Automation and IIoT Through YABA YABA is an acronym and a concept being developed. The acronym is Yet Another Backplane Architecture (YABA). The concept is to bridge the gap between PLC/PAC and open source hardware. The YABA Bridge to IoT YABA is designed to be a robust, open hardware controller that will be a simple but effective midpoint or bridge to the approach of modern industrial technologies in the automation and IoT sector, especially production lines in industrial settings. Where YABA is in Process The process is midstage right now, with a prototype coming. There is an IndieGoGo campaign, but it is at the development stage right at this moment. The developer has reported that the team is about two months out of a working prototype, which should put them an efficient schedule timeline. The project has the backplane, CPU, I/O boards at about 75% complete, and just working towards […]
Khadas VIM3 Linux Benchmarks and Comparison to Raspberry Pi 4
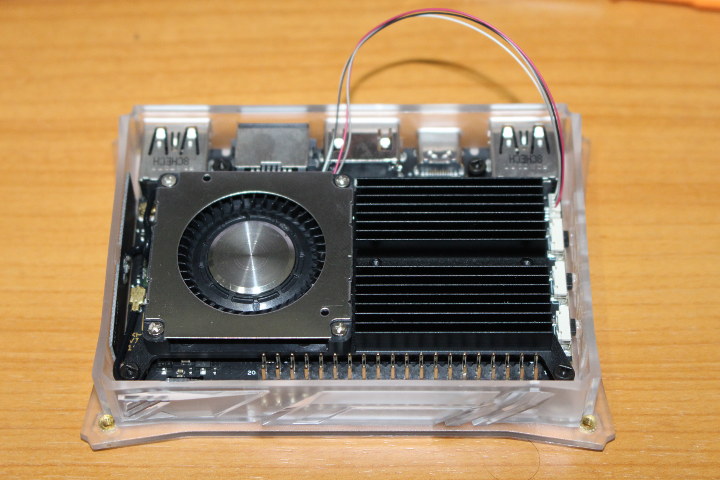
I received Khadas VIM3 Amlogic A311D SBC in early July and started testing it with Android running some benchmarks and playing games last month. I was impressed by graphics performance and overall benchmark results in Android, especially the results I got with a heatsink matched Khadas own results with heatsink + fan. So I installed the latest Ubuntu 18.04 available at the time (July 19) in order to repeat benchmarks in Linux and see how it goes. System info in Ubuntu 18.04:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
khadas@Khadas:~$ cat /etc/lsb-release DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu DISTRIB_RELEASE=18.04 DISTRIB_CODENAME=bionic DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS" khadas@Khadas:~$ uname -a Linux Khadas 4.9.179 #73 SMP PREEMPT Fri Jul 19 09:56:46 CST 2019 aarch64 aarch64 aarch64 GNU/Linux khadas@Khadas:~$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev 305M 0 305M 0% /dev tmpfs 187M 9.5M 177M 6% /run /dev/rootfs 15G 2.6G 12G 19% / tmpfs 931M 0 931M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs 931M 0 931M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs 187M 12K 187M 1% /run/user/1000 khadas@Khadas:~$ free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1861 358 1100 10 402 1479 Swap: 930 0 930 |
I decided to install armbianmonitor to draw some nice temperature charts as I did with Raspberry Pi 4:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
wget https://github.com/armbian/build/raw/master/packages/bsp/common/usr/bin/armbianmonitor sudo cp armbianmonitor /usr/bin/ sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/armbianmonitor sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com 2C0D3C0F sudo wget http://goo.gl/vewCLL -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/rpimonitor.list sudo armbianmonitor -r |
But I had some error during installation:
|
1 2 3 4 |
sudo armbianmonitor -r Installing RPi-Monitor. This can take up to 5 minutes. Be patient please/usr/bin/armbianmonitor: line 189: /etc/armbian-release: No such file or directory Now you're able to enjoy RPi-Monitor at http://192.168.1.8:8888 |
And while I can load the webpage with top menu appearing, it won’t show any data, as its name implies it may only work in Armbian. SBC Bench on Khadas VIM3 Let’s download SBC bench:
|
1 |
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ThomasKaiser/sbc-bench/master/sbc-bench.sh |
Note that I had […]
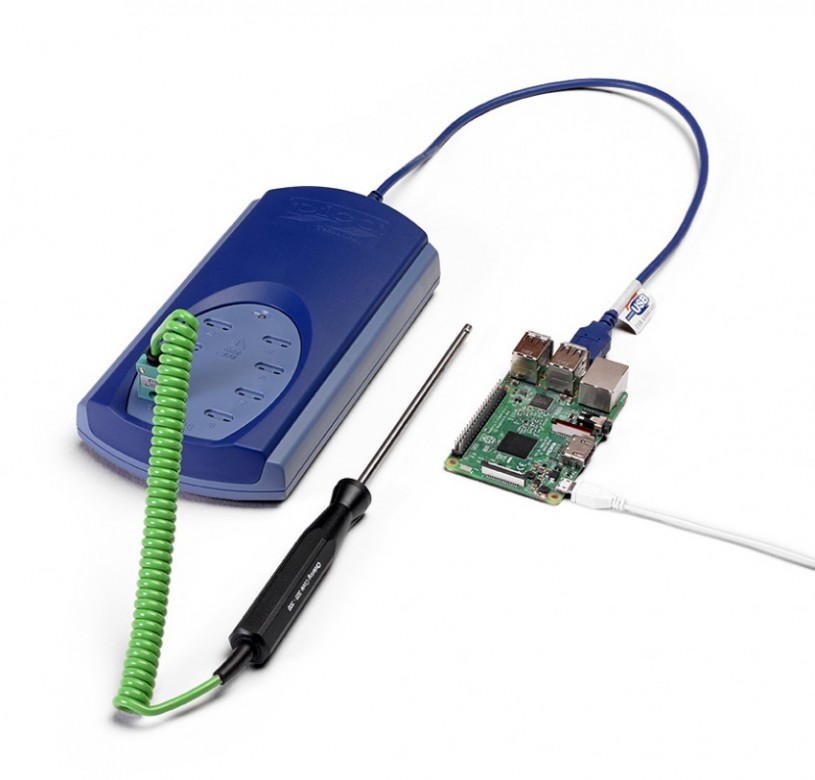
PicoLog 6 Beta supports Raspberry Pi 4, 3B and 3B+
One of the most popular computer platforms, Raspberry Pi has not been supported for Pico’s advanced datalogging software, up until now. The PicoLog 6 datalogging software is now compatible with Raspbian Stretch or later OS. The software has been designed for quick access to simple or complex acquisitions, and enabled to record, analyze or view data of almost any type. TC-08 Thermocouple Datalogger with Raspberry Pi 3 board Real Power It is essentially the same software that runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux, with a few differences to take advantage of the capability of the lower-powered Arm processors. Producing a powerful datalogger for the Raspberry Pi SBC platform. The PicoLog 6 is optimized for Raspbian Stretch and runs the Raspberry Pi 4, 3B and 3B+ SBC’s. The core of the utility is an easy to use visual interface that allows for an almost out-of-box use to the program. Features Making […]
Raspberry Pi 4 Benchmarks & Mini Review
Raspberry Pi 4 has just been released with many improvements over Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ including a faster processor, a proper Gigabit Ethernet port, USB 3.0 interfaces, and 4K video support. That’s the theory, but how does it work in practice? I can now let you know as I’ve received a Raspberry Pi 4 sample courtesy of Cytron, and ran some tests and benchmarks on the very latest boards from the Raspberry Pi foundation. System Info Before starting with the benchmarks, let’s go through some basic system info:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ cat /etc/issue Raspbian GNU/Linux 10 \n \l pi@raspberrypi:~ $ uname -a Linux raspberrypi 4.19.46-v7l+ #866 SMP Fri Jun 7 18:00:39 BST 2019 armv7l GNU/Linux pi@raspberrypi:~ $ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/root 13G 4.7G 7.4G 39% / devtmpfs 334M 0 334M 0% /dev tmpfs 463M 0 463M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 463M 6.4M 456M 2% /run tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs 463M 0 463M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mmcblk0p6 253M 40M 213M 16% /boot tmpfs 93M 0 93M 0% /run/user/1000 /dev/sda4 200G 175G 24G 89% /media/pi/USB3_BTRFS /dev/sda2 241G 181G 48G 80% /media/pi/USB3_EXT4 /dev/sda1 245G 182G 63G 75% /media/pi/USB3_NTFS pi@raspberrypi:~ $ cat /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 3 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 270.00 Features : half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls vfpv4 idiva idivt vfpd32 lpae evtstrm crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd08 CPU revision : 3 .... processor : 3 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 3 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 270.00 Features : half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls vfpv4 idiva idivt vfpd32 lpae evtstrm crc32 CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x0 CPU part : 0xd08 CPU revision : 3 Hardware : BCM2835 Revision : a03111 Serial : 00000000ea51204b |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
$ inxi -Fc0 System: Host: raspberrypi Kernel: 4.19.46-v7l+ armv7l bits: 32 Console: tty 1 Distro: Raspbian GNU/Linux 10 (buster) Machine: Type: ARM Device System: Raspberry Pi 4 Model B Rev 1.1 details: BCM2835 rev: a03111 serial: 00000000ea51204b CPU: Topology: Quad Core model: ARMv7 v7l variant: cortex-a72 bits: 32 type: MCP Speed: 1500 MHz min/max: 600/1500 MHz Core speeds (MHz): 1: 1500 2: 1500 3: 1500 4: 1500 Graphics: Device-1: bcm2835-vc4 driver: vc4_drm v: N/A Device-2: bcm2835-hdmi driver: N/A Display: tty server: X.org 1.20.4 driver: modesetting unloaded: fbdev tty: 80x24 Message: Advanced graphics data unavailable in console. Try -G --display Audio: Device-1: bcm2835-audio driver: bcm2835_audio Device-2: bcm2835-hdmi driver: N/A Sound Server: ALSA v: k4.19.46-v7l+ Network: Message: No ARM data found for this feature. IF-ID-1: eth0 state: up speed: 1000 Mbps duplex: full mac: dc:a6:32:00:9e:9c IF-ID-2: wlan0 state: up mac: dc:a6:32:00:9e:9d Drives: Local Storage: total: 946.35 GiB used: 540.58 GiB (57.1%) ID-1: /dev/mmcblk0 vendor: SanDisk model: SL16G size: 14.84 GiB ID-2: /dev/sda type: USB vendor: Seagate model: Expansion size: 931.51 GiB Partition: ID-1: / size: 12.68 GiB used: 4.71 GiB (37.1%) fs: ext4 dev: /dev/mmcblk0p7 ID-2: /boot size: 252.0 MiB used: 39.3 MiB (15.6%) fs: vfat dev: /dev/mmcblk0p6 Sensors: Message: No sensors data was found. Is sensors configured? Info: Processes: 179 Uptime: 4h 37m Memory: 1000.5 MiB used: 324.1 MiB (32.4%) gpu: 76.0 MiB Init: systemd runlevel: 5 Shell: bash inxi: 3.0.32 |
For reference, you’ll find Raspberry Pi 4 Linux boot log here. Phoronix benchmarks Let’s go ahead and install the latest version of Phoronix benchmarks:
|
1 2 3 |
sudo apt install php-cli php-gd php-xml php-zip wget http://phoronix-test-suite.com/releases/repo/pts.debian/files/phoronix-test-suite_8.8.1_all.deb sudo dpkg -i phoronix-test-suite_8.8.1_all.deb |
Now let’s run the test to compare the performance of Raspberry Pi 4 model B to some other Arm Linux boards including Raspberry Pi 3 Model B.
|
1 |
phoronix-test-suite benchmark 1709271-TY-1704029RI26 |
For reference, my office has an […]
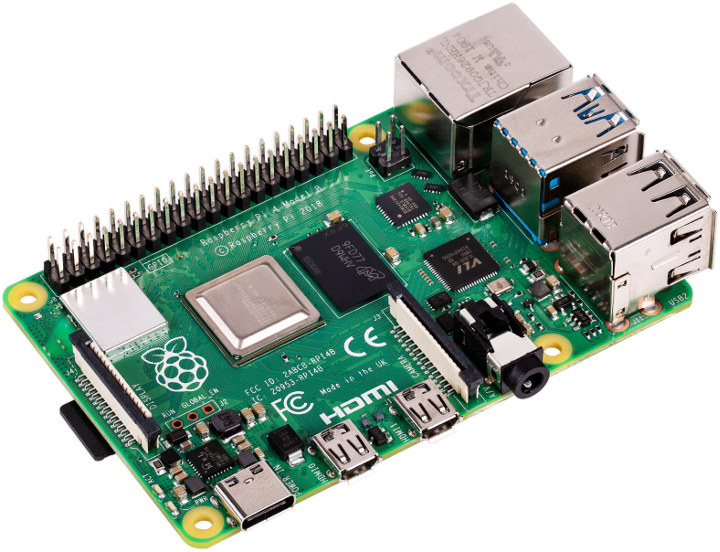
Raspberry Pi 4 Features Broadcom BCM2711 Processor, Up to 4GB RAM
Long expected, the Raspberry Pi 4 model B has finally launched, and it should not disappoint with a much more powerful Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 processor clocked at up to 1.5 GHz, 1 to 4GB LPDDR4, 4K H.265 video decoding and output support, a proper Gigabit Ethernet port, as well as USB 3.0 and 2.0 ports. Raspberry Pi 4 comes with all those extra features, but the form factor remains the same, and importantly the price is still $35 for the version with 1GB RAM, making Raspberry Pi alternatives suddenly much less interesting. Raspberry Pi 4 specifications: SoC – Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARMv8) @ 1.5GHz with VideoCore VI GPU supporting OpenGL ES 3.0 graphics System Memory – 1GB, 2GB or 4GB LPDDR4 Storage – microSD card slot Video Output & Display I/F 2x micro HDMI ports up to 4Kp60 (Currently 1080p60 max. in dual-display configuration, although 2x 4Kp30 is […]
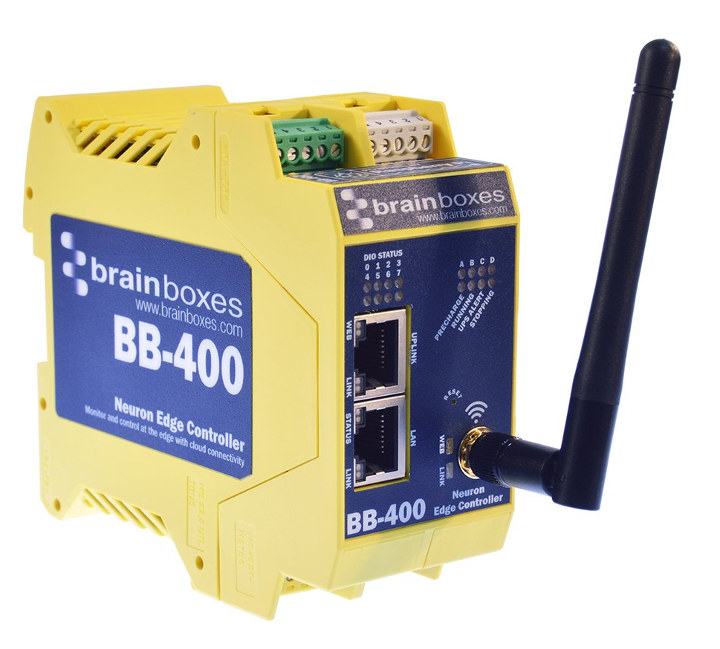
BB-400 Neuron Edge Dual Ethernet Industrial Controller Combines Raspberry Pi CM3+ and Arduino MCU
While the Raspberry Pi boards are mostly promoted as tools to teach STEM to kids and adults alike, they have found their way in a fair amount of industrial products, including ModBerry M500 industrial computer, Janz Tec emPC-A/RPI3 industrial embedded controller, and Kunbus RevolutionPi RevPi Core among others. There’s yet another option with Brainboxes BB-400 Neuron Edge industrial controller that was announced last year with Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3, but recently got an upgrade to Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3+. The controller features two Ethernet ports and also includes an Arduino compatible microcontroller to control the system’s eight configurable digital inputs and outputs. BB-400 Neuron Edge industrial controller specifications: SoM – Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3+ with Broadcom BCM2837B0 quad-core , Cortex-A53 processor @ 1.2GHz, 1 GB LPDDR2, 32GB eMMC Flash storage MCU – Unnamed Microchip Atmel Arduino compatible microcontroller Connectivity Ethernet Uplink Port – 1x RJ45 jack, 10/100Mbps […]
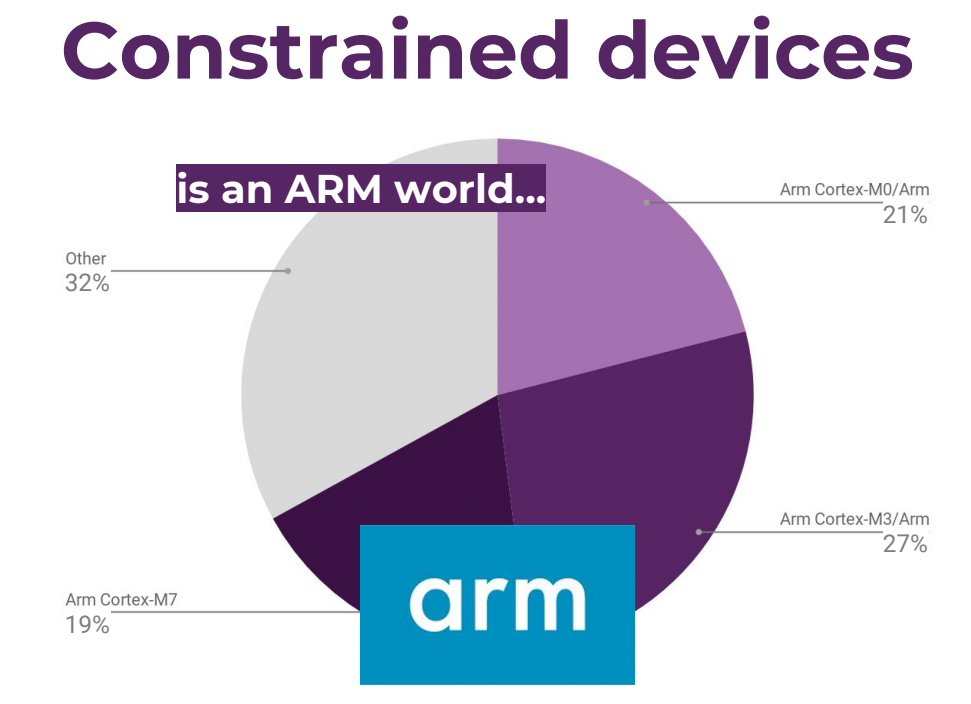
Eclipse IoT Survey Report Reveals Arm & Linux Dominate, Security Concerns
The Eclipse IoT Working Group has just released a report asking the global IoT developer community to share their perceptions, requirements, and priorities. And with over 1,700 individuals taking the survey between February and March 2019, the key findings are interesting: IoT drives real-world, commercial outcomes today. 65% of respondents are currently working on IoT projects professionally or will be in the next 18 months. IoT developers mostly use C, C++, Java, JavaScript, and Python AWS, Azure, and GCP are the leading IoT cloud platforms Top three industry focus areas remain the same as last year: IoT Platforms, Home Automation, and Industrial Automation / IIoT. MQTT remains the dominant IoT communication protocol leveraged by developers The Eclipse Desktop IDE is the leading IDE for building IoT applications The last point may be slightly biased because the survey was done by the Eclipse IoT Working Group, so most respondents were already […]
Raspberry Pi Suddenly Not Working? You May Have to Repair your microSD Card
Automatic updates are great because they keep your system up-to-date with the latest features and/or security fixes. That’s as long as the firmware is not messed up of course, as Bootlin and others found out when they discovered their Raspberry Pi board(s) had become inaccessible after an ill-fated Raspbian update. What happened is that raspi-copies-and-fills package, which implements optimized low-level memory functions for the ARM processor, was updated on March 11th, and the update somehow made some programs completely fail to run. This explains why Bootlin guys were unable to access their Raspberry Pi over SSH. The fix is simple, as long as you have physical access to your Raspberry Pi’s micro SD card, remove it from the board, and insert it into your computer, and…: Repair the rootfs partition with
|
1 |
e2fsck -f /dev/mmcblk0p2 |
Delete etc/ld.so.preload Unmount the micro SD card, and reinsert it into your Raspberry Pi board. If you’ve installed […]