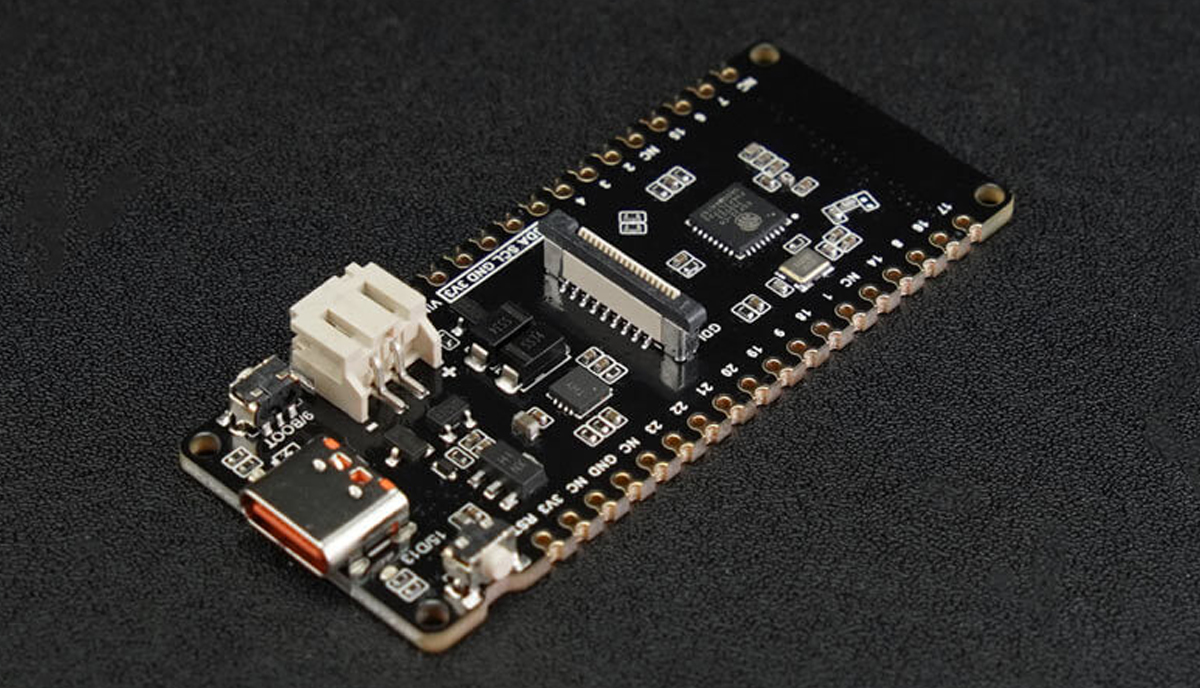
DFRobot’s FireBeetle 2 ESP32-C6 is an IoT Development Board with 802.11ax (now called Wi-Fi 6), Bluetooth 5, Zigbee 3.0, Thread 1.3, and flexible power options including USB Type-C, 5V DC, and a CN3165 Lithium Ion battery charger for solar-powered systems. This isn’t the first solar-based board we’ve covered. We’ve also explored boards like Conexio Stratus, Wisblock Kit 2, and RAK8211-NB iTracker along with other solar-powered devices such as solar-powered laptops, solar-powered headphones, and even a solar-based power supply. FireBeetle 2 ESP32-C6 IoT Development Board Specifications: Processor – ESP32-C6 RISC-V single-core, 160 MHz Memory SRAM – 512KB ROM – 320KB Flash – 4MB RTC SRAM – 16KB USB – USB 2.0 CDC Wi-Fi Protocols – IEEE 802.11b/g/n, IEEE 802.11ax (20 MHz-only non-AP mode) Bandwidth – Supports 20 MHz and 40 MHz at 2.4 GHz Modes – Station, SoftAP, SoftAP+Station Frequency – 2.4GHz Frame Aggregation – TX/RX A-MPDU, TX/RX A-MSDU Bluetooth Protocol […]
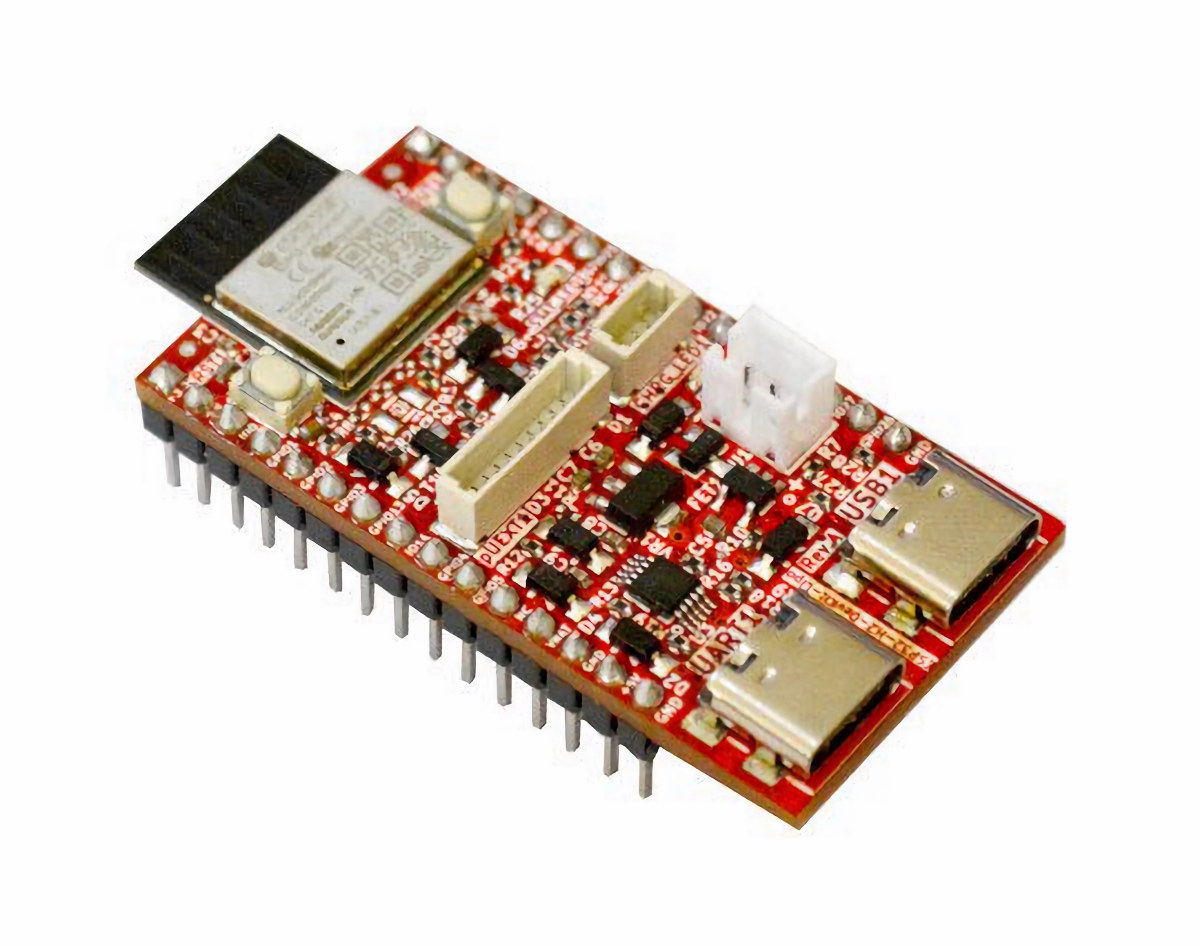
8 Euros ESP32-H2-DevKit-LiPo is an open-source hardware Bluetooth 5 LE and 802.15.4 (Zigbee/Thread/Matter) board
Olimex ESP32-H2-DevKit-LiPo is an open-source hardware board based on ESP32-H2-MINI-1-N4 wireless module with Bluetooth 5 Low Energy (LE) and an 802.15.4 radio for Zigbee, Thread, and Matter connectivity, and that can be powered by a LiPo battery. The ESP32-H2 RISC-V microcontroller is coupled with 4MB flash in the wireless module, and the board comes with two rows of 15 pins for up to 19 GPIOs with alternate functions such as ADC, SPI, UART, I2C, etc… plus pUEXT and Qwiic/Stemma connectors for expansion modules. The board also features two USB-C ports, one for connected directly to the ESP32-H2 and the other for USB to UART programming/debugging. ESP32-H2-DevKit-LiPo specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-H2-MINI-1-N4 MCU – Espressif Systems ESP32-H2 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller at up to 96 MHz with 320 KB SRAM, 128 KB ROM, 4 KB LP memory, Bluetooth 5.2 LE/Mesh and 802.15.4 (Zigbee/Thread/Matter) radios. Storage – 4MB flash storage PCB antenna Dimensions […]
Arduino and Silicon Labs collaborate to bring Matter to Arduino boards and IDE
Arduino and Silicon Labs have joined hands to both bring Matter-compatible SiLabs wireless microcontrollers to the Arduino IDE and then design an upcoming Arduino Nano based on SiLabs MGM240 Arm Cortex-M33 microcontroller with Matter, Thread, Zigbee, and Bluetooth LE protocols. Available now: Arduino Core for Silicon Labs devices The first phase of the collaboration involves getting Arduino core for Silicon Labs development boards so that compatible devices can be programmed in the IDE. The good news is that it’s available now and works with four existing wireless boards: SparkFun Thing Plus Matter MGM240P based on MGM240PB32VNA Arm Cortex-M33 MCU with Matter, Thread, Zigbee 3.0, and Bluetooth 5.3 LE connectivity SiLabs xG27 Dev Kit based on EFR32BG27C140F768IM40 Arm Cortex-M33 MCU with Bluetooth LE 5.3, Bluetooth Mesh, Proprietary 2.4 GHz connectivity SiLabs xG24 Explorer Kit based on EFR32MG24B210F1536IM48 Arm Cortex-M33 MCU with Bluetooth 5.3 LE, Bluetooth Mesh, Matter, OpenThread, Zigbee, Proprietary 2.4 […]
Silicon Labs partners with Nabu Casa to support Home Assistant development
Silicon Labs has entered an official partnership with Nabu Casa, the company behind the popular Home Assistant home automation software, to support the development of Home Assistant open-source software and Silicon Labs-based hardware platforms. Most open-source embedded software projects start as a one-person (or a small team) effort as the vendor-provided firmware and related software may not have the features set needed by this user or group of users. So they hack existing hardware to build something that better fits their requirements often without input/help from the silicon vendor or product manufacturer. But sometimes the project becomes popular enough that large companies start to help it with support and funding. That’s apparently the case for Home Assistant project with Silicon Lans and Nabu Case entering an official partnership. The announcement does not provide details about the partnership but explains this should lead to better support and improvements for both Home […]
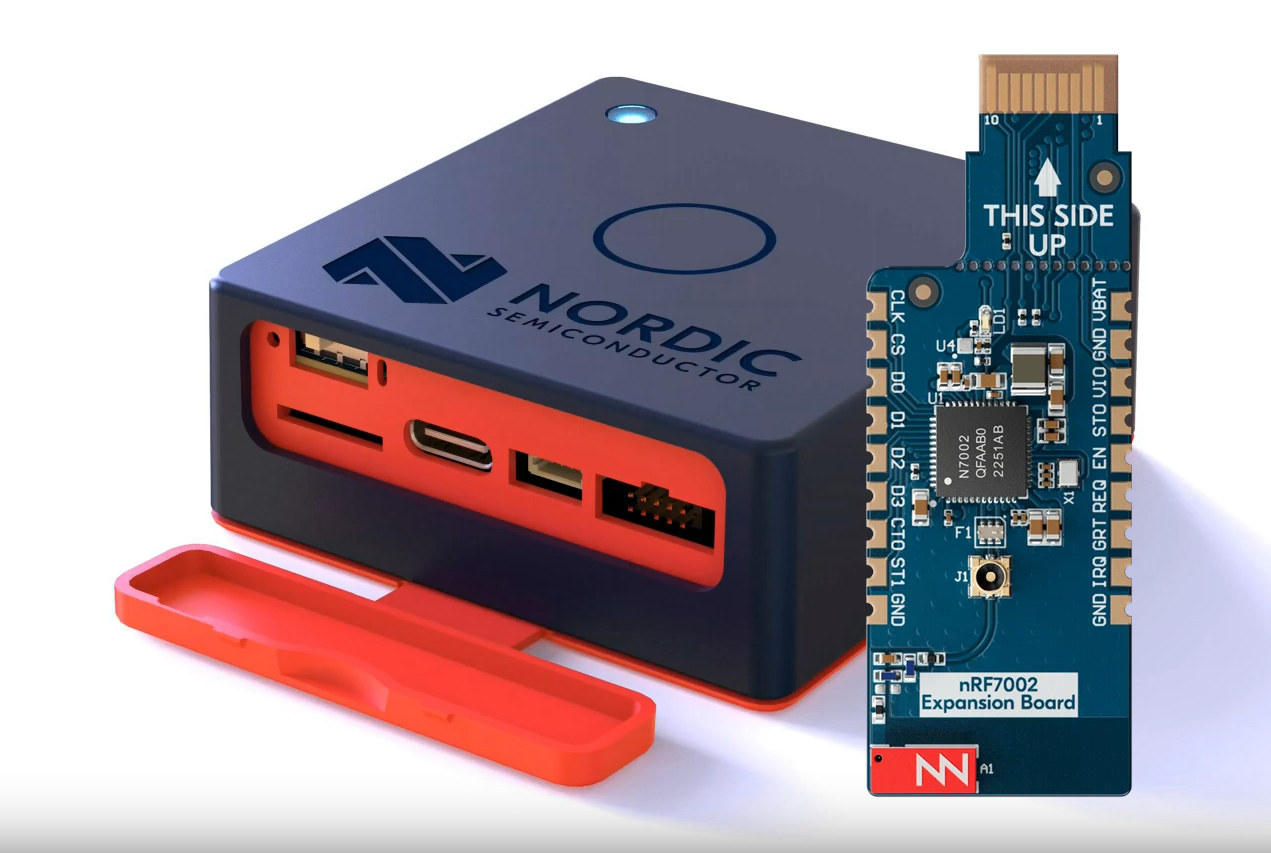
nRF7002 Expansion Board adds WiFi 6 to Nordic Thingy:53 devkit
Nordic Semi keeps adding more nRF7002 WiFi 6 boards with the launch of the nRF7002 Expansion Board adding WiFi 6 connectivity to the Thingy:53 IoT prototyping platform and transforming it into an all-in-one wireless devkit with Matter, Bluetooth Low Energy, Thread, and WiFi 6 support. The new “nRF7002 EB” board follows the nRF7002 DK development kit combining the nRF7002 WiFi 6 with nRF5340 multiprotocol wireless SoCs, and the nRF7002 EK evaluation kit in Arduino UNO shield form factor adding WiFi 6 to existing Nordic development kits. nRF7002 Expansion Board specifications: Chipset – nRF7002 Wi-Fi Companion IC with support for features such as OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access), Beamforming, Target Wake Time, and SSID-based locationing Antenna – 2.4 GHz / 5 GHz ceramic antenna I/Os Castellations for all pins on nRF7002 Thingy:53 expansion connector with SPI and a 3-wire coexistence interface to allow seamless coexistence with other wireless protocols Misc […]
Giveaway Week 2023 – GL.iNet GL-S200 Thread Border Router devkit
It’s already day 4 of CNX Software Giveaway Week 2023 and today, we’ll be giving away GL.iNet GL-S200 Thread Border router kit that also includes three USB or battery-powered Thread development boards to experiment with various Thread topologies. The GL-S200 router comes with a Qualcomm QCA9531 MIPS router processor running a fork of OpenWrt and provides two Fast Ethernet WAN/LAN ports, 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi 4 802.11b/g/n up to 150 Mbps, and support for Thread (via an 802.15.4 radio) and Bluetooth 5.0. The development boards are based on the Nordic Semi nRF52840 microcontroller and each features a potentiometer+button, a PIR sensor, and two RGB LEDs. I reviewed the GL-S200 Thread Border router kit using the router’s dashboard interface and demo firmware provided for the three development boards. This enabled me to test star topology and mesh networking, and play around with demo scripts and code samples to display sensor and potentiometer […]
Nordic nRF54L15 Cortex-M33 wireless MCU halves Rx power consumption over nRF52 chips
Nordic Semiconductor has recently unveiled the 128 MHz nRF54L15 Cortex-M33 multi-protocol wireless microcontroller, the first from the nRF54L Series, and the second from the wider nRF54 family after the more powerful 320 MHz nRF54H20 dual-core Cortex-M33 MCU was introduced last Spring. While the nRF54H20 was designed to enable new types of IoT devices with a leap in performance and lots of resources with up to 2 MB flash and 1MB SRAM, the new nRF54L15 aims to be an upgrade to the nRF52 series with twice the performance and much better power efficiency, with for instance, half the Rx power consumption over its predecessor. Nordic Semi nRF54L15 key features and specifications: CPU Arm Cortex-M33 @ up to 128 MHz with up to 1.5 MB Flash + 256 KB SRAM RISC-V coprocessor for “software-defined peripheral” Wireless Bluetooth 5.4 LE with direction-finding, Bluetooth mesh, etc… Ready for future Bluetooth releases 802.15.4 radio for […]
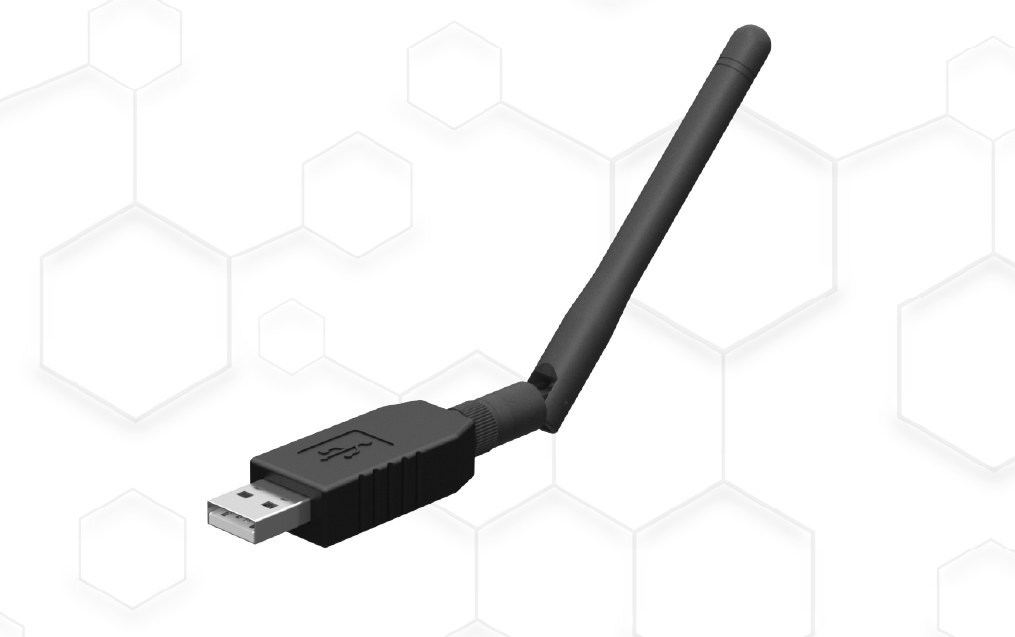
SMLIGHT SLZB-07 – A low-cost, compact Zigbee 3.0 USB adapter
SMLIGHT SLZB-07 is a low-cost, compact Zigbee 3.0 USB adapter based on Silicon Labs EFR32 microcontroller and CP2102 USB to serial chip designed to work with multi-vendor software systems such as Zigbee2MQTT and Home Assistant ZHA. The adapter lets you easily integrate any Zigbee devices into Smart Home automation systems such as Home Assistant, OpenHub, or HomeSeer and offers an alternative to products like the official SkyConnect USB stick and SONOFF ZBDongle-E. It’s also Thread and Matter ready. SMLIGHT SLZB-07 specifications: Wireless SoC – Silicon Labs EFR32MG21 Arm Cortex-M33 microcontroller @ 80 MHz with 352KB flash, 1024KB ROM for protocols and library functions, 96KB SRAM, integrated power amplifier, Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy and 802.15.4 radios (Zigbee and Thread) Connectivity Zigbee 3.0 support, including Zigbee Green Power. Thread/Matter ready +3dB SMA antenna included USB – USB Type-A port for data and power Power Supply Input – 5V/60mA via USB-A Overvoltage protection […]