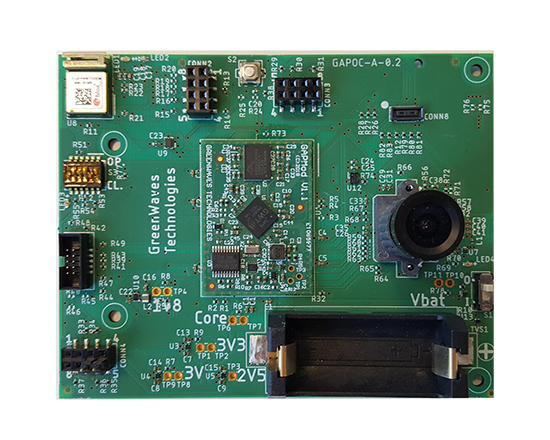
GreenWaves has developed a development board based on the GAP8 chip which can be evaluated from a GAPuino board, a generic board that can run off a low power external power source or USB and is compatible with the Arduino ecosystem. Recently the company moved beyond the generic board to the GAPPoc, platform which stands for GAP8 Proof of Concept. The GAPPoc is focused on a class of applications which can be embedded on a single board and able to carry hardware such as crystal or external memory, sensors, a radio fit, and a battery. The board will be geared towards a set of low power functions for a particular class of applications. This is a family of boards designed to increase the range of abilities in edge Artificial Intelligence. At this time there is only a single board with a platform to enhance AI, targeting Computer Vision in the […]
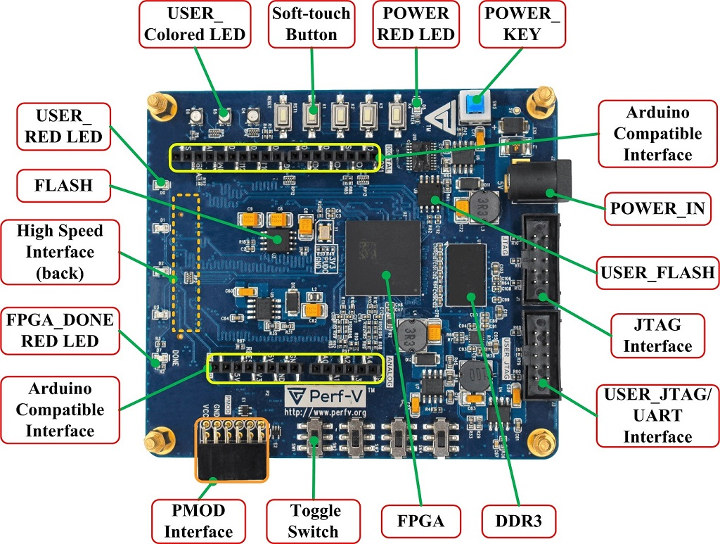
Perf-V is another FPGA based RISC-V Development Board
There are already some RISC-V development boards with silicon featuring RISC-V instruction set such as SiFive’s HiFive1 or Kendryte KD233 board. But beauty of RISC-V is that you can customize the instructions set, and if that’s your goal, an FPGA board provides the flexibility you need. While in theory you could use pretty much any FPGA board with enough logic elements, it may help to get started with boards that are designed for this purpose since the company already ported a RISC-V core to their platform and you can start from there. We’ve already covered a few of those including LicheeTang and Fomu boards, as well as ARIES M100PF PolarFire FPGA system-on-module. Today, I’ve come across another of those RISC-V FPGA board. Meet Perf-V board with the following specifications: FPGA – Xilinx Artix-7 XC7A35T-1FTG256C with 33280 Logic Cells, 90 DSP, 41600 CLBs, 1800 Kbit Block RAM, and 5 CMTs; Optional […]
Kazan Software Vulkan Implementation is Optimized for RISC-V Processors
More and more people want to run fully open source systems due to philosophical, privacy and security concerns, but on embedded systems with a GPU is often hard to achieve due to closed-source binary blobs. Projects such as Freedreno and Etnaviv have freed Qualcomm Adreno and Vivante GPUs, but it takes years to implement workable reverse-engineered open source GPU drivers. One solution to get an open source graphics driver from the get-go is to implement the rendering into the CPU, but the problem is that it’s usually really slow, and GPU’s are much faster thanks to their ability to quickly handle parallel tasks. Kazan is a software-rendering Vulkan implementation, but it may be eventually end up as a low-end soft-GPU in some RISC-V SoCs thanks to specific instructions. I found out about Kazan through the Libre RISC-V M-Class chip project that aims to be a low-power, mobile-class, 64-bit quad-core SoC […]
More Investments into RISC-V – Qualcomm Backs SiFive, OpenHW Group Created
Some may doubt RISC-V will ever challenge Arm at least in some markets, but the industry is investing in solutions based on the royalty-free open source ISA, with this week SiFive securing $65.4 Million from various investors including Qualcomm Ventures LLC, and the announcement of the launch of the OpenHW Group, a new not-for-profit global organization aims to boost the adoption of open-source processors currently backed by 13 companies, and aiming to reach 25 sponsors by year’s end. SiFive gets more interest from investors Here’s the main part of the announcement of SiFive’s new series D funding: SiFive, Inc., the leading provider of commercial RISC-V processor IP and silicon solutions, today announced it raised $65.4 million in a Series D round led by existing investors Sutter Hill Ventures, Chengwei Capital, Spark Capital, Osage University Partners and Huami, alongside new investor Qualcomm Ventures LLC. This Series D round brings the total […]
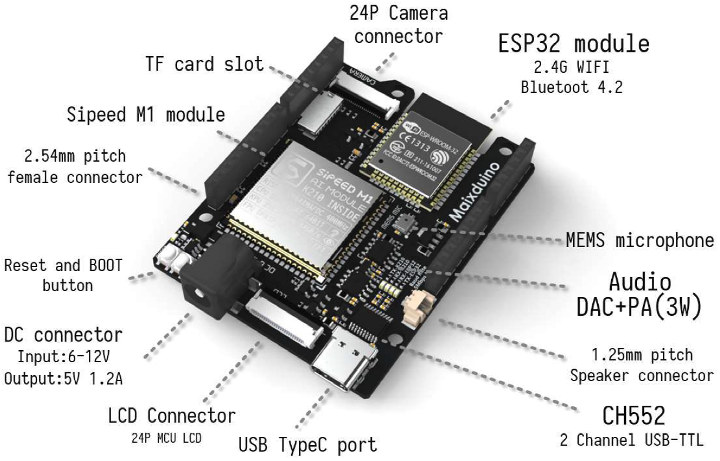
Maixduino SBC Combines RISC-V AI, Arduino Form Factor, and ESP32 Wireless Module
Last year RISC-V cores made it into low-cost hardware with neural network and audio accelerator to speed up artificial intelligence workloads at the edge such as object recognition, and speech processing. More precisely, Kendryte K210 dual-core RISC-V processor was found in Sipeed MAIX modules and boards going for $5 and up. Since then a few other variants and kits have been made available including Seeed Studio Grove AI HAT that works connected to a Raspberry Pi or in standalone mode. Seeed Studio has now released another board with Kendryte K210 RISC-V AI processor, but based on Arduino UNO form factor and equipped with an ESP32 module for WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity. Meet Sipeed Maixduino SBC. Sipeed Maixduino specifications: AI Module – Sipeed M1 with Kendryte K210 dual-core RISC-V processor @ 600 MHz, KPU Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) hardware accelerator, APU audio hardware accelerator, 8 MB general purpose SRAM including 5.9MB […]
SiFive RISC-V Processors to Support Imagination PowerVR GPU and NNA IP Cores
RISC-V is getting more popular and mature as development progress, but if you want a system with RISC-V and a GPU so far you had to use a PCIe graphics card which is not cost-effective nor practical for most applications based on RISC-V processor. What is needed is some GPU IP that will glue with RISC-V core. Developing a new GPU is not an easy task (understatement of the month) so it would make sense to go with solutions available on the market. However, Arm Mali is tied to Arm Cortex cores and Arm is unlikely to want to help RISC-V take away their market share, and Adreno and VideoCore are owned by respectively Qualcomm and Broadcom which are unwilling to provide their GPU IP to third parties. This basically leaves us with Vivante and Imagination. Vivante may have made the most sense since open-source graphics drivers do exist (Etnaviv), […]
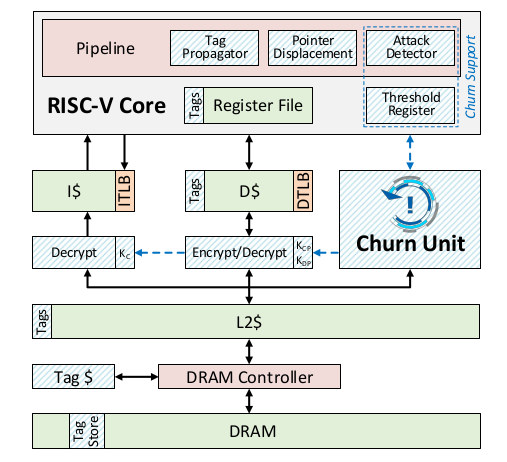
MORPHEUS Claims to be an Unhackable RISC-V Processor Architecture
Code gets continuously written and updated for new features, optimizations and so on. Those extra lines of code sometimes come at a cost: a security bug gets inadvertently introduced into the code base. The bug eventually gets discovered, a report is filled, and a software fix is committed to solve the issue, before the new software or firmware to push to the end user. This cycle repeats ever and ever, and this means virtually no software or device can be considered totally secure. The University of Michigan has developed a new processor architecture called MORPHEUS, and that blocks potential attacks by encrypting and randomly reshuffling key bits of its own code and data several times per second through a “Churn Unit”. The new RISC-V based processor architecture does not aim to solve all security issues, but focuses specifically on control-flow attacks made possible for example by buffer overflows: Attacks often […]
Linux 5.1 Release – Main Changes, Arm, MIPS & RISC-V Architectures
Linus Torvalds has just announced the release of Linux 5.1: So it’s a bit later in the day than I usually do this, just because I was waffling about the release. Partly because I got some small pull requests today, but mostly just because I wasn’t looking forward to the timing of this upcoming 5.2 merge window. But the last-minute pull requests really weren’t big enough to justify delaying things over, and hopefully the merge window timing won’t be all that painful either. I just happen to have the college graduation of my oldest happen right smack dab in the middle of the upcoming merge window, so I might be effectively offline for a few days there. If worst comes to worst, I’ll extend it to make it all work, but I don’t think it will be needed. Anyway, on to 5.1 itself. The past week has been pretty calm, […]