, Raspberry Pi 2, Raspberry Pi 3 and Raspberry Pi 0, destined to be used for Internet of Things (IoT) and home automation applications thanks to 5x I2C headers, a relay, an LCD interface and more. I’ve received a small kit with RabbitMax Flex boards, a BMP180 temperature & barometric pressure I2C sensor, and a 16×2 LCD display. RabbitMax Flex specifications: Relay – Songle SRD-05VDC-SL-C supporting 125V/250VAC up to 10A, 30VDC up to 10A Storage – EEPROM with some system information for identification IR – IR LED, IR receiver Misc – Buzzer, Button, RGB LED Expansion Header for LCD character display + potentiometer for backlight adjustment 5x 4-pin headers for I2C sensors Dimensions – Raspberry Pi HAT compliant The assembly of the kit is child’s play as you don’t even need […]
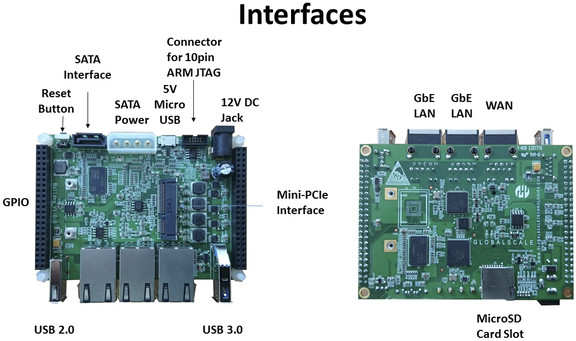
Marvell ESPRESSOBin Board with Gigabit Ethernet, SATA, mini PCIe, and USB 3.0 To Launch for $39 and Up (Crowdfunding)
I can often read people hoping for an inexpensive community board for network, storage and connectivity applications with high speed interface like SATA, multiple Gigabit Ethernet port, USB 3.0 and/or mini PCIe, and that’s exactly what Globalscale Technologies is about to offer with their Marvell ARMADA 3700 based ESPRESSOBin development board to go for $39 and up via Kickstarter. Marvell ESPRESSOBin board specifications: SoC – Marvell Armada 3700LP (88F3720) dual core ARM Cortex A53 processor up to 1.2GHz System Memory – 512MB DDR3 or optional 1GB DDR3 Storage – 1x SATA interface, 1x micro SD card slot with footprint for an optional 4GB EMMC Network Connectivity 1x Topaz Networking Switch 2x GbE Ethernet LAN 1x Ethernet WAN 1x MiniPCIe slot for Wireless/BLE periphereals USB – 1x USB 3.0, 1x USB 2.0, 1x micro USB port Expansion – 2x 46-pin GPIO headers for accessories and shields with I2C, GPIOs, PWM, UART, […]
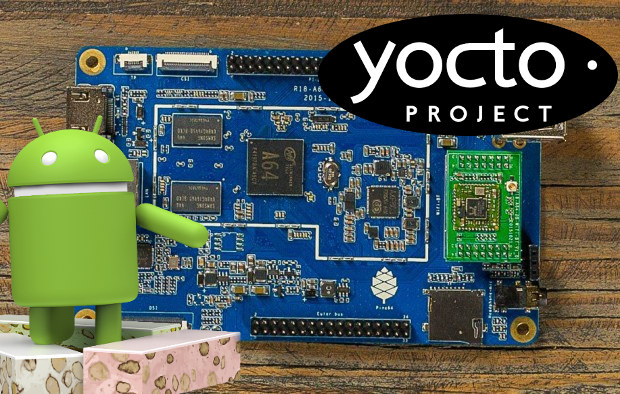
Android 7.0, Android TV 7.0, and Yocto Project Ported to Pine A64 Boards
A few weeks ago, Raspberry Pi 3 got an Android 7.0 Nougat port, and it’s usable for some app even simple games like Angry Bird, but there are still problems with 3D graphics, and hardware video decoding. But thanks to Pine64 forum’s member Ayufan, we now have Android 7.0 and Android TV 7.0 for Pine A64 boards with 1GB or more memory with 3D graphics, and hardware video acceleration for most apps. Everything is said to pretty much work, but there are some known issues, such as camera support (being worked on now), touchscreen support (not tested), YouTube is limited to 360p/480p as it does not support hardware video decoding, and Widevine DRM is not supported. Android 7.0 has also been shown to be about 10 to 15% faster than Android 5.1.1 in GeekBench. Ronnie Bailey has shot a video showing Pine A64 running Android TV 7.0 Nougat. If you […]
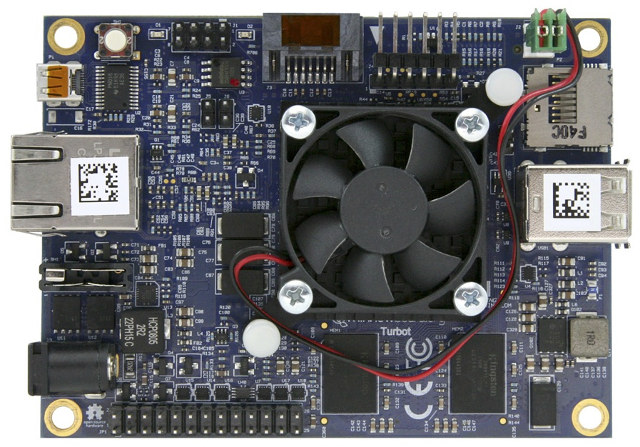
MinnowBoard Turbot SBC Gets a Quad Core Atom E3845 Processor, Better Ethernet, and a Fansink
MinnowBoard Turbot open source hardware SBC was released in 2015 with an Intel Atom E3826 dual core Bay Trail-I processor, 2GB RAM, SATA and Gigabit Ethernet support, and a new version – MinnowBoard Turbot Quad – with a more powerful quad core processor, an heatsink and fan, and better Ethernet connectivity will be launched in December. MinnowBoard Turbot Quad “MBT-4210” board specifications: SoC – Intel Atom E3845 quad core Bay Trail-I processor @ 1.92 GHz with Intel HD graphics @ 542 / 792 MHz (10W TDP) System Memory – 2GB DDR3L 1067 MT/s (Soldered) Storage – 1x SATA2 3Gbs, 1x micro SD card slot, , 8 MB SPI Flash for firmware (Tianocore UEFI, Coreboot, SeaBIOS) Video & Audio Output – 1x micro HDMI connector Connectivity – 10/100/1000M Ethernet RJ-45 connector (Intel i211 instead of Realtek NIC on first board) USB – 1x USB 3.0 host, 1x USB 2.0 host Debugging […]
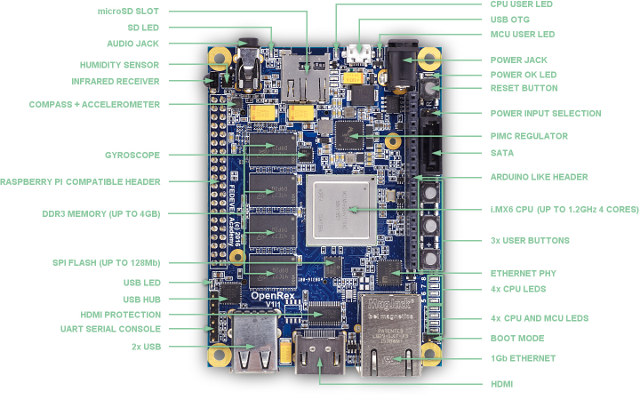
OpenRex Open Source Hardware NXP i.MX6 Board Launched for 199 Euros and Up
OpenRex is an open source hardware board powered by NXP i.MX6 Cortex A9 processor designed by Fedevel for their hardware design course, and manufactured by Voipac, both companies based on Slovakia. The schematics, PCB layout, gerber files and other manufacturing files were released in February, but the company has only started selling the board a few days ago with OpenRex Basic SBC and OpenRex Max SBC boards. OpenRex Basic and Max boards specifications: SoC OpenRex Basic – NXP i.MX 6Solo single core Cortex A9 processor @ 1 GHz with 2D and 3D GPU OpenRex Max – NXP i.MX 6Quad quad core Cortex A9 processor @ 1 GHz with 2D and 3D GPU MCU – NXP LPC1345FHN33 ARM Cortex-M3 micro-controller @ 72 MHz System Memory Basic – 512 MB DDR3-1066 (400MHz) Max – 2GB DDR3-1066 (533 MHz) Storage Basic – micro SD slot, 1x 2Kbit I2C EEPROM, 1x 32Mbit SPI flash Max […]
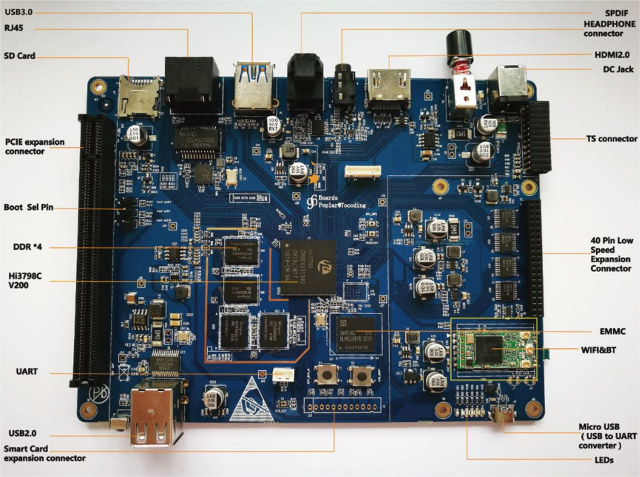
$79 HiSilicon Poplar is the First 96Boards TV Platform Compliant Board
At the end of last month I wrote about 96Boards TV Platform specifications, and noticed Hisilicon had one such boards, but details were sparse. Linaro has now officially unveiled HiSilicon Poplar board, the first 96Boards TV Platform board, sold for $79 + shipping on Aliexpress. Poplar board specifications: SoC – HiSilicon Hi3798C V200 quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 CPU up to 2.0 GHz per core with ARM Mali-T720 GPU supporting OpenGL ES 3.1/3.0/2.0/1.1/1.0, OpenVG 1.1, OpenCL 1.2/1.1 Full Profile, RenderScript, and Microsoft DirectX 11 FL9_3 Memory – 1 or 2 GB DDR3 (Specs are conflicting depending where you look) Storage – 8GB eMMC flash + micro SD card slot Video Output – HDMI 2.0a with HDCP 2.2 up to 4K @ 60Hz Video Decoding – H.265/HEVC Main/Main10 and VP9 up to 4K @ 60 fps Audio Output – HDMI, optical S/PDIF, 3.5mm audio jack Connectivity – Gigabit Ethernet, 802.11 b/g/n/ac WiFi […]
Intel Unveils Joule Compute Module and Devkit for IoT based on Atom T5500 & T5700 Processors
As the Intel Developer Forum 2016 is now taking place in San Francisco, Intel has unveiled the Joule Compute Module and development kit targeting IoT applications. The module is not for low cost and low power sensor nodes however, as it features a powerful quad core Atom processor running at 1.5+ GHz, so it more suited to IoT gateways, or other application requiring lots of processing power to handle sensor data. Two models of the Joule module have been introduced: Intel Joule 570x platform SoC – Intel Atom T5700 64-bit quad-core processor @ 1.7 GHz / 2.4 GHz (Burst frequency) with Intel HD Graphics with 4K video capture and display System Memory – 4GB LPDDR4 RAM Storage – 16GB eMMC memory Connectivity – 802.11ac Wi-Fi with MIMO and Bluetooth 4.1 Other interfaces – USB 3.0, MPI CSI and DSI interfaces, and multiple GPIO, I2C, UART interfaces Intel Joule 550x platform […]