LinuxCon (North America) 2012 will take place on August 29 – 31, 2012 at Sheraton Hotel & Marina, in San Diego, California. The event will be co-located with the Linux Kernel Summit, the Linux Plumbers Conference, and CloudOpen 2012. LinuxCon consists of 3 days of keynotes, business and developers related sessions as well as tutorials. There will be over 80 sessions and keynotes during those 3 days. I’ll highlight a few sessions that I find particularly interesting and related to embedded Linux, software development and ARM. August 29 10:45 – 11:30 – Life After BerkeleyDB: OpenLDAP’s Memory-Mapped Database by Howard Chu, Symas Abstract: OpenLDAP’s new MDB library is a highly optimized B+tree implementation that is orders of magnitude faster and more efficient than everything else in the software world. Reads scale perfectly linearly across arbitrarily many CPUs with no bottlenecks, and data is returned with zero memcpy’s. Writes are on […]
AnDevCon IV Classes and Workshops Schedule
AnDevCon is a technical conference for software developers building Android apps, and the fourth Android developer conference will take place in San Francisco on December 4-7, 2012. The organizers have already listed the schedule, including details about the workshops and classes which will take place at the conference. The 4th of December is reserved for workshops, and the other 3 days can be spent on shorter classes. All workshops will provide sample code, as well as most classes, excluding the overview session and business related sessions. There will be three full day Android workshops: Android Development Boot Camp – Hands-on introduction to Android application development and the tools essential to the process. Beyond an introduction to the basics, this workshop also covers some of the common hurdles met with development, and how to overcome them. You will also have the opportunity to build an Android app of your own where […]
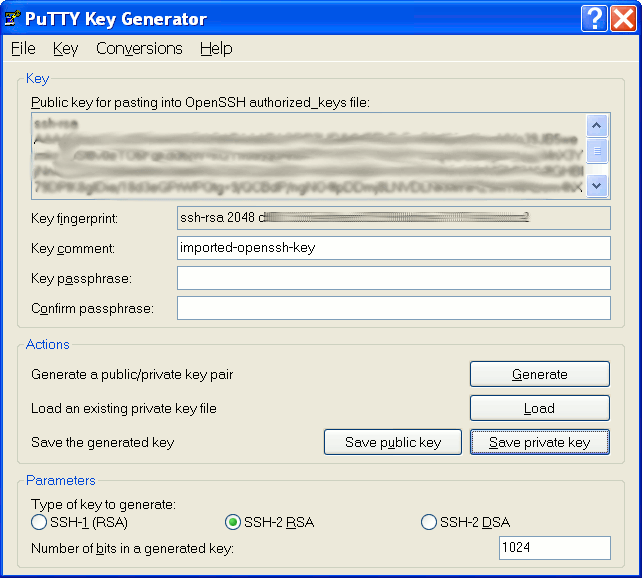
How To Use Putty with an SSH Private Key Generated by OpenSSH
I have access to a remote server where I am only allowed to login via SSH with a key, and I can’t add an extra key by myself, as described in “No Password SSH” post. The private key (RSA) has been generated with ssh-keygen in Linux, and I can login from Linux without issue. This morning, I wanted to do the same with Putty in Windows XP, so I just copied the private key to Windows and loaded it in Putty, but it failed:
|
1 |
Unable to use key file "F:\Downloads\cnxsoft\a1000\id_rsa" (OpenSSH SSH-2 private key) |
After a few minutes of research, I found my answer on UbuntuForums, and the reason it fails is because Putty does not support openssh keys, but uses its own format. Here’s what I had to do: Convert OpenSSH private key to Putty private key with Putty Key Generator (puttygen) Start puttygen, and click on Conversions->Import key, then click Browse and select the private key generated with […]
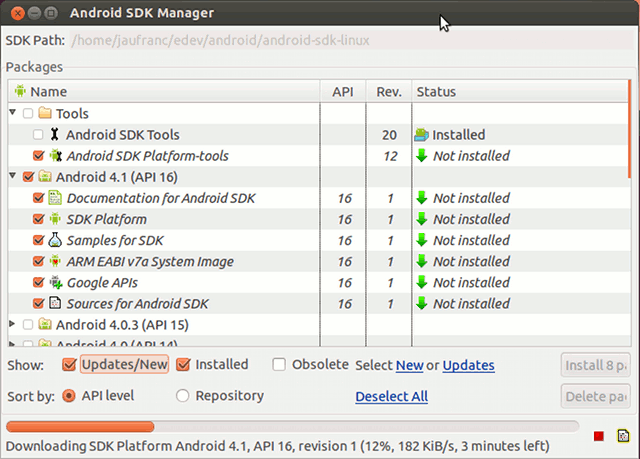
Installing Android SDK on Ubuntu 12.04
The official instructions to install Android SDK do not appear to be really up-to-date for Ubuntu 12.04, so I’ll post how I’ve installed the Android SDK and Eclipse on Ubuntu 12.04. First download and decompress Android SDK for Linux:
|
1 2 |
wget http://dl.google.com/android/android-sdk_r20-linux.tgz tar xzvf android-sdk_r20-linux.tgz |
on 64-bit Ubuntu:
|
1 |
apt-get install ia32-libs |
Sun Java is not part of Ubuntu packages anymore, so you’ll need to use openjdk instead
|
1 |
apt-get install openjdk-6-jdk |
Now install the SDK
|
1 2 |
cd android-sdk-linux/tools ./android sdk |
Android SDK Manager should show up. Use the default recommended packages and platforms, as well as any extra packages you may need, and click on Install x packages, accept all licenses and after installation is complete, the Android SDK is installed. Eclipse IDE is optional, but it’s the most widely used IDE to develop Android apps. You can install Eclipse as follows:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install eclipse-jdt |
Once both Android packages and platforms, and eclipse are installed, start eclipse:
|
1 |
eclipse |
Then in the top menu, click on Help->Install […]
Hardware Packs for AllWinner A10 Devices and Easier Method to Create a Bootable Ubuntu 12.04 SD Card
Linaro has a tool called linaro-media-create to install Linaro Ubuntu to an SD card by passing the device, hardware pack file, the rootfs and the board as arguments. Hardware packs are files that contains hardware specific binaries and configs files (e.g. bootloader, kernel…). I’ve done something similar (albeit more basic) for AllWinner A10 devices so that you can easily install and run Ubuntu (and possibly other distributions) on an SD card. I’ve written 2 scripts for this: a10-hwpack-bld.sh – Script to generate evb.bin, build the latest u-boot and linux kernel, retrieve some config files and compress all this in an hardware pack file a1x-media-create.sh – Script to make a bootable SD card for AllWinner A10 devices. You can get the scripts with git:
|
1 |
git clone git://github.com/cnxsoft/a10-tools.git |
I’ve only tested it with Mele A1000, but if you have other A10 devices such as MK802 mini PC or MINI X media player, it should […]
Importing Source Code to Github
Github is a hosting service for software development projects using the Git revision control system. GitHub offers free accounts for open source projects (public repositories) and commercial plans for private repositories. I’ve been using github for a while to clone source code, but I had never imported existing source code to github. Here are the steps to follow: If you don’t have an account yet, sign-up for github. Setup github for Linux, Windows or Mac OS X. Create a repository as shown as explained here. You should now have a URL in github, something like [email protected]:user/repo_name.git, which we’ll use below. Go to the directory with your existing source code and create a local repo:
|
1 2 3 |
git init git add . git commit -m "Initial commit" |
Finally, type the commands below to add your code to your new repository:
|
1 2 3 |
git remote add somename git@github.com:user/repo_name.git git pull git@github.com:user/repo_name.git git push somename master |
That’s it, anybody should now be able to clone you code as follows:
|
1 |
git clone git://github.com/user/repo_name.git |
NB: If your existing source code (or […]
Getting Started with MultiArch (armel / armhf) in Ubuntu
Until now, I used xapt and dpkg-cross to install cross libraries for armel, but since I’ve upgraded to Ubuntu 12.04, it appears to be broken. I’ve contacted Linaro about this issue, and the “cross-building” expert at Linaro (wookey) recommended me to use multiarch instead, as xapt/dpkg-cross will be eventually deprecated. He provided me an example showing how-to use multiarch to build Chromium. I’ve been looking for a “How-to multiarch”, but haven’t been able to find something really clear and simple, so I thought I would post it here. In the example, they used a chroot for cross-building, which is probably a good idea to avoid messing up with the system. It’s also possible multiarch is not 100% reliable, and I’ve read stories where people messed up their system when using multiarch with i386 (32-bit) and amd64 (64-bit). Preparing a chroot for cross-building I’ll use a 32-bit Ubuntu precise chroot, but […]
Glark, an alternative to Grep
grep is a very useful tool to search or filter strings in order to look for files, parse useful info in log files and more. glark is an alternative to grep, it has few features that grep does not such as complex expressions, Perl-compatible regular expressions, and excluding binary files. It also has a more fancy way of display results. It is described as follows in the manpage: Similar to “grep”, “glark” offers: Perl-compatible regular expressions, color highlighting of matches, context around matches, complex expressions (“and” and “or”), grep output emulation, and automatic exclusion of non-text files. Its regular expressions should be familiar to persons experienced in Perl, Python, or Ruby. File may also be a list of files in the form of a path. glark is not installed by default. To install it in Debian/Ubuntu/Mint: sudo apt-get install glark It does not appear to be available in Fedora and […]