Beelink’s latest Intel mini PC offerings includes the AP34 and AP42 which are their first models using Intel Apollo Lake processors. The former uses an Intel Apollo Lake Celeron N3450 processor (burst frequency 2.2GHz, Intel HD Graphics 500 with Graphics Burst Frequency 700MHz and 12 Execution Units) while the latter uses the slightly more powerful Pentium N4200 (burst frequency 2.5GHz, Intel HD Graphics 505 with Graphics Burst Frequency 750MHz and 18 Execution Units). Both support Windows 10 (Home) and Beelink’s marketing claim they “support Linux system”. GearBest has given me the chance to review running Linux on the AP42 model so here are my findings. Normally I first make a disk image before booting Windows or installing Linux. However initial attempts at booting a Live USB with a variety of Linux systems failed so both the reseller and manufacturer were contacted for comment. Interestingly there was no immediate reply but early […]
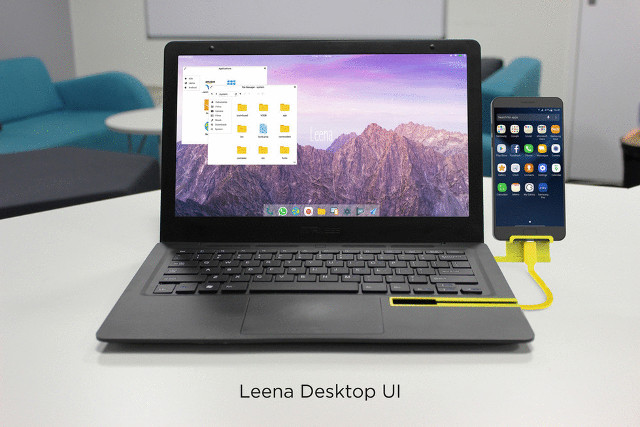
Mirabook is Laptop Dock for Smartphones, Development Boards (Crowdfunding)
Motorola Lapdock may have been ahead of its time, as laptop docks for smartphone are back in vogue with products like NexDock, and Apple could soon launch their own iPhone laptop dock. Another option is Miraxess Mirabook laptop dock with a 13.3″ display, and a battery lasting up to 24 hours, that works for smartphones, development boards, and HDMI TV sticks thanks to its USB type C port. Mirabook specifications: Display – 13.3″ IPS display with 1920×1080 resolution (non-touch, except if they raise $2 millions…) Audio – Speakers, 3.5mm audio jack Video Output – HDMI port Storage – SD card slot QWERTY keyboard & multi-touch trackpad USB Integrated USB type C cable to connect to phone, board or HDMI TV stick USB type C port to charge the Mirabook battery 2x USB type A host port Battery – TBD capacity good for 24 hours while charging your phone Dimensions – […]
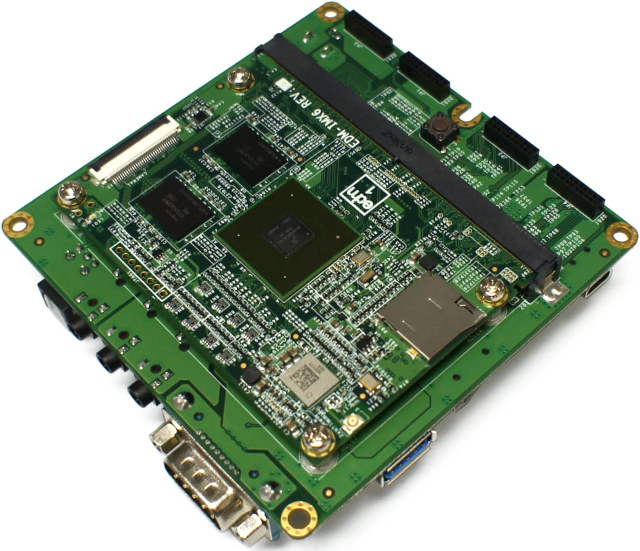
Wandboard QuadPLUS Development Board Gets i.MX 6QuadPlus Processor, 802.11ac WiFi and Bluetooth 4.1
The first Wandboard development boards launched in 2012 nearly 5 years ago based on Freescale i.MX6 Solo and Dual processor, with Wandboard Quad launched a few months later. The boards were fairly popular at the time due to their better specifications, and especially Freescale’s much better documentation and software compared to the competition such as Broadcom (Raspberry Pi) and Allwinner (Cubieboard). Since the boards are based on TechNexion EDM system-on-modules they could also be used by companies working on their own products based on the system-on-module. It’s also a good platform if you want to test various version of Android, because the company released Jelly Bean, Kitkat, Lollipop, and Marshmallow images for the boards, and I’m expecting a Lollipop version soon. However, albeit the company worked on other NXP boards such as PICO-IM6UL Android Things, there had not been any hardware upgrade for Wandboard for nearly 4 years, but last […]
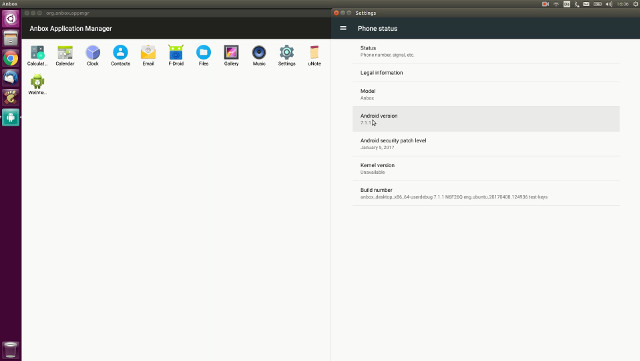
Anbox Allows You to Run Android Apps Natively in Ubuntu Linux
It’s been possible to run Android app in computers for a while with solutions such as Bluestacks or ShashLik, as well as running Android-x86 ISO in a virtual machine. But all those solutions rely on emulation, may not have the best performance, and at the time I tried them did not really work well, or were inconvenient to use. Anbox is different as instead of running its own Linux kernel for Android, it leverages the Linux kernel in Ubuntu for better integration and performance, and use an LXC container to run Android. Anbox has been tested with Ubuntu 16.04, but should also work with other recent Ubuntu distributions. Installing Anbox (Alpha) is easy, and can be done with a single command line:
|
1 |
sudo snap install --classic anbox-installer && anbox-installer |
The command will modify your system with the following: Add the anbox-support ppa ppa:morphis/anbox-support to the host system Install the anbox-modules-dkms deb package from the ppa which will […]
Canonical Refocuses Ubuntu Development Efforts on Cloud and IoT, Drops Convergence and Mobile
Mark Shuttleworth has published a new blog post in Ubuntu Insights, and this is not all good news, as the title “Growing Ubuntu for Cloud and IoT, rather than Phone and convergence” implies. Canonical has decided to drop Unity8, and replace it with Gnome in Ubuntu 18.04, and by extension stop any investment in Ubuntu phone and convergence. The main reasons given for the drop were that few commercial partners were interested in the project, preferring to stick with the most popular mobile operating systems like Android, and the community did not see the work as innovation, but instead fragmentation, probably referring to the Mir vs Wayland saga. On the better news, Canonical is still committed to work on Ubuntu desktop, and will focus on the Cloud and IoT applications such as automotive, robotics, networking, and machine learning, for which the company has gone well so far with multiple commercial […]
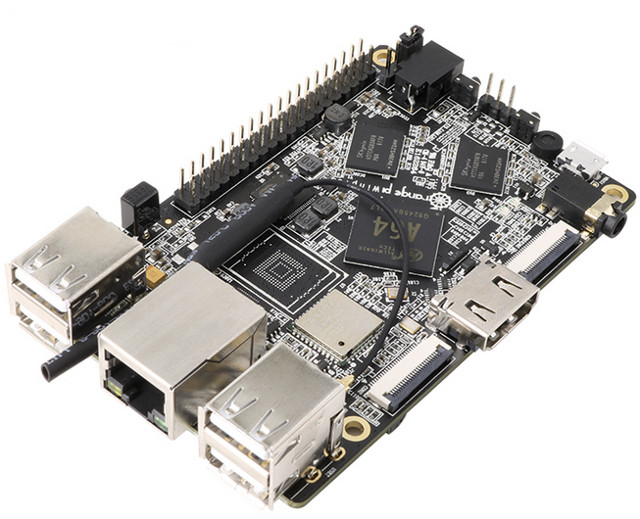
Shenzhen Xunlong Releases Two Orange Pi Boards with 64-Bit ARM Processor, 2GB RAM
Shenzhen Xunlong has already been selling 64-bit ARM development board with their Orange Pi PC 2 & Orange Pi Zero Plus 2 H5 boards based on Allwinner H5, as well as Orange Pi Win board powered by Allwinner A64 processor. However, so far none of them are equipped with much memory, with the only options being 512MB or 1GB RAM. The company has recently launched two new boards with 2GB RAM, namely Orange Pi Win Plus featuring Allwinner A64 SoC, and Orange Pi Prime equipped with Allwinner H5 SoC. Orange Pi Win Plus That board is just an update to Orange Pi Win board with the only difference I could find being the 2GB RAM: SoC – Allwinner A64 quad core ARM Cortex A53 processor @ 1.2 GHz with Mali-400MP2 GPU System Memory – 2GB DDR3 Storage – 2MB SPI flash, micro SD slot up to 64GB, footprint for optional […]
NanoPi NEO2 Board Benchmarks with Ubuntu 16.04.2 using Linux 3.10 and Linux 4.10
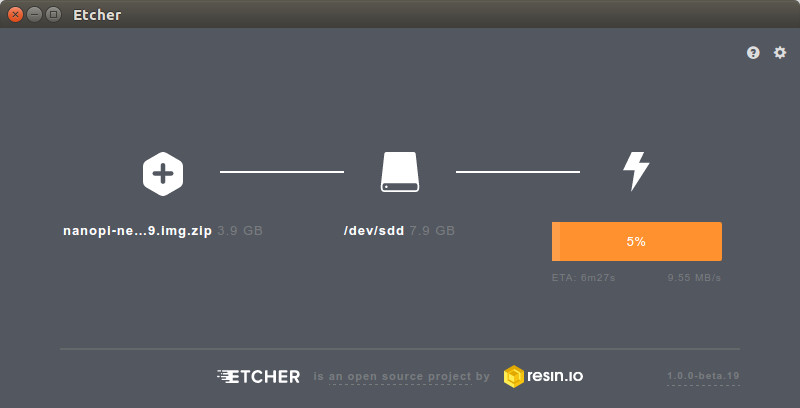
I’ve received NanoPi NEO 2 boards, add-boards and sensor modules last week, where we could see how small the boards were, and how it could be suitable for IoT projects or “hardware hacking” education. Before testing the board with the add-ons, I have to select the image to run on the board, and currently we have two choices: Ubuntu 16.04.2 FriendlyELEC image with Linux 3.10 “legacy” kernel, or Armbian Ubuntu 16.04.2 Xenial nightly build with Linux 4.10 “mainline” kernel. So I decided to try both: dfssf nanopi-neo2-ubuntu-core-qte-sd4g-20170329.img.zip (296 MB) is the image from FriendlyELEC (previously FriendlyARM) Armbian_5.27.170401_Nanopineo2_Ubuntu_xenial_dev_4.10.0.7z (222 Mb) is the image from Armbian, which I downloaded on March 31st despite the filename including “170401” string You can flash the image with Win32DiskImager (Windows) or dd (linux) to a micro SD card the usual way, and while I’ve never personally had troubles with dd, I’ve been told Etcher was better, […]
isorespin.sh Script Updates Ubuntu ISO Files with Mainline Linux Kernel
Devices based on Intel Bay Trail and Cherry Trail processors have been popular due to their integration into low cost system (for an Intel platform), but Intel did not prioritize Linux development for those processors, so while Linux could run, you’d have various problems with HDMI audio, system freezes, and wireless drivers, unless you used a custom kernel. The goods news is that Linux 4.11 will feature fixes for HDMI audio and system freeze, and so you won’t need a custom kernel anymore. Ian Morrison (Linuxium), who has been working on improving Linux for those devices since they were first released, has now released isorespin.sh script to automatically update any Ubuntu ISO image to the latest mainline Linux RC kernel built by Canonical, but not integrated by default in the ISO. Once you’ve downloaded isorepin.sh and your ISO of choice, e.g. ubuntu-16.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso, you can update the ISO with mainline Linux […]