Collabora and Fluendo have recently announced the availability of GStreamer’s Software Development Kit for Android, which allows developers to create multimedia playback applications for Android smartphones and tablets using Gstreamer and the Android NDK.. The GStreamer SDK for Android targets Android 2.3.1 Gingerbread or higher (API Level 9 or greater). However, due to some of the restrictions of previous versions of Android, some features such as hardware acceleration are only available on Android 4.1 Jelly Bean (API Level 16 up). Normally, you’d need the GStreamer SDK which can be installed on Linux (Ubuntu, Fedora and Debian), Windows (XP/Vista/7/8) and Mac OS X (10.6 to 10.8). But for developing Android applications using Gstreamer, you don’t. What you do need first is a typical Android development environment with the latest Android SDK, the latest Android NDK, and optionally, but recommended, the Eclipse IDE with Android ADT and NDK plugins. Once everything is […]
Jolla Unveils Sailfish OS based on Meego and Sailfish SDK
Last July, a company called Jolly announced it would design, develop and sell smartphones based on the Meego operating system. This is now closer to reality as a demo has been showcased running on Nokia N950, except the operating system is now called Sailfish OS. Internally, Sailfish OS is built on top of the Mer project and Qt. The UI is built with QML and QtQuick and the standard QtMobility APIs are supported. For software development, you’ll need to use a special version of QtCreator. The development flow looks very similar to what you would do to develop applications for Symbian or Harmattan phones. More precisely, the Sailfish SDK consists of QtCreator, a virtualised Mer Platform SDK and Sailfish components. Code is developed in Qt-Creator on the host device, then the code is passed to the virtualised Mer SDK where it compiles inside the Virtual Machine. If you want to […]
Android Jelly Bean 4.2 SDK, Source Code and Binary Images Are Now Available
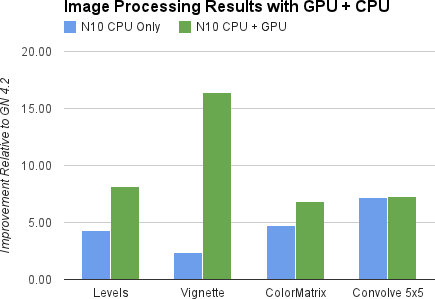
As the Nexus 4 smartphone and Nexus 10 tablet became available for purchase yesterday, Google released Android 4.2 SDK for developers and pushed Android 4.2 to AOSP. The Android 4.2 (Jelly Bean) SDK platform (API level 17) brings the following key improvements: Performance – Renderscript computation can be run directly in the GPU on the Nexus 10. This is a first since Exynos 5250 is the first ARM processor capable of supporting GPGPU (via Mali-T604 GPU). See the chart of the right showing results between CPU and CPU+GPU computation of some multimedia benchmarks. Lock screen widgets – Users can now place interactive lock screen widgets directly on their device lock screens. This only requires a small update to adapt existing widgets to run on the lock screen. Daydream – An interactive screensaver mode that can be used when the device is charging or docked to a desk dock. Better external […]
Qt Creator 2.6 Release and Qt for Android (Necessitas) Merged to The Qt Project
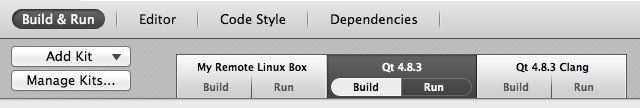
Qt Creator Version 2.6.0 has been released yesterday. The most notable change is the introduction of “Kits” to replace “Targets” that were used in previous versions of Qt Creator. Previously, “Targets” such as Desktop or Remtoe Linux were added to a project’s configuration in order to use predefined configurations. “Kits” extend the use of “Targets” and contain settings for which device type to develop for, the sysroot, the compiler, the debugger and the Qt version to use, and possibly even more settings. Users can define their own “Kits”, which should facilitate control of build and run environment and projects sharing. Other changes include full screen support on Mac OS Lion and later, numerous fixes and additions to the qrc file editor, direct rebuilding and cleaning of .pro file based subprojects, more C++11 fixes, and more. On the platform side, QNX/Projects support was added, but Symbian (no maintainer) and Meego (due to […]
Rockchip RK3066/RK30xx Processors Documentation, Source Code and Tools
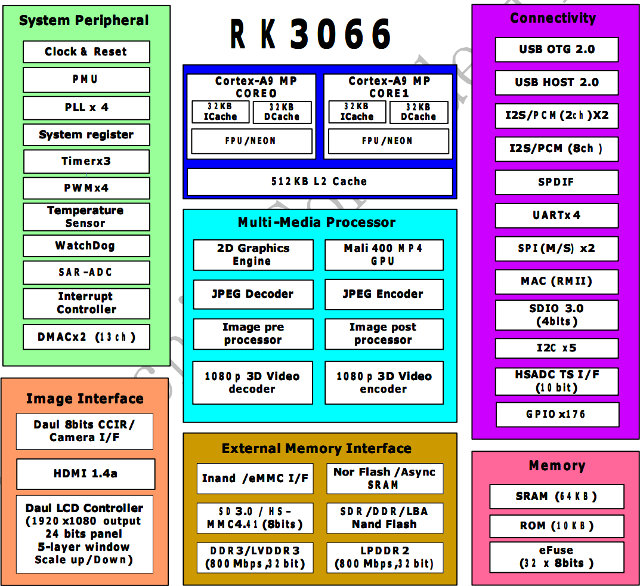
Rockchip RK3066 (part of RK30xx family) is a Chinese dual ARM Cortex A9 SoC targeting multimedia products such as tablets (e.g. Cube U30GT), mini PC (e.g UG802, MK808) and in theory set-top boxes, but I can’t find any products based on this Rockchip processor. It seems mini PCs/ HDMI TV sticks have taken over this market. RK3066 Processor The processor features two ARM Cortex A9 clocked at up to 1.6 Ghz with a quad core Mali-400MP GPU. It can support 1080p (3D) encoding/decoding, provides HDMI 1.4a, VGA, composite, component and LVDS video outputs (Dual display support), USB 2.0 Host and OTG ports, a MAC interface (Ethernet), and much more… Here are the key features of Rockchip RK3066 processor: Dual Core A9 + Quad Core Mali-400MP GPU 2 banks, 8/16 bit Nor flash / SRAM interface 8 banks, 8/16 bit async NAND flash, LBA NAND flash and 8-bit sync ONFI NAND […]
Timesys Unveils LinuxLink BSP/SDK for MityARM-3359 SoM (TI AM335x)
Critical Link is an electronics product development company that provides “MityDSP” and “MityARM” System on Modules and Timesys is a software company working on Embedded Linux, which provides LinuxLink, a software development framework for embedded Linux application development. Both companies have partnered to offers LinuxLink BSP/SDK for MityARM-3359 SoM based on Texas Instruments Sitara AM335x Cortex A9 processor. LinuxLink (for MityARM-335x) comes in 2 versions: A free version which includes: A wizard-based interface that simplifies the selection of a Linux kernel, software packages and tools Kernel, toolchain and debugger Access to hundreds of open-source software packages Support by Timesys for build/boot issues. A PRO version (Starts at $5495 per developer) which includes extra “features” such as: TimeStorm IDE – A desktop-based development environment Tools for advanced customization and integration unmetered support Everything is built on Timesys servers, but the web interface makes it quite customizable and offers lots of options […]
ISEE Announces Low Cost IGEP COM ELECTRON & SPIN Computers-on-Module
ISEE, the manufacturer of the IGEPv2 board, has recently announced 2 new industrial grade computers on module based on TI Sitara AM3703 Cortex A8 Processor: IGEP COM ELECTRON – AM3703 with 256 MB RAM / 512 MB Flash – 59 Euros IGEP COM SPIN – AM3703 with 64 MB RAM / 128 MB Flash – 49 Euros Here are the specifications of IGEP COM ELECTRON module: CPU – Texas Instruments AM3703 @ 1GHz with L1 cache (112 KB (DSP) / 64 KB (ARM)) and L2 cache (96 KB (DSP), 256 KB (ARM)) System Memory – 256 MB Mobile DDR @ 200 MHz (32-bit) Storage: 512 MB NAND FLASH On board micro-SD socket Connectors: 1 x USB 2.0 OTG interface + USB mini-AB connector 1 x MICRO-SD socket 2 x EXPANSION 70-pin connector Device: 1 x USB 2.0 HOST (connector NOT included) 1 x DOUBLE LED INDICATOR Expansion connectors – 2 […]
Oracle releases JDK for Linux ARM (Soft-Float Only)
Oracle announced the availability of JDK 7 Update 6 which introduces a JDK for Linux on ARM v6 and v7 architecture. This JDK is aimed at “general purpose” ARM systems, such as ARM micro-servers and ARM development platforms. This new JDK for Linux on ARM is licensed under the Oracle Binary Code License, and can be downloaded at no cost for development and production use on general-purpose platforms. For embedded use such as an industrial controller or a kiosk appliance, a commercial license would be required. Here’s how Oracle summarizes the ARM Linux JDK features: This port provides 32-bit binary for ARMv6 and v7, with full support for Swing/AWT, both client (C1) and server (C2) compilers and runs on most Linux distributions. One caveat is that the current binary is softfloat ABI only, so it won’t work with (for example) the Raspbian distribution which uses the hardfloat ABI. We are […]