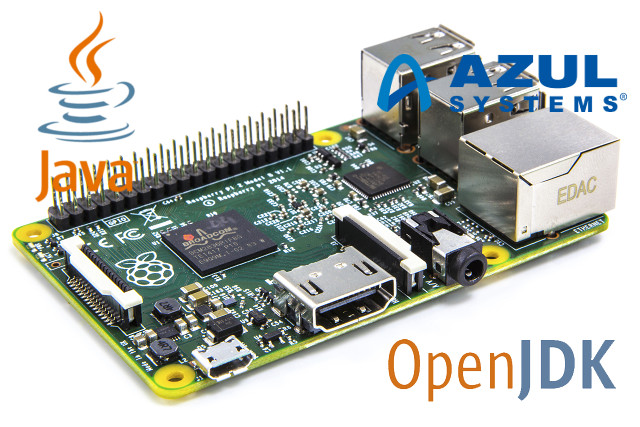
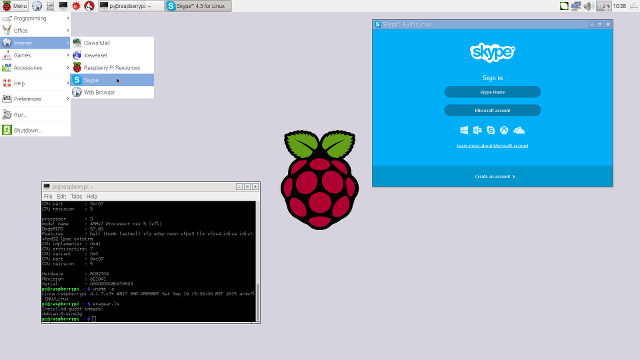
Yesterday as I wrote about the Embedded Systems Conference 2017 schedule I came across a potentially interesting talk entitled “Building A Brain With Raspberry Pi and Zulu Embedded JVM” by Azul Systems that will explain how to build a brain emulator using a cluster of Raspberry Pi boards. I wanted to find more about it, but I have not been able to find any details about the project/demo at this stage. However, I could still learn a bit more about Zulu Embedded, which is said to be an open source Java Virtual Machine based on OpenJDK, compliant with Java SE standard, working on 32-bit & 64-bit ARM & x86, MIPS, and PowerPC, as well as multiple operating systems. Some of the key features of Zulu Embedded include: Java Support – Java 6, 7, 8, and 9 when available Java Configurations – Headless, headful, or compact Java Compact Profiles Hardware – […]
Gumstix Nodana 96BCE 96Boards Compatible Baseboard Takes Intel Joule Module
96Boards is an initiative from Linaro, an engineering organization focusing on ARM development, to define some hardware and software specifications for development boards. But since 96Boards specifications are open, Gumstix decided to create the first x86 board compliant with 96Boards CE hardware specifications with Nodana 96BCE baseboard powered by Intel Joule Module. For obvious reasons, this will never be an officially supported 96Boards.org platform. Nodana 96BCE board specifications: SoM – Intel Joule Module based on Intel Atom T5700 or T5500 processor with up to 16GB storage, 4GB RAM. External Storage – 1x micro SD card Video Output – 1x HDMI port USB – 2x USB 3.0 ports, 1x USB 3.0 type C port Expansion Headers 96Boards Low Speed connector with I2C, SPI and UART 96Board High Speed connector with MIPI DSI and USB 2.0 Power Supply – 8 to 18 V (if it follows 96Boards CE specs) Dimensions – 85 […]
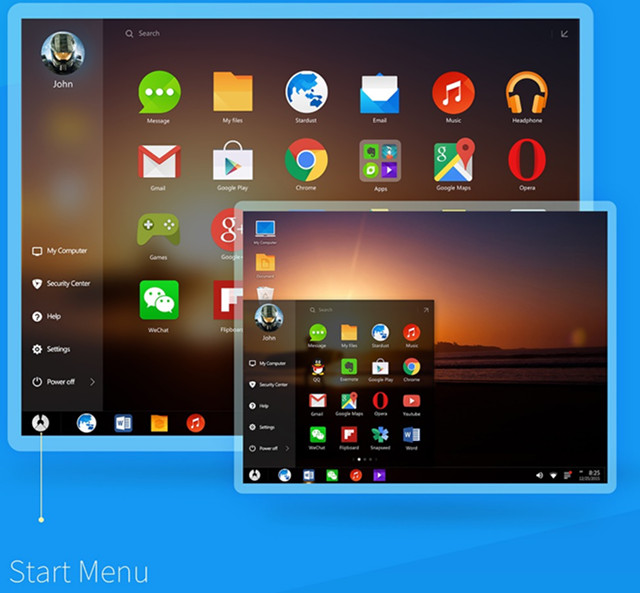
Phoenix OS is Another Desktop Oriented Android Distribution for ARM and x86
After Light Biz OS, Remix OS, and Console OS, here’s another Android distribution that aims at creating better desktop experience in Android. Phoenix OS works on some ARM platforms, namely Nexus 9 and Nexus 10, as well as 64-bit x86 processors and like the x86 version of of Remix OS is based on Android-x86 project. Just like other alternatives, it adds features usually found in Windows or Linux distributions such as a start menu, a task bar, multi-window support, notification handling via the taskbar, etc… If you’d like to try it out in a computer with an Intel or AMD computer, you can follow the instructions below from a Windows machine: Prepare a 4GB+ flash drive Download the latest Zip file of Phoenix OS (x86) to your PC, currently Phoenix-x86-1.0-32-beta.zip Download and install USBMaker tool to your PC Start USBMaker.exe, select the flash drive and Zip file, and press “Write” […]
Is Console OS just a Scam Based on a Fork of Android-x86 with Little Modifications?
Console OS is supposed to be a version of Android Lollipop running on various Intel platforms, and optimized for desktop use with new features like DVR support for digital TV tuners, a desktop friendly file manager, and so on. The project launched on Kickstarter and was successful enough to raise $78,497 from 5,695 backers. But according to Chih-Wei Huang, Android-x86 project leader, and Console OS users, the Console OS developer simply forked Console OS, with some minor modifications like changing the project name, and under-delivering on the promised features. The first part is fine, as that’s the beauty of open source code, you can fork somebody else work, and add your own improvement, and long as you keep the license and credits, that’s what open source is all about. Now the project raised funds specifically for development, and as promised the source code is available on github. Here what has been […]
How to Build Brillo Operating System from Source Code and Run Brillo Emulator
Google formally launched Brillo operating system a few weeks ago. The new operating system is a stripped down version of Android that targets Internet of Things (IoT) applications, and more recently the company pushed the source code to their servers. So I’ve given it a try by checking out the code, building Brillo emulator for Intel/AMD, and running it in Ubuntu 14.04 64-bit. First you’ll need to retrieve the source code:
|
1 2 3 4 |
mkdir brillo-master cd brillo-master repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/brillo/manifest -b master repo sync -j8 |
It took a few hours here with some errors the first time, so I tried again and I finally got the code a few hours later. Once this is done, set the build environment and configuration:
|
1 |
source build/envsetup.sh && lunch |
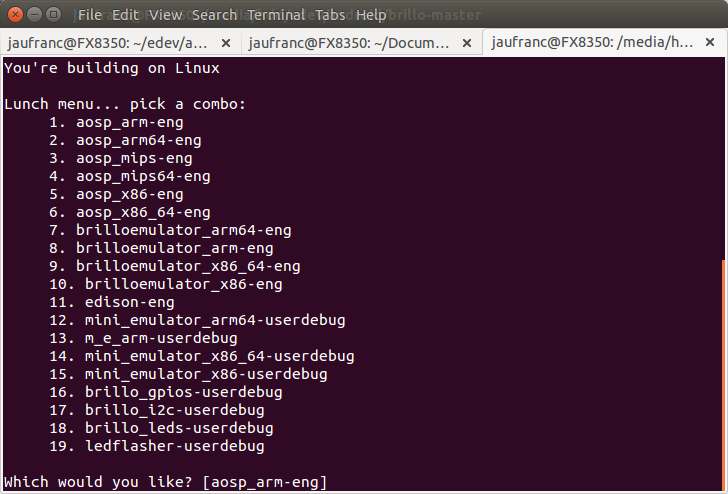
Lunch will bring a list of possible builds:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
You're building on Linux Lunch menu... pick a combo: 1. aosp_arm-eng 2. aosp_arm64-eng 3. aosp_mips-eng 4. aosp_mips64-eng 5. aosp_x86-eng 6. aosp_x86_64-eng 7. brilloemulator_arm64-eng 8. brilloemulator_arm-eng 9. brilloemulator_x86_64-eng 10. brilloemulator_x86-eng 11. edison-eng 12. mini_emulator_arm64-userdebug 13. m_e_arm-userdebug 14. mini_emulator_x86_64-userdebug 15. mini_emulator_x86-userdebug 16. brillo_gpios-userdebug 17. brillo_i2c-userdebug 18. brillo_leds-userdebug 19. ledflasher-userdebug Which would you like? [aosp_arm-eng] 9 |
You could also run the “Brillo emulator” on ARM, and edison-eng must be the build for Intel Edison board. Now you can start the build:
|
1 |
make -j8 |
It has to complete 21491 different tasks, […]
Run x86 Linux and Windows applications in Raspberry Pi and other ARM Linux Devices with Exagear
A few weeks ago, I finally decided to buy a Raspberry Pi 2 board as it could always be useful for some testing, at least for comparison purposes. I ended up buying it from Ebay for $40, as it’s $3 to $5 more expensive locally. Nevertheless, I was not sure what I’ll use it first for, but after seeing a tweet for Exagear Desktop software that allows ARM boards to run x86 Linux or Windows applications, the latter through wine. The program is available for Raspberry Pi, Raspberry Pi 2, and ARMv7 devices for $19.95 to $29.95. I asked for a version for testing purposes, and I was given a Google Drive link to download Exagear for Raspberry Pi 2, as well as a 3-month trial key. Installation is very easy. I started by downloading and installing Raspbian Jessie the usual way on a 32GB micro SD card. It went […]
Intel Unveils Three New Micro-controllers for IoT: Quark D1000, Quark D2000, and Quark SE
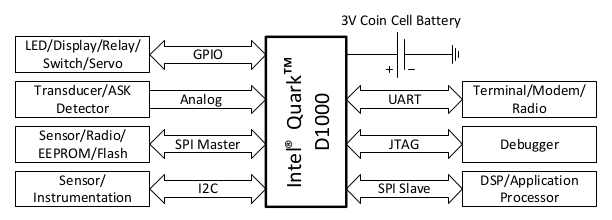
Intel’s subsidiary, Wind River, has recently announced two operating systems for the Internet of things with Rocket RTOS and Pulsar Linux supported respectively by Quark MCUs, and Intel Atom processors, as well as some ARM SoCs. But it’s not the only “IoT” announcement made by Intel in the last week, as I found out via EETimes that the company also unveiled three new Quark SoCs, namely Quark D1000, and Quark D2000, and Quark SE. Intel Quark D1000 Contrary to previous Quark processor and the upcoming D2000 and SE processors, D1000 is not compatible with x86 instructions set, and features the following: 32-bit Harvard CISC CPU @ 33 MHz with single cycle barrel shifter, two cycle multiplier, multi-cycle divider, integrated 32-bit timer, programmable interrupt controller, and JTAG debugger. 128-bit wide 32 kB code flash and 8 kB ROM 32-bit wide 8 kB SRAM and 4 kB data flash Osciallators 20-33 MHz […]
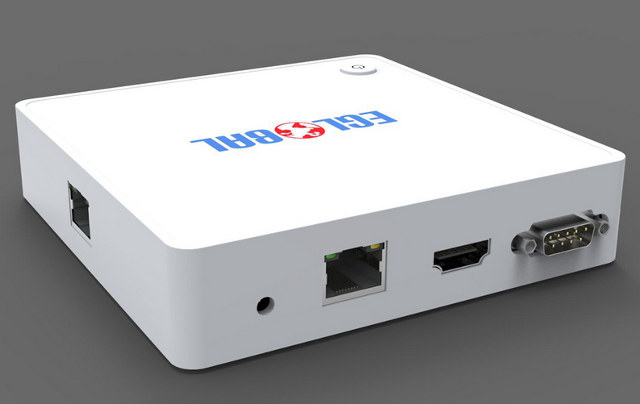
Eglobal K8 Z3735F mini PC Includes Up to 2 Ethernet Ports, a COM Port and an IR Receiver (As options)
Most mini PCs based on Intel Atom Z3735F have very similar specifications, but at least one company – Eglobal Technology – is providing some extra options with their mini PC as they offer dual Ethernet (which they call “Router”), a COM port and an IR receiver as options. Eglobal K8 specifications: SoC – Intel Atom Z3735F “Bay Trail” quad core processor @ 1.33 GHz (Bust freq: 1.83 GHz) with Intel HD graphics System Memory – 2 GB DDR3L Storage – 32 GB eMMC + micro SD card slot (up to 128GB) Video Output – HDMI Audio I/F – HDMI, 3.5mm earphone jack, 3.5mm microphone jack Connectivity Standard – 1x 10/100M Ethernet, 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth 4.0 Option – One extra 10/100M Ethernet port USB – 4x USB 2.0 host Misc – Power Button, optional IR receiver, optional COM port (DB9) Power Supply – 5V/2A Dimensions – 107 x 107 […]