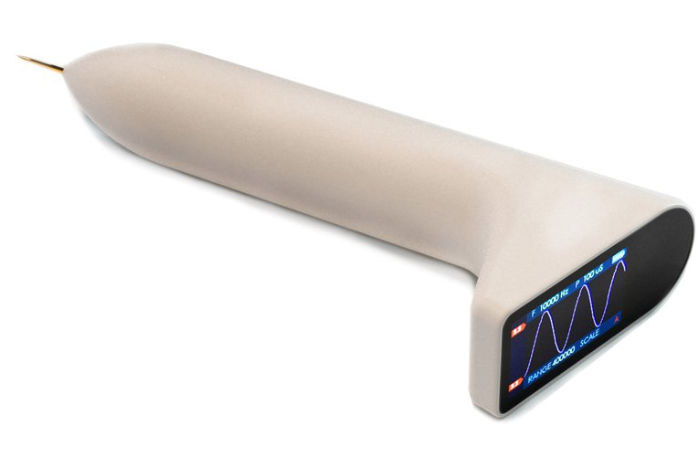
QUARK may look like the perfect weapon to hijack a plane, but instead, it’s an open-source, Arduino-based wireless multitool for hardware engineers equipped with a full-color screen and touch-based controls. Based on ESP32 WiFI & Bluetooth wireless SoC, Mulin Group’s QUARK is an ultra-portable multimeter, signal generator and oscilloscope, a bit like IkaScope WiFi Pen-Oscilloscope, except having a laptop or phone to visualize measurements is only optional. The company also compares it to DT71 smart tweezers which do not have an oscilloscope function due to the tiny display. QUARK features & specifications: WiSoC – ESP32 dual-core processor with WiFI & Bluetooth connectivity Display – 240 x 134 IPS display Measurements Voltage – 0 to 26 V Current – 0 to 3.2 A Resistance from 0 to 2 MΩ Capacitance from 2 pf to 1000 uF Inductance up to 1 H Sampling rate for oscilloscope function – 400 ksps Features – […]
Cynthion board enables USB Hacking through Lattice ECP5 FPGA (Crowdfunding)
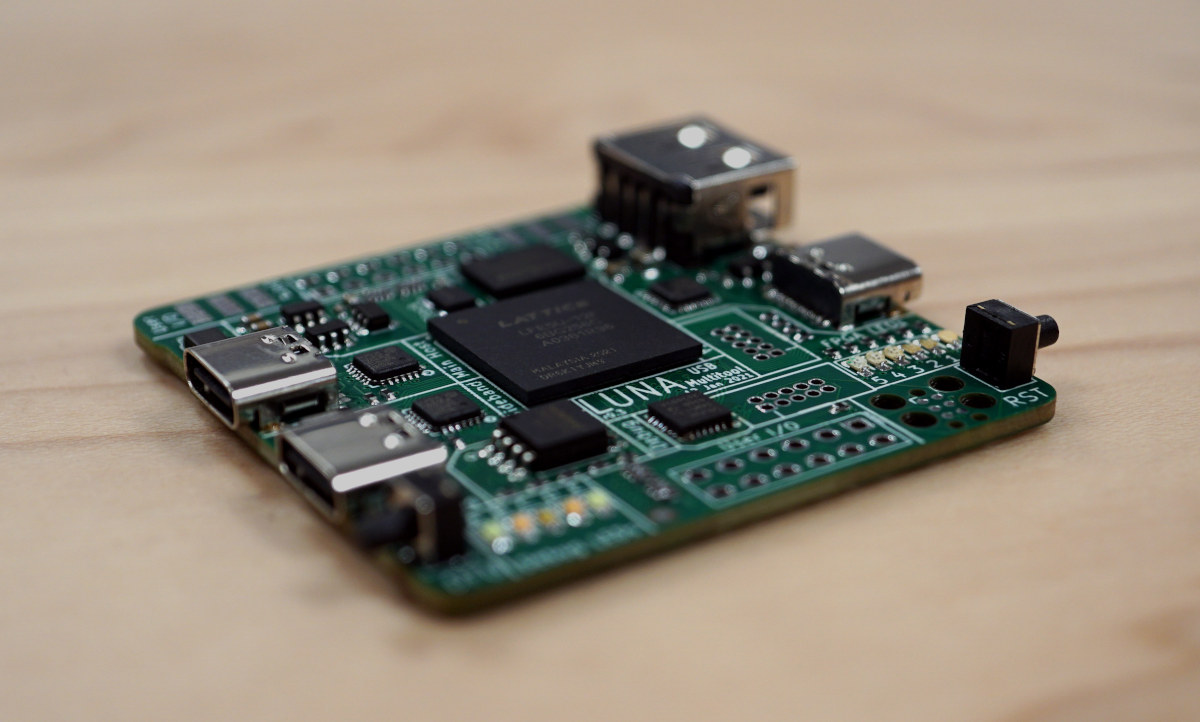
Update 16/02/2023: The LUNA board has been renamed to Cynthion, but the gateware framework continues to be called LUNA. Several USB hacking/debugging boards were launched in 2020 either based on microcontrollers or FPGA with the likes of Tigard (FTDI FT2232HQ), Ollie (STM32F042), Glasgow Interface explorer (Lattice Semiconductor iCE40), or Protocol Droid (STM32). All those were launched on Crowd Supply, and there’s now another one with LUNA “multi-tool for building, analyzing, and hacking USB devices” based on a Lattice Semiconductor LFE5U-12F ECP5 FPGA that raised over $100,000 in a few days. Cynthion hardware specifications: FPGA- Lattice Semiconductor LFE5U-12F ECP5 FPGA with 12K LUTs System Memory – 64 Mbit (8 MiB) RAM for buffering USB traffic or for user applications Storage – 32 Mbit (4 MiB) SPI flash for PC-less FPGA configuration USB – 3x High-Speed USB interfaces, each connected to a USB3343 PHY capable of operating at up to 480 Mbps. […]
WARP-V: A RISC-V CPU Core Generator Supporting MIPS ISA
If you have been working on open standard RISC-V ISA CPU cores, there is a high chance that you have come across WARP-V. For newbies, WARP-V is a RISC-V CPU core generator written in TL-Verilog (Transaction-Level Verilog) that supports not only RISC-V but also MIPS ISA. WARP-V has been in discussion for a while due to its unparalleled architectural scalability in a small amount of code. The famous proverb “Necessity is the mother of invention” applies to the invention of TL-Verilog and with that this WARP-V CPU core generator. For decades, hundreds of engineers have been working on designing a single CPU core that was more complex in the race to achieve higher single-core performance. But with recent developments in the semiconductor industry, developer and engineer Steve Hoover, with decades of experience in designing CPU cores, has come up with the idea of developing a WARP-V core in just 1.5 […]
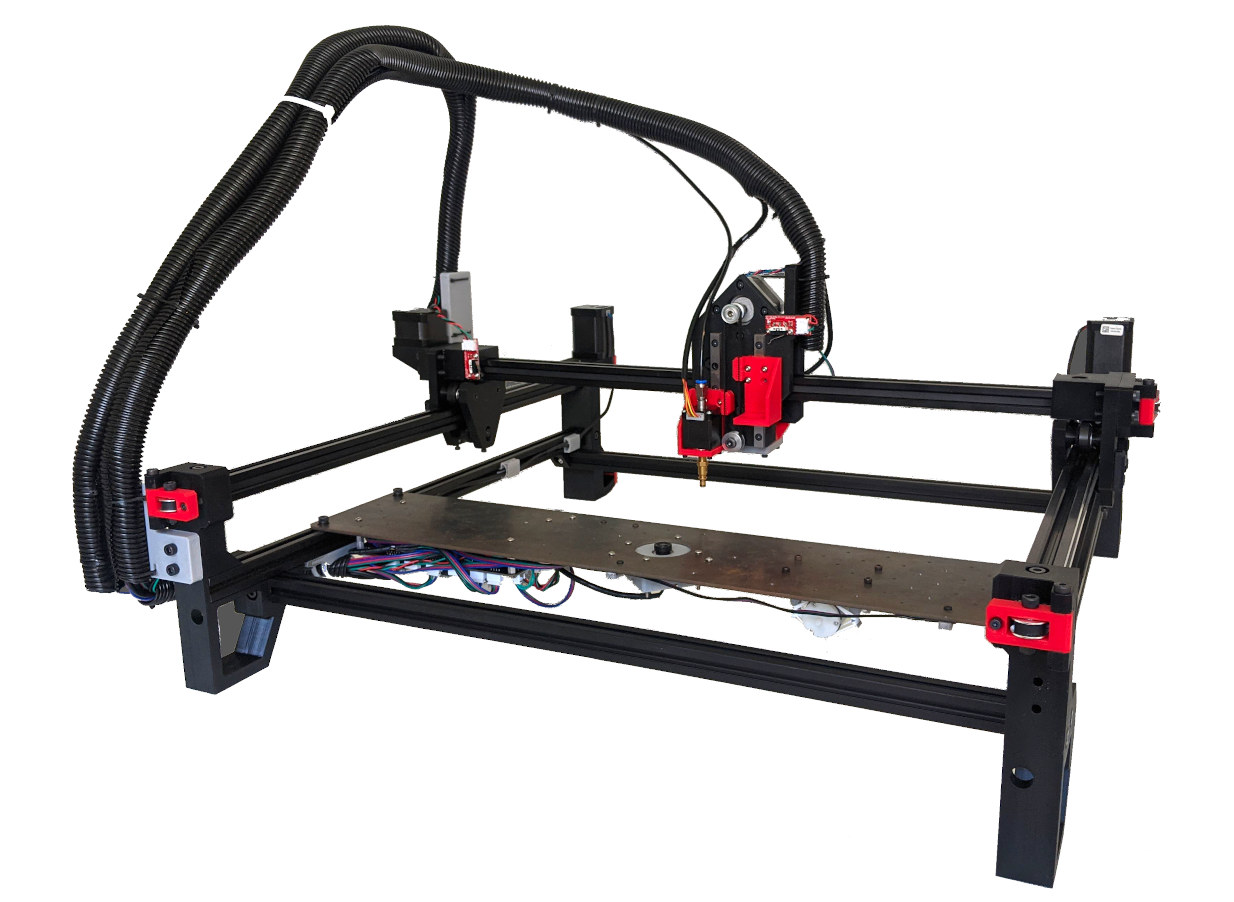
Index PnP – An open-source pick-and-place machine for mid-scale manufacturing
We’ve previously written about one open-source pick-and-place machine, SimplePNP aiming to provide a low-cost solution for several hundred dollars and relying on OpenPnP open-source control software. But Stephen Hawes found out this type of solution did not cut it for mid-scale manufacturing (100 to 5000 units per year), so he decided to build his own. Meet Index PnP, an open-source pick-and-place machine designed for mass-production volumes typical of crowdfunding projects. The project was introduced launched with the following requirements Automated – no human interaction necessary from attaching the paste-applied board to the machine to having a board ready for reflow Capable of picking and placing components down to 0603 passives Integrated up and down vision for fiducial scanning and on-nozzle component alignment Automatic nozzle tip changer to support a wide range of component sizes Frame and motherboard design capable of future upgrades Mechanical and Electrical support for conveyor belt module […]
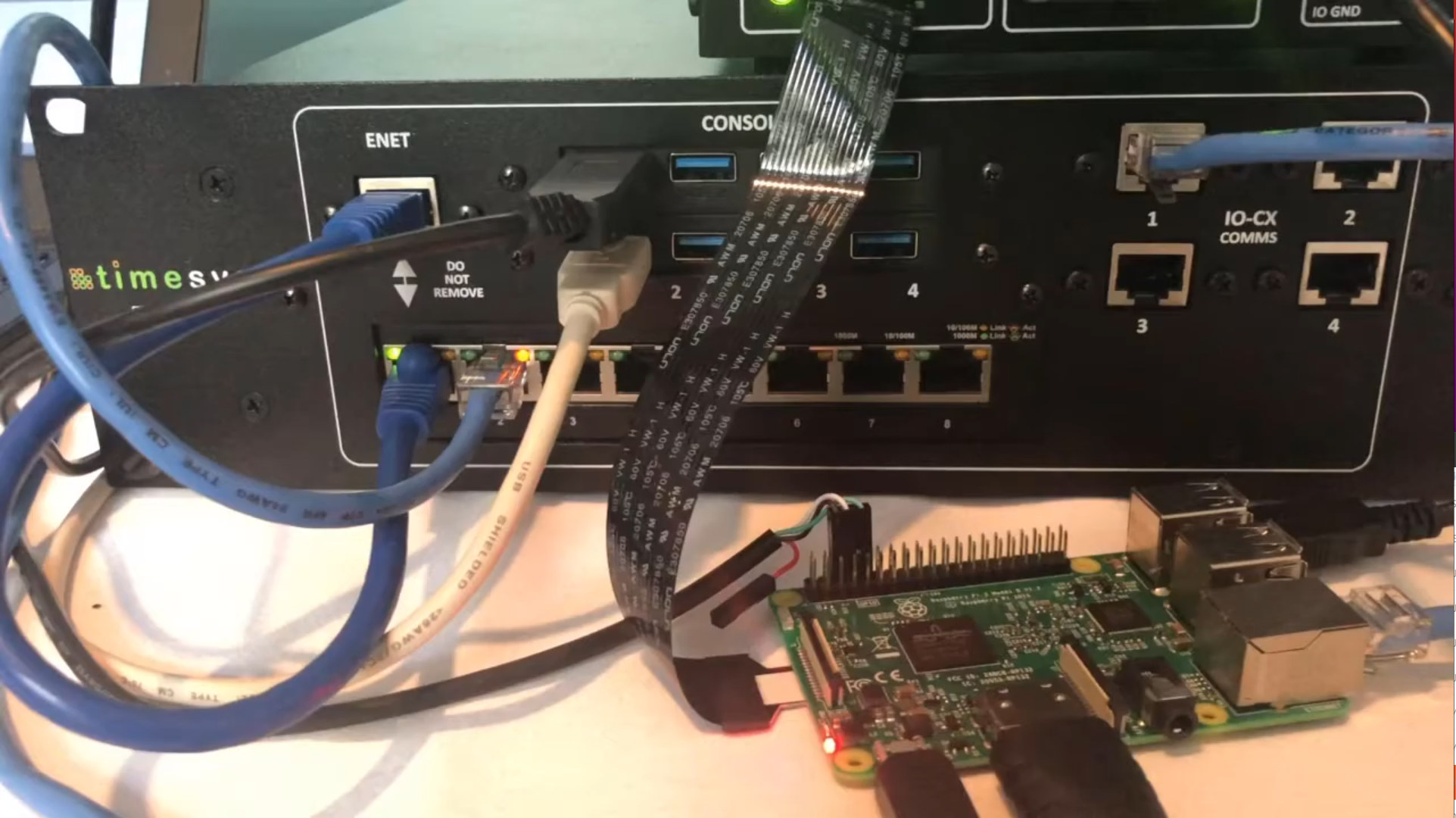
Timesys Embedded Board Farm enables remote access to hardware for software development & QA
When you design a new board with an international team working in multiple locations, there may only be a couple of boards available for testing, and that’s mean some members of the team may not have access to the hardware. The same problem can be true for test farms with a larger number of boards. So it would be good to have a solution to remotely access and control the hardware to speed up development. A few years ago we wrote about MuxPi board using NanoPi NEO SBC to enable remote testing of development boards, but now Timesys has come up with a more advanced solution with the Embedded Board Farm (EBF) capable of sharing multiple boards across teams spread around the world. The solution is comprised of three main components besides the target boards: The Master Server integrated with LAVA test automation framework – It handles docker images, firmware/file […]
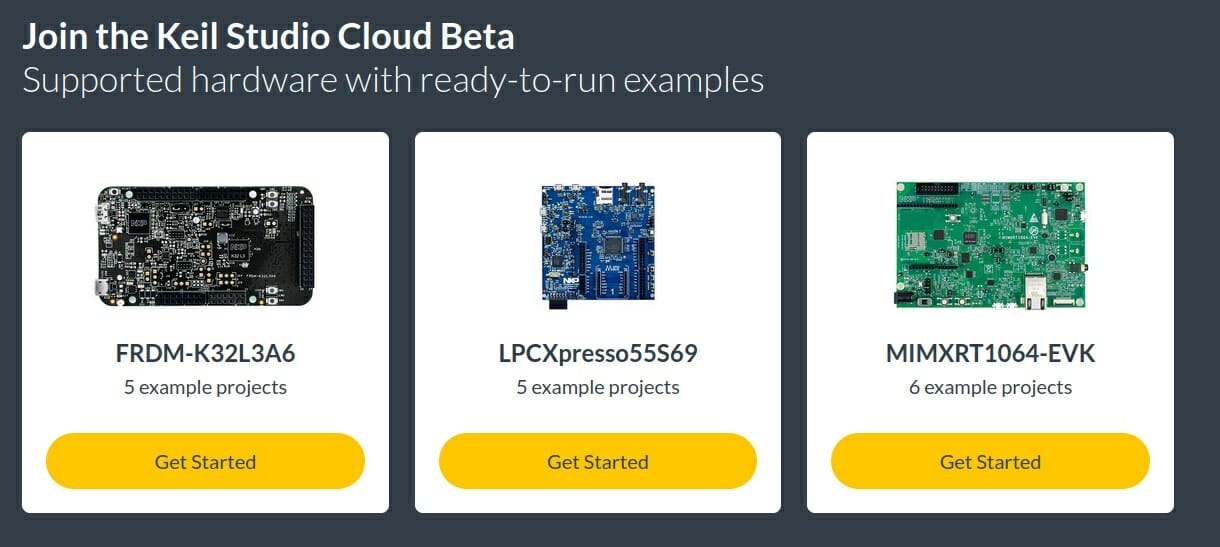
Arm introduces Open-CMSIS-Pack and Keil Studio Cloud for MCU software development
Arm has just announced two new initiatives that aim to boost the productivity embedded, IoT, ML, and MCU software developers: the Open-CMSIS-Pack project and Keil Studio Cloud. The Open-CMSIS-Pack Project The Cortex Microcontroller Software Interface Standard (CMSIS) packs have been around for years providing a vendor-independent hardware abstraction layer for microcontrollers, mostly Cortex-M based, but others too, and currently support close to 9000 different microcontrollers. I always assumed CMSIS was open-source as the source code is available in Github under an Apache 2.0 license. But apparently, not all components are, and Arm has now announced the Open-CMSIS-Pack project that will move part of CMSIS into the open project in collaboration with the Linaro IoT and Embedded Group. Linaro, Arm, and other partners like STMicro and NXP will initially focus their work on command-line tools and CMake workflows, with the ultimate goal of making the CMSIS-Pack technology into a true open […]
The OSFPGA Foundation aims to promote open-source FPGA tools and IP blocks
There are been some initiatives to work on open-source tools for FPGA. Major FPGA vendors have made limited efforts, with for example Xilinx recently releasing the source code for HLS FPGA tool’s front-end, but most of the work is done by the community with projects like Symbiflow dubbed the GCC of FPGAs, or Project IceStorm for Lattice Semi FPGAs. Industry veterans and academics have decided to launch the Open-Source FPGA (OSFPGA) Foundation that aims to bring together companies, universities, and individuals to advance open-source FPGA capabilities, establish cooperation channels, promote outreach and education, and coordinate joint efforts around an open-source FPGA ecosystem. The OSFPGA Foundation goals go beyond just providing open-source tools, as the vision statement also mentions “open-source FPGA & eFPGA fabrics”, the Github page also includes IP blocks with the FuseSoC package manager for IP cores, the Skywater Open-source FPGAs, and LiteDRAM lightweight, configurable DRAM core. Current board […]
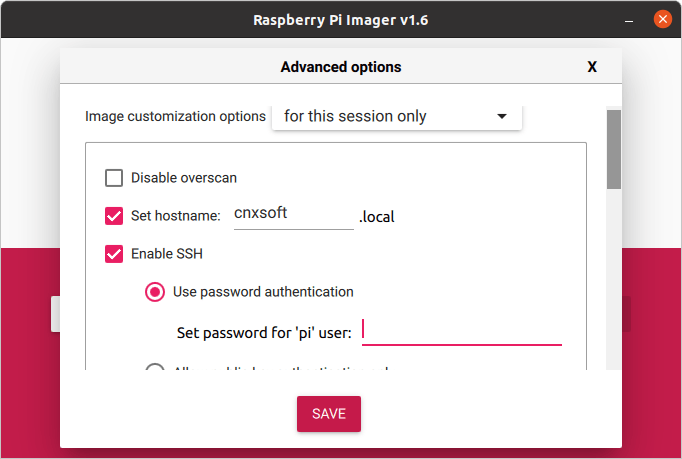
It’s now easier to customize Raspberry Pi OS images
When I need to flash a Raspberry Pi OS image, I usually download the image from the Raspberry Pi website before flashing it to a MicroSD card with either balenaEtch or USBimager. The Raspberry Pi Foundation released the Raspberry Pi Imager last year, but I never used it, except to try it out, because at the time, it would just flash the image to the MicroSD card like other tools, and since I’m working with SBCs from different vendors it did really not bring any benefits to me. But with the v1.6 release, the Raspberry Pi tool has become more useful to advanced users, notably those who like to set up the image in a headless Pi. Before we had to flash the image, mount the MicroSD card, and go edit /boot/config.txt to enable SSH and other settings. Now, it’s possible to do the same from Raspberry Pi Image v1.6 […]