For some reasons, people who decide to name things like to give one name for technical people, and another for consumers. A few years ago, I went to buy a 1080p TV, but at first the seller was confused when I asked, and then I talked about resolution, and when he asked “Full HD” or “HD Ready”? It was my turn to me confused. There are several other example such as Bluetooth Low Energy for geeks may be Bluetooth Smart for consumers, and now the Wi-Fi alliance has just announced that IoT devices and gateway featuring the latest 802.11ah standard will be designed as Wi-Fi HaLow devices. They have not come up with a Wi-Fi Halow logo yet… Nevertheless, apart from the name, nothing appears to have changed. HaLow/802.11ah is still the same Wi-FI standard operating at 900MHz targeting IoT applications with low power, long range (up to 1km), and […]
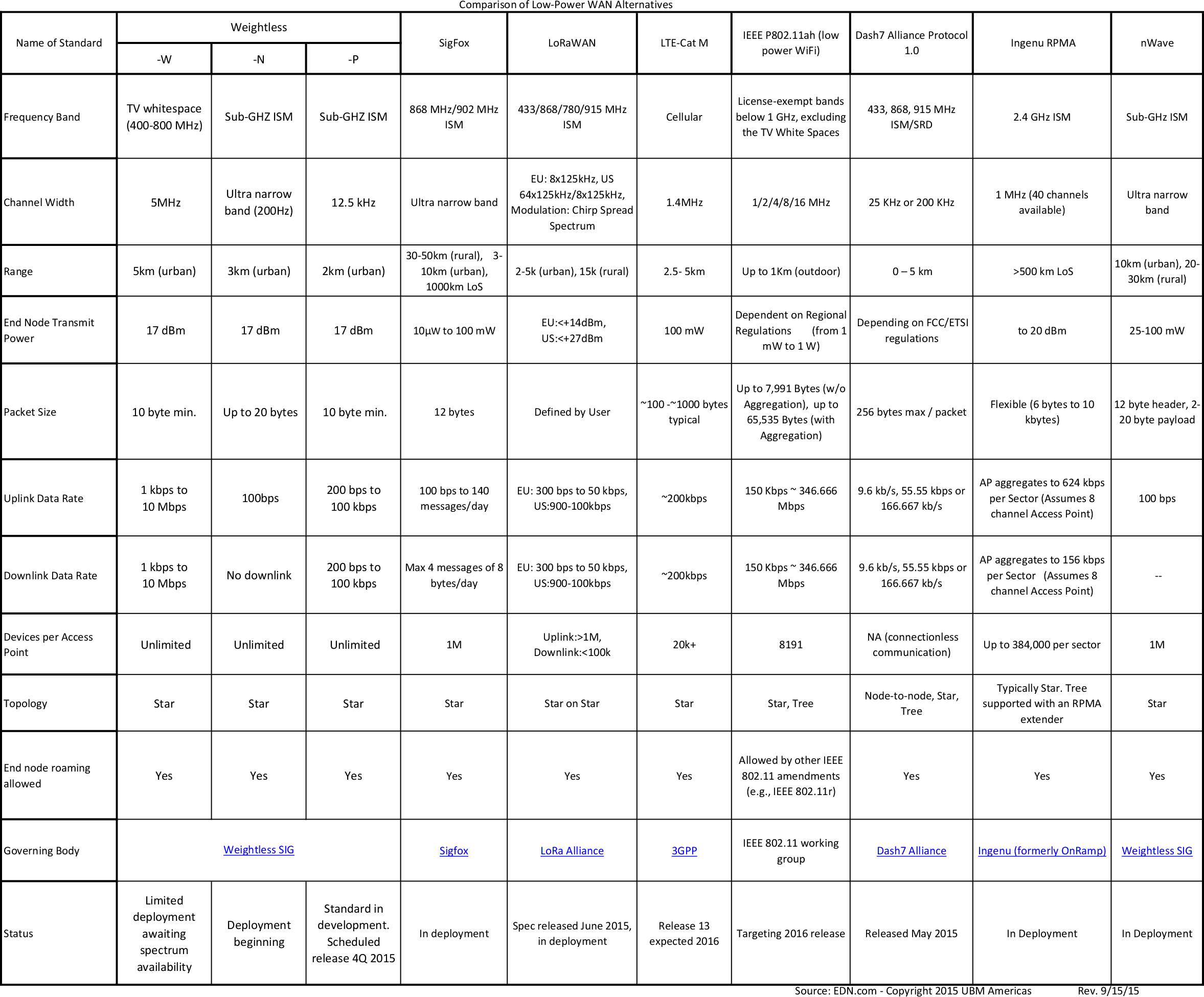
Comparison Table of Low Power WAN Standards for Industrial Applications
WiFi, Bluetooth and Zigbee are commonly found in consumer devices part of the “IoT ecosystem”, but the range, cost, power consumption, and/or scalability of these wireless standards are not suitable. For example, agricultural and forestry applications normally require long distance, and smart parking or city lighting may requires scalability to a great number of nodes, so alternatives are needed. EDN wrote a thorough article comparing 10 alternative wireless standards: Weightless-W, Weightless-N, Weightless-P, SigFox, LoRaWAN, LTE-Cat M, IEEE P802.11ah, Dash7, Ingenu RPMA, and nWave. The table includes the frequency band, channel width, range, transmit power, packet size (minimal or maximal), downlink and uplink data rates, maximum number of connected devices, topology, roaming capability, and status. If you had to implement something today, four to five solutions are “in deployment”: SigFox, Ingenu RPMA, nWave, LoRa, and possibly Dash7, while the other are only starting to get deployed, or will be finalized in […]
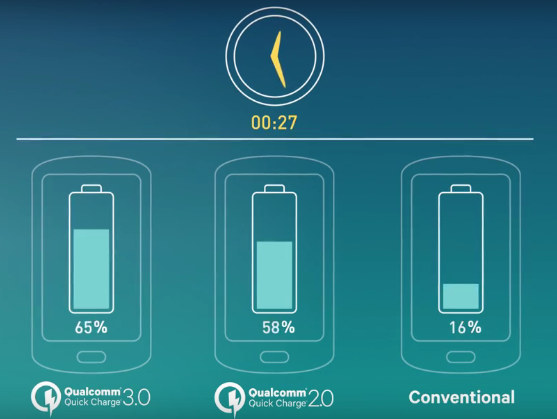
Qualcomm Quick Charge 3.0 Promises to Charge Phones About 3x Faster Than Conventional Devices
Qualcomm has recently announced the latest version of its Quick Charge technology that allows to charge supported smartphones much faster than typical smartphones using a 5V charger. The company claims that Quick Charge 3.0 enabled smartphones can typicallly charge from zero to 80 percent in about 35 minutes compared to almost 90 minutes with conventional devices. Quick Charge 3.0 adds support for Intelligent Negotiation for Optimum Voltage (INOV), a new algorithm developed by Qualcomm Technologies that allows mobile devices to request optimal power transfer (3.6V to 20V in 200mV increments), while maximizing efficiency, which – together with other improvements – increases power efficient by 38% compared to Quick Charge 2.0, and allows charging the device twice as fast as possible with Quick Charge 1.0. That means the voltage and amperage will change during charging between 3.6V to 20V by 200mV increments, instead of 5V, 9V, 12V, and 20V for QC […]
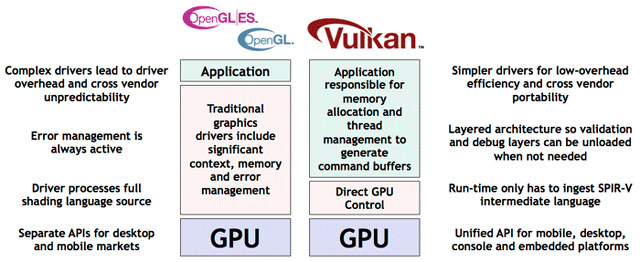
Google Plans Vulkan API Support for Android, Imagination Shows a Demo
Vulkan graphics API is the successors to OpenGL and OpenGL ES API, which will support multi-threaded rendering, move some of the complexity to the applications, and simplify graphics drivers, which may not be a bad things since these tend to be closed source, and bugs may be hard to get fixed. Google, which is now a subsidiary of a new company called Alphabet, has recently announced that Vulkan will be implemented in future versions of Android, although OpenGL ES will still be supported, so developers can select their preferred graphics API for their apps, as Vulkan will be more complex for application programmers than OpenGL ES. Separately, Imagination technologies showcased their Vulkan driver for PowerVR Rogue GPU on the Nexus Player powered by an Intel SoC including a PowerVR G6430 GPU, and compare the Vulkan demo to the same demo using OpenGL ES 3.0 drivers. The difference between Vulkan and OpenGL […]
Weightless-P Standard is Designed for High Performance, Low Power, 2-Way Communication for IoT
Weightless was unveiled over two years ago, as a new standards for IoT leveraging “white space” spectrum, previously used by analog TV broadcasts, for free M2M / IoT communication using low power (10 years battery life) and cost-efficient hardware ($2 hardware) offering a range of 5 to 10 km. Development kits and base stations were scheduled for Q2 2014, but there’s either been some delays or they are only available to Weightless members, as you need to register to get notified once hardware becomes available. The Weightless SIG (Special Interest Group) has not stopped working on the standard as there are now three Weightless standards: Weightless-W (using White band spectrum), Weightless-N (sub-GHz spectrum), and and newly announced Weightless-P offering similar features as 3GPP carrier grade solutions, but at lower costs and lower power consumption. The key features of Weightless-P are shown below: Excellent capacity and scalability for IoT deployment FDMA+TDMA […]
96Boards Enterprise Edition Specification Published
When AMD announces its 96Boards Enterprise Edition complaint server board, I could read quite a few complains because the board used a non-standard form-factor such as mini-ITX. The first version 96Boards Enterprise Edition specification has now been published, and the goods news is that there are two versions: the low cost ($199 to $399) “Standard version” with the new proprietary format, and likely more expensive “MicroATX version” that must complies with MicroATX v1.2 specs. The minimum hardware requirements are listed as follows: Small form factor Standard EE version – 160 x 120mm microATX EE version – 244 x 244mm Design is SoC independent (targets 32 or 64 bit SoCs) 1GB RAM (16GB strongly recommended for server software development) Minimum on-board connectors and expansion I/O 1x Serial over USB UART with microUSB interface 2x USB 1x RJ45 Ethernet Standard version board power from low cost 12V DC Jack connector or standard […]
Perseus Video Codec Claims 2 to 3 Times Better Compression than H.265 using Legacy Hardware
H.265 (aka HEVC) is supposed to half the video bandwidth / bitrate required compared to H.264 by delivering the same quality, and VP9 should also offer equivalent compression, but it’s just not as broadly supported in media processors. UK based V-Nova claims its Perseus codec can even beat that, by providing 2 to 3 times better compression than H.265 thanks to a new approach to video encoding, that allow the codec to leverage existing hardware, meaning it can be encoded with existing computers, and decoded by leveraging the CPU and GPU parallel processing capabilities in existing mobile & computing devices. Perseus codec highlights: Highly efficient – >3x compression vs. state-of-the-art in practical use cases. Benefits further increase with increasing resolutions & frame rates. Extremely fast – Significant processing time reduction thanks to massively parallel architecture. Designed to take advantage of modern hardware Multi-scale (continuously hierarchical) – Single bit stream for […]
Meet Vulkan, The Successor of OpenGL and OpenGL ES 3D Graphics APIs
So far embedded systems are typically using SoCs with GPU supporting OpenGL ES, a subset of the full fledge OpenGL API used in desktop computers and workstations. These royalty-free standards are defined by Khronos Group non-profit organization, and as features in the embedded space and traditional computers merge, the group has now revealed the next-generation OpenGL specs will be called Vulkan. The new API will run on GPUs supporting OpenGL ES 3.1 or greater, take less CPU resources than its predecessors, and support multiple command buffers that can be created in parallel. More work will be required at the application level, but direct GPU control by the drivers will apparently result in less memory copies improving performance, or at least off-loading the CPU. It might be transparent to developers using game engines. GPU drivers will also be less complex. Vulkan will also use the new SPIR-V language shared with OpenCL […]