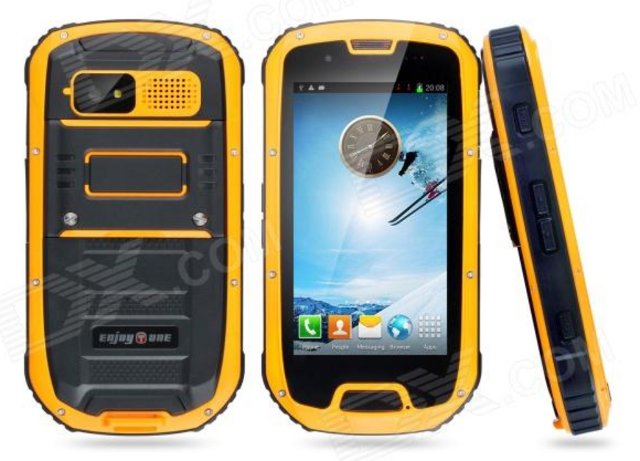
If you need a truly waterproof and dustproof smartphone, the Samsung Galaxy S4 Active, compliant with IP67 standard, is probably the most popular phone with this particular feature. However, the phone sells for nearly $600 on site like Amazon, and it may be nice to have some lower cost options. Today, I’ve come across two smartphones powered by Mediatek dual and quad core SoC that are both compliant with IP67 standard, and although their specs do not match the Galaxy S4 Active, the features found in these phones are still pretty good, and they can be purchased at a much lower price. The smartphones I’ll feature in this post are also rugged, which is not really the case for the Samsung device. IP67 standard? What does that mean in practice? The IP Code, Ingress Protection Rating, aka International Protection Rating, classifies and rates the degree of protection provided against the […]
SD Association Announces Ultra High Speed (UHS) Speed Class 3 for 4K2K Video Recording
SD card are not the fastest storage devices, but they are usually good enough for the job. One of the main use case is storage for video cameras, but with devices supporting 4K2K (2160p) recording they are close to their minimum limits. That’s why the SD association announced Ultra High Speed (UHS) Speed Class 3 (U3), which provides at least 30 MB/s write speed. The updated SD card speed classes are shown in the table below. Marks Operable Under Applications SD Memory Card Speed Class High Speed Bus I/F Full HD video recording HD still consecutive recording SD, miniSD, microSD SDHC, miniSDHC, microSDHC SDXC, microSDXC Normal Bus I/F HD ~ Full HD video recording SD video recording UHS Speed Class UHS-I Bus I/F UHS-II Bus I/F Full higher potential of recording real-time broadcasts and capturing large-size HD videos (UHS Speed Class1 denotes a 10 MB/s minimum write speed) SDHC […]
Weightless Roadmap – Silicon, Modules, SDKs, Base Stations and Networks
The Weightless Standard aims at using the “white space” spectrum, previously used by analog TV broadcasts, for free M2M / IoT communication coupled with low power and cost-efficient hardware offering a range of over 10 km. Longer term the target is to reach $2 hardware cost, and $2 yearly servicing costs. Companies involved with Weightless include Neul, ARM, CSR and Freescale among others. You can read my previous post about Weightless for a longer overview. The Weightless Special Interest Group (SIG) has recently revealed the hardware roadmap for the new standard, which I’ll summarize below. Weightless Chip Neul Iceni, the first weightless silicon, was officially announced in February 2013. The latest version of the chip taped in May 2013 integrates UHF radio operating between 410 and 790 MHz supporting both TV white space and narrowband operation. It is suitable for low volume production applications. A third generation will be taped […]
USB 3.1 Specifications Published, Supports Speeds Up to 10 Gbps
USB 3.0 specifications has been introduced in 2008 with support for up to 5Gbps bandwidth. Although, my PC has two USB 3.0 ports, I’m still very much living in a USB 2.0 world, as I’ve yet to use USB 3.0 peripherals… But progress never stops, and the USB 3.0 Promoter Group just approved the new USB 3.1 specification (PDF file) which can support data speeds up to 10 Gbps. So after Full Speed (12 Mbps, USB 1.1), High Speed (480 Mbps, USB 2.0), SuperSpeed (5Gbps, USB 3.0), we’ve now got SuperSpeed 10Gpbs (SUPERSPEED+) with USB 3.1. The standard is backwards compatible with USB 3.0 and USB 2.0, but apparently not USB 1.1. It will also allow for up to 100W to be sent through a USB cable. If you are a developer, three developer conferences are planned in order to provide technical details about USB 3.1: USB 3.1 Developers Day […]
Ittiam HEVC Decoder To Provide H.265 Video Decoding for Existing ARM Cortex-A Devices
H.264 is now the favorite codec for many applications, and all ARM SoC providing multimedia capabilities support it. However, a new codec called H.265 (aka HEVC) is coming with twice the compression ratio with the same quality saving a lot of money for those who have to pay for the bandwidth. The transition between video codecs is normally a slow process, but as it happens you may wonder if you’ll be able to play H.265 videos on your existing ARM Cortex A9/A15 devices which do not support H.265 hardware video decoding. The answer appears to be “Yes You Can!”, as Ittiam Systems announced an HEVC decoder specifically designed for ARM Cortex A processors. More specifically their software decoder will support: ARMv7 Cores with NEON – Cortex A8, Cortex A5, Cortex A9, Cortex A15, Cortex A7 and the multi core variants Qualcomm Snapdragon APQ8064/MPQ8064 , MSM8960 Ittiam HEVC decoder mainly targets devices such […]
H.265/HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding) Status and How-To Encode Videos to H.265
Now H.264 is the main standard used for video compression, and most devices that can support video playback feature an SoCs capable of H.264 hardware video decoding. Since 2004, however, work has been done to improve H.264, and a new standard called High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also referred to as H.265, will eventually replace H.264, even though this will take a few more years to really gain traction. HEVC will be able to double the data compression ratio compared to H.264 with the same quality, or improve the quality using the same bitrate, and it can support 8K UHD (Ultra High Definition) with a resolution of 7680×4320 (4320p). This new video codec is a big deal for those who pay for video bandwidth (80% of internet traffic according to Ericsson), and it should also be welcomed by consumers, as it will magically double their storage device capacity, and they may […]
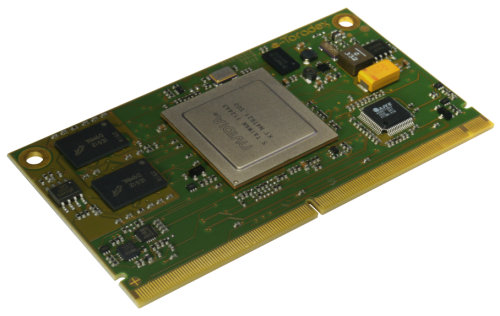
Toradex Releases Apalis Computer on Module Architecture Specification
Last month, Toradex released the preliminary specification for Apalis, a Computer on Module (CoM) architecture. Although the Apalis specification has been initially designed with ARM based processors in mind such as the Nvidia Tegra, Freescale i.MX and Texas Instruments OMAP processor families, it aims at being device and chip architecture independent. The Apallis specification defines the following: Interface Specifications: Signal Naming Convention – Rules to name pins (e.g. VCC, PWM1, PWM2, ) which are used for all modules. Signal Definition – Details about the pins named above Physical Pin Definition and Location Mechanical Specifications: Mounting and Fixation Module Size – Standard: 82 x 45mm | Extended: 82 x 56mm Pin Numbering – There is a total of 321 pin numbers (but a few less actually pins) Electrical Specifications: Power Supplies Power Control Back Feed Protection This specifications also defines mounting mechanisms for active cooling (e.g. heat spreaders) in case those […]
IEEE Updates 802.11 Standard to Support 600Mb/s Wi-Fi and Approves 802.1aq Standard for Large Ethernet Networks
IEEE has recently announced a standard update for WiFi (802.11-2012) which adds support for 3.7 GHz bands, 600Mb/s throughput and mesh networking among other things, and approved 802.1aq Shortest Path Bridging standard, which will streamline the creation and management of large Local and Metropolitan Area networks by using the next-generation VLANs. IEEE Wi-Fi 802.11-2012 Standard IEEE 802.11-2012 is the 4th revision of the Wi-Fi standard. It has been expanded by supporting faster and more secure devices, while offering improved Quality of Service and cellular network hand-off. Key amendments to the standard: IEEE 802.11n now defines MAC and PHY modifications to enable throughput up to a maximum of 600Mb/s Direct-link setup “Fast roam” Radio resource measurement Operation in the 3650-3700MHz band Vehicular environments, mesh networking, security, broadcast/multicast and unicast data delivery Interworking with external networks and network management. IEEE 802.11 is available for purchase for $5 at the IEEE Standards Store. […]