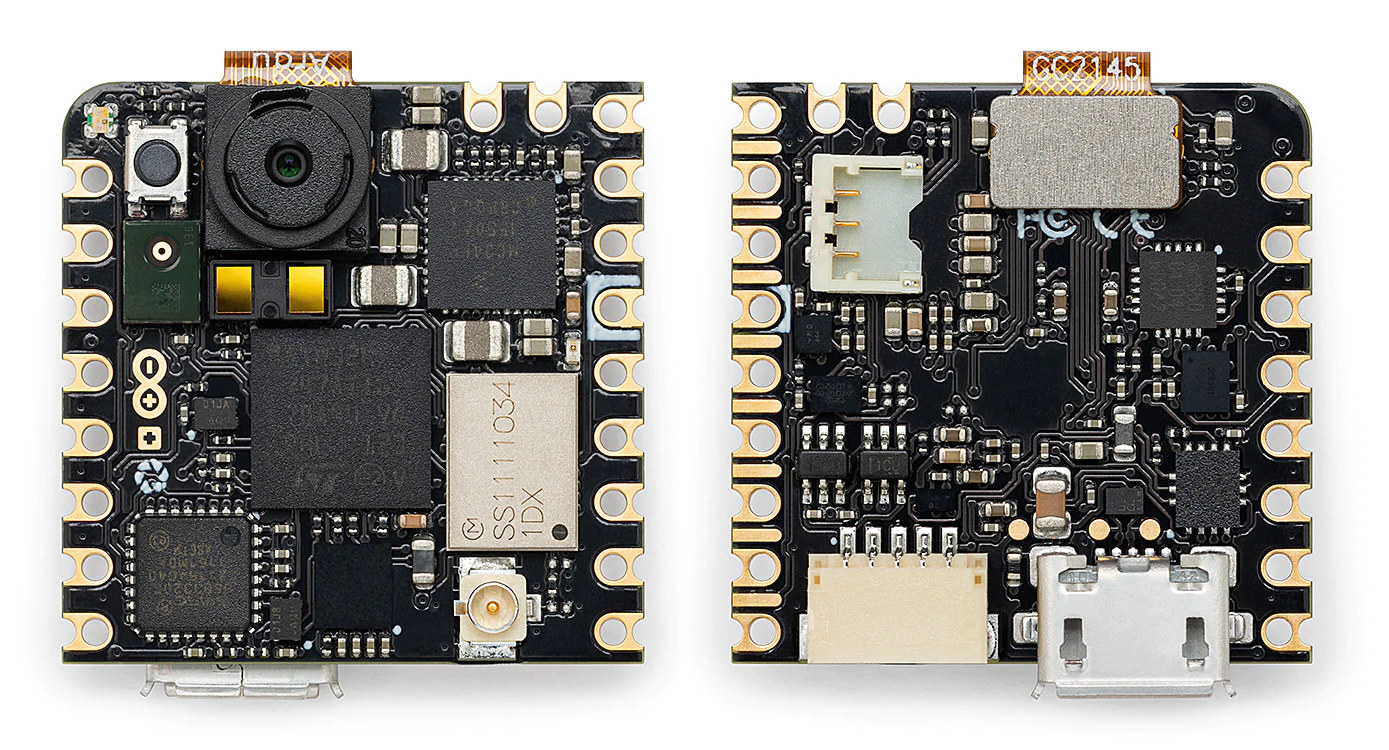
Arduino Nicla Vision is an ultra-compact (~2.3×2.3 cm) board powered by an STMicro STM32H7 dual-core Cortex-M7/M4 microcontroller, and equipped with a 2MP camera, a WiFi & Bluetooth LE module, and a few sensors. Those features make the board suitable for machine vision and edge computing applications such as asset tracking, image detection, object recognition, and predictive maintenance. For instance, image detection, facial recognition, automated optical inspection, vehicle plate reading, or gesture recognition can be added to projects, either using Nicla Vision as a standalone board or in combination with Portenta or MKR boards. Arduino Nicla Vision specifications: Microcontrollers – STMicro STM32H757AII6 dual-core MCU with Arm Cortex M7 @ 480MHz, Cortex-M4 @ 240MHz, 2 MB flash, 1MB RAM Storage – 16MB QSPI flash Connectivity – 2.4GHz WiFi 802.11b/g/n up to 65 Mbps and Bluetooth 5.1 BR/EDR/LE via Murata 1DX module Camera – 2MP GC2145 color camera. USB – Micro USB port […]
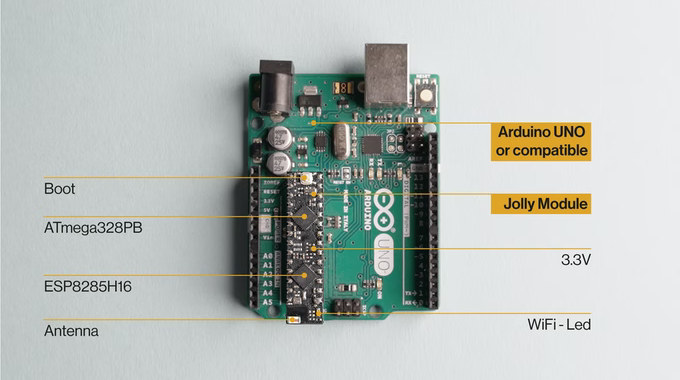
ESP8285 WiFi DIP module replaces ATMega328P MCU on Arduino UNO board (Crowdfunding)
Released over 10 years ago, Arduino UNO is still the best-selling Arduino board, but lacking WiFi in the IoT era is not ideal, so Gianluca Martino, Arduino co-founder and working with the company until 2015, decided to design the Jolly DIP module based on ESP8285 WiFi chip that can replace the ATmega328P 8-bit AVR DIP-40 microcontroller. Since ESP8285 cannot provide all I/Os, notably analog inputs offered by ATmega328P, Gianluca combined it with the ATMega328PB microcontroller in a compact SMD package to offer firmware compatibility plus WiFi connectivity in the same DIP form factor. Jolly module specifications: MCU – Microchip ATMega328PB 8-bit AVR microcontroller with 32 KB ISP Flash, 1 KB EEPROM, 2 KB SRAM (Based on data from the datasheet) Wireless chip – Espressif Systems ESP8285H16 WiFi SoC with 2MB integrated flash plus ceramic antenna Communication interfaces between the two chips – SPI + UART (the latter exclusively for ESP8285 […]
M5Stamp C3U IoT module relies on ESP32-C3’s own USB interface for firmware programming
M5Stamp C3U is an update of the M5Stamp C3 RISC-V IoT module with heat-resistant cover, support for WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0, that does without CH9102 USB to TTL chip, relying instead on the internal USB interface of ESP32-C3 processor to handle serial programming of the firmware, and gaining on extra GPIO pin in the process. While several ESP32 processors come with a built-in USB interface, many boards still use an external USB to TTL chip such as CH340 or CP2102 to handle the serial interface used for debugging and flashing the firmware likely because of limitations when using ESP32-C3’s USB serial/JTAG controller console, but M5Stack probably considered those to be workable, and the small cost-saving beneficial. M5Stamp C3U specifications: WiSoC – ESP32-C3FH4 32-bit single-core RISC-V processor @ up to 160 MHz, with 384KB ROM, 400KB SRAM, 8KB RTC SRAM, 4MB embedded flash, WiFi and Bluetooth Connectivity 2.4 GHz WiFi […]
Sonoff ZBBridge gateway can be used as a Zigbee router/repeater
Sonoff ZBBridge WiFi to Zigbee gateway was introduced in April 2020, and a few months later got support for Tasmota ESP8266 firmware and Gecko firmware for either Home Assistant or Zigbee2MQTT support. But there’s now a new Tasmota firmware that converts Sonoff ZBBridge into a Zigbee router (a.k.a. Zigbee Signal Repeater or Zigbee Range Expender) following a request on Tastoma Github’s issue tracker from last year. The firmware, unofficial yet signed, was released a few days ago by xsp1989 Github’s user with a link to the firmware on Google Drive. Digiblur successfully tried it out on its own Sonoff Zigbee bridge and published the instructions. Assuming you already have Tasmota flashed to the device, switching to the router software is basically a firmware upgrade from the Tasmota web interface. Once the update is complete, you’ll still need to access the console in Tasmota in order to run a command to […]
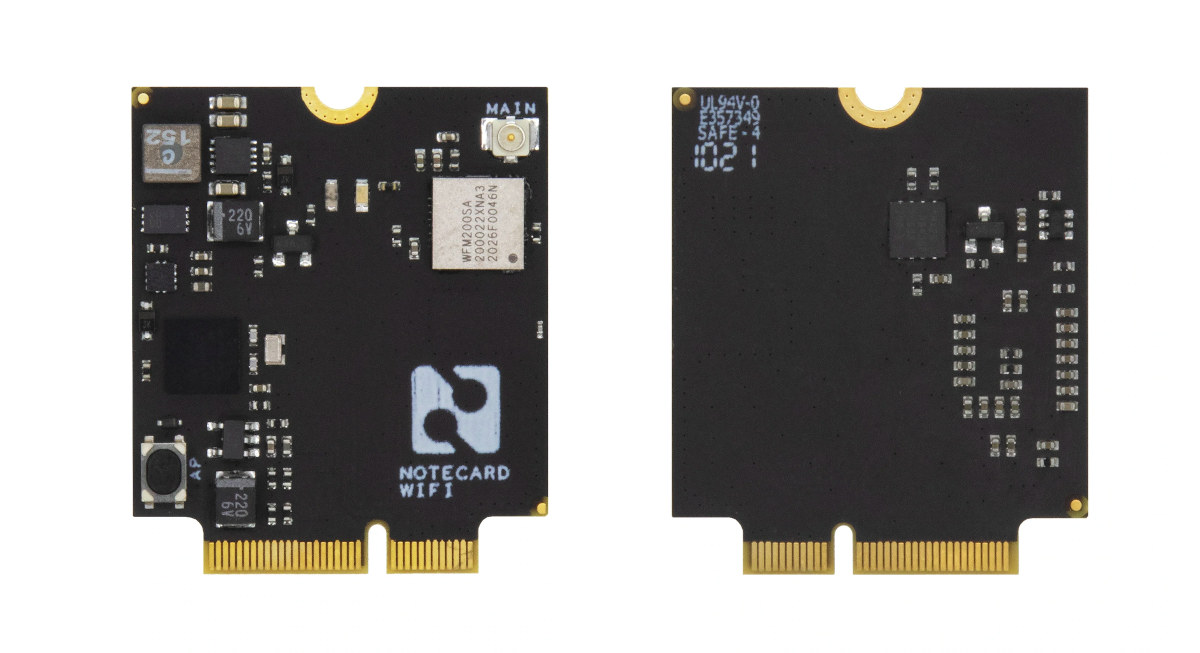
Blues Wireless launches Wi-Fi Notecard for mixed cellular & WiFi IoT deployments
Blues Wireless has just launched the Wi-Fi Notecard M.2 module that can be used as a replacement to the company’s Notecard LTE Cat-M / NB-IoT M.2 modem that sells with 10 years of connectivity up to 500MB for $49 and up. The Wi-Fi Notecard came to be as some customers wanted to have mixed deployments where cellular makes sense in some locations, while Wi-Fi is better suited to other sites. Others preferred to use WiFi during development or prototyping to save on Notecard cellular data usage. Wi-Fi Notecard specifications: MCU – Arm Cortex-M4 MCU with 2MB flash Wireless Silicon Labs WFM200S Wi-Fi transceiver module with a 2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n radio supporting up to 72 Mbps link u.FL antenna connector Host interface – M.2 edge connector with I2C, UART, USB Sensor – 3-axis accelerometer and temperature sensor Security – STSAFE Secure Element with hardware crypto, true hardware random number generator, and […]
Ai-Thinker BW16 is a dual-band WiFi & Bluetooth 5.0 IoT module (Sponsored)
Many users prefer the ESP32 when implementing WiFi & Bluetooth into their IoT projects. But Ai-Thinker BW16 offers dual-band WiFi 4 & Bluetooth 5.0 connectivity through Realtek’s RTL8720DN chipset which may provide more reliable connectivity where the 2.4 GHz band is crowded. The module integrates an Arm Cortex-M4F compatible high-performance MCU, an Arm Cortex-M0 compatible low power MCU, WiFI 802.11 a/b/g/n, MAC, Bluetooth and RF baseband, and provides a set of configurable GPIO ports to control peripheral devices. BW16 module One significant difference between BW16 and ESP32 module is that it has two serial port interfaces, so attention should be paid to the wiring of the UART interfaces. The following diagram shows the two serial interfaces of the BW16 module. One of the module serial interfaces is used to send and receive AT commands to control connectivity from a host processor or microcontroller, while the other serial port is used […]
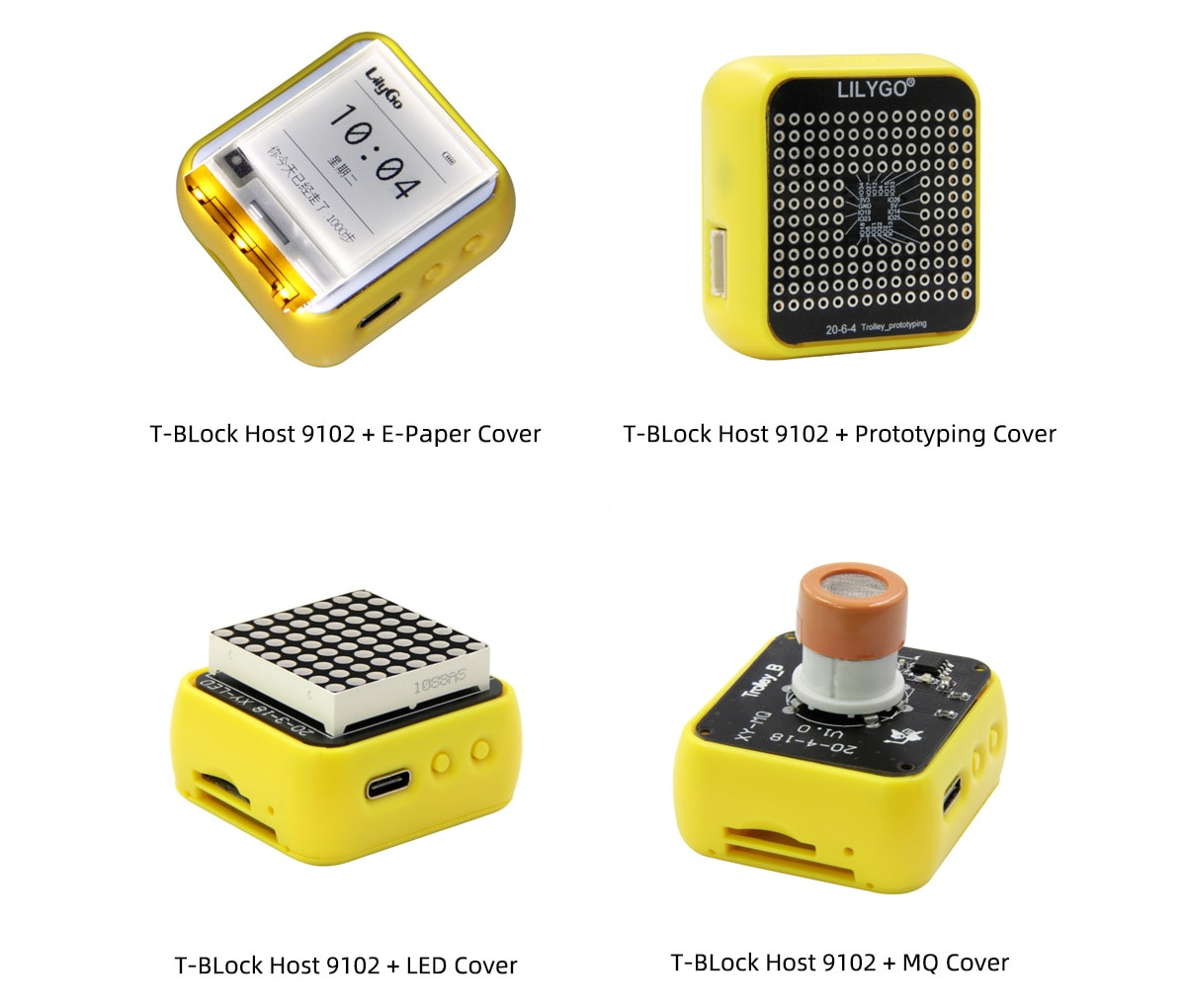
TTGO T-Block modular ESP32 devkit supports “Trolley” covers acting as display, buttons, sensor, proto area, etc…
When I first LilyGO TTGO T-Block ESP32 devkit with an enclosure and a display it reminded me of the M5Stack Core2 devkit, but it’s actually different as LilyGO designed a modular system that allows users to change the functionality of the top cover with expansion boards called “Trolleys”. That means TTGO T- Block can be fitted with a small e-Ink display, a prototyping cover, an RGB LED matrix, a small board that supports various MQ gas sensors, touch buttons, or a Trolley board equipped with headers compatible with common Arduino modules. TTGO T-Block Host 9102 preliminary specifications: WiSoC – ESP32 dual-core processor @ 240 MHz with 520KB SRAM, WiFi 4 and Bluetooth LE 4.2/5.x connectivity Memory – 8MB PSRAM Storage – 16MB SPI flash, MicroSD card slot USB – 1x USB Type-C for power and programming via CH2104 USB to TTL chip Trolley interface – 20-pin connector with 17x GPIO, […]
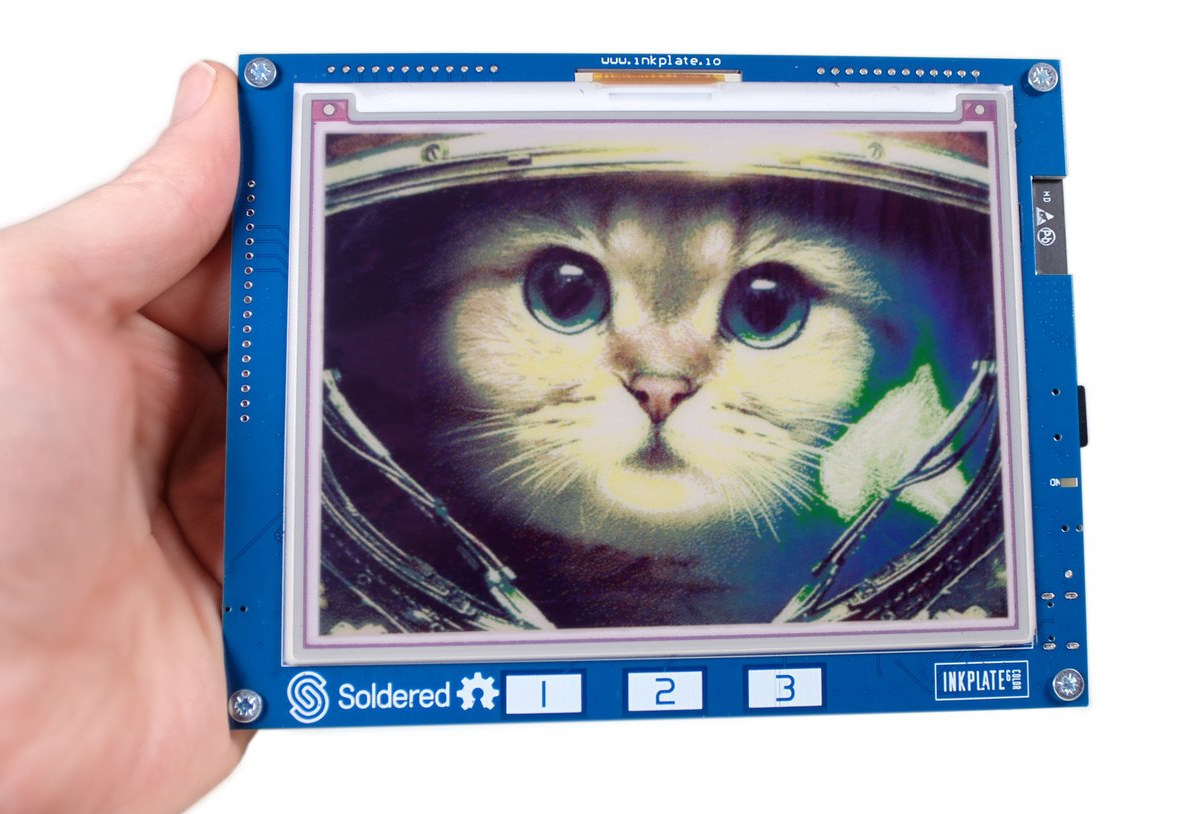
Inkplate 6COLOR – A 5.8-inch e-paper color wireless display (Crowdfunding)
Inkplate 6COLOR is a 5.8-inch color e-paper display equipped with ESP32 WiSoC to provide WiFi and Bluetooth LE connectivity, and programmable with the Arduino IDE or MicroPython. We’ve covered Inkplate ESP32-based e-paper displays since Inkplate 6 was launched in 2019, and since then the company introduced a larger model and an upgraded variant with a touchscreen display and higher resolution. But so far, all were grayscale models, and Inkplate 6COLOR is the first to come with color, or more exactly 7 colors. Inkplate 6COLOR specifications: Wireless module with dual-core ESP32 processor, Wi-Fi 4 & Bluetooth 4.0 (BLE) connectivity External storage – MicroSD card socket Display – 5.8-inch, 600 x 448 e-paper display with 7 colors (Black, White, Red, Yellow, Blue, Green, Orange) 128 DPI 25 seconds refresh time (manufacturer); tested by Inkplate: 10 to 11 seconds USB – 1x USB Type-C port for programming and power Expansion – Headers for […]