Last August, Qualcomm unveiled Snapdragon 670 processor with performance and efficiency Kryo 360 cores believed to be based on Cortex-A75 and Cortex-A55 cores, but the company has just announced an update with Snapdragon 675 mobile platform powered by Kryo 460 cores which are based on Arm Cortex-A76 according to Anandtech, and so far, Cortex-A76 was only found in “premium” processors such as HiSilicon Kirin 980. Beside the upgrade cores, the company also claims the processor brings “outstanding gaming, a leap in artificial intelligence (AI) capability and a cutting-edge camera”. Snapdragon 675 main specifications: CPU 2x Kryo 460 (Cortex-A76 based) @ 2.0GHz with 256KB L2 6x Kryo 460 (Cortex-A55 based) @ 1.8GHz with 64KB L2 GPU – Adreno 612 DSP – Hexagon 685, Qualcomm AI Engine Display – Support for FHD+ display Camera – Spectra 250L ISP with triple-camera support Audio – Qualcomm aptX and Aqstic Modem – Snapdragon X12 LTE […]
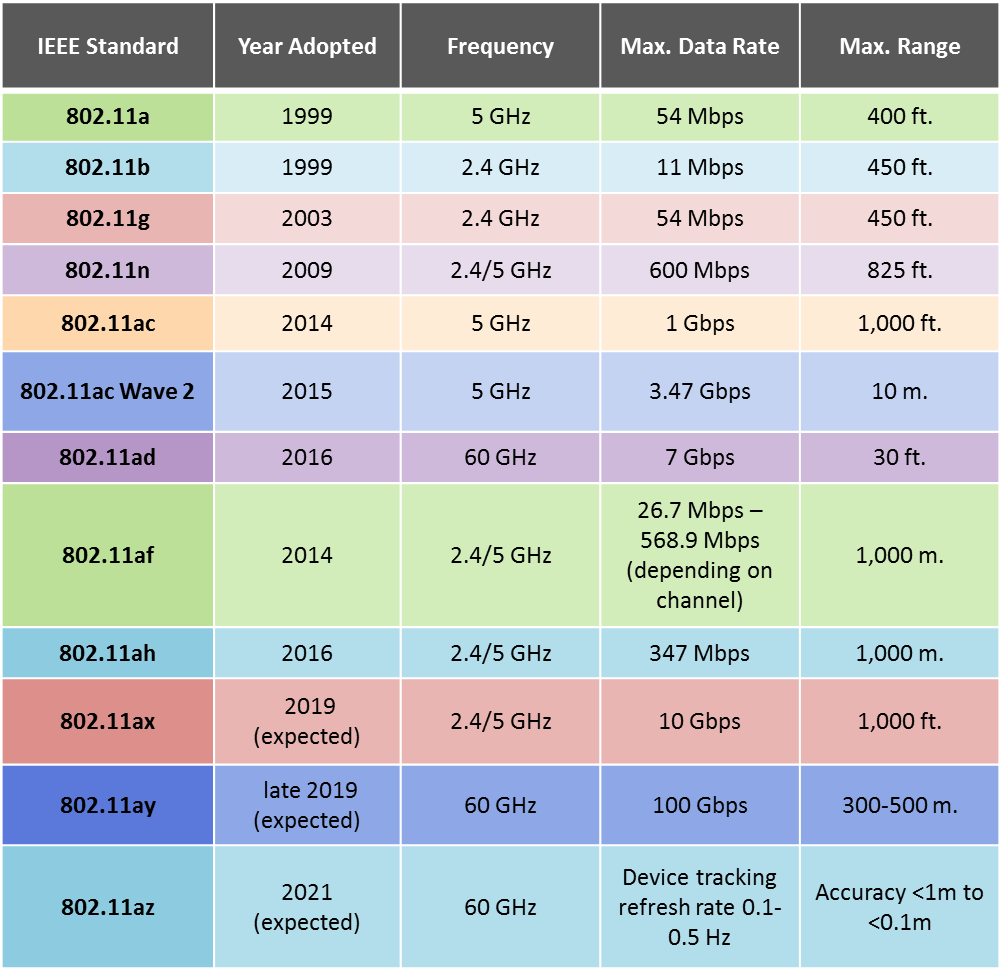
Qualcomm QCA64x8 and QCA64x1 802.11ay WiFi Chipsets Deliver 10 Gbps Bandwidth
WiFi has evolved in recent years with the introduction of 802.11ad and 802.11ax (now called WiFi 6). THe latter is now official, and in the last year several 802.11ax chipsets and WiFi 6 routers have been announced, but I’ve not heard much about 802.11ad with claims of up to 7Gbps bandwidth at 60 GHz when unveiled in 2016. The latter have been supplanted by 802.11ay, with Qualcomm having just unveiled QCA64x8 and QCA64x1 802.11ay chipsets capable of delivering 10Gbps and operating at a frequency of 60 GHz. According to Wikipedia, 802.11ay is not really a new standard, but just an evolution of 802.11ad adding four times the bandwidth and up to 4 MIMO streams. Qualcomm chipsets will enable 10+ Gps speeds with wire-equivalent latency, while keeping the power consumption low, and bring the ability to play 4K UltraHD videos over WiFi, virtual / augmented reality games, fixed wireless mesh backhaul, […]
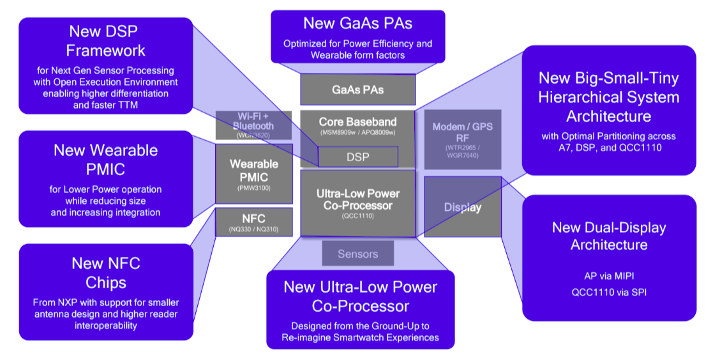
Snapdragon Wear 3100 Smartwatch Platform to Deliver Longer Battery Life
Qualcomm introduced Snapdragon Wear 2100 in 2016 for wearables, and the processor ended up in several products such as LG Watch Style / Sport smartwatch. Since then the company released other Wear platform for specific applications such as 4G kid watches with Snapdragon Wear 2500, or wearable IoT applications with Snapdragon Wear 1250 offering NB-IoT and eMTC connectivity. The company has now announced Snapdragon Wear 3100 “smartwatch platform” still based on four Arm Cortex A7 cores, but also including a new ultra-low power co-processor to further extend battery life. Snapdragon Wear 3100 “MSM8909w” or “APQ8009w” specifications: CPU – Quad core Arm Cortex-A7 processor @ up to 1.2 GHz GPU – Qualcomm Adreno 304 GPU Co-processor – QCC1110 Display – Up to 640×480 at 60fps via MIPI and/or SPI interfaces Cellular Qualcomm Snapdragon X5 LTE modem with peak download speed of 1 Gbps, and peak upload speed of 150 Mbps RF […]
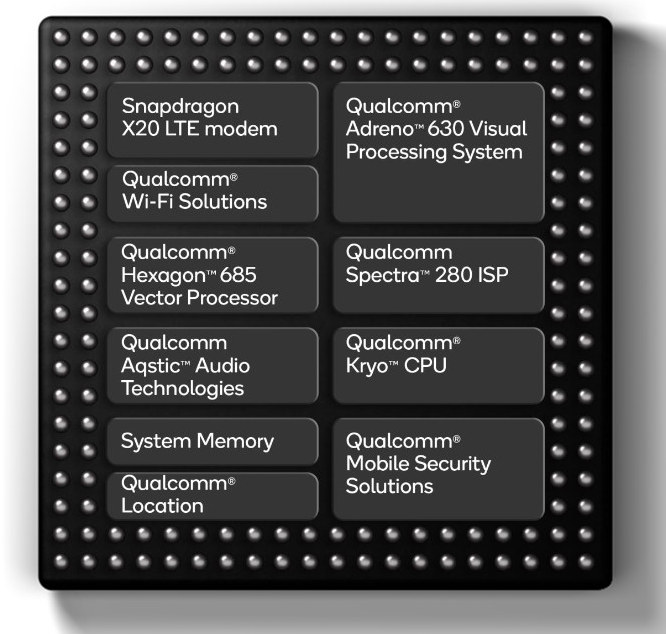
Snapdragon 670 Launched with Better Performance and Camera Capabilities, Artificial Intelligence Tech
Qualcomm has just introduced another of their “Mobile Platforms” with Snapdragon 670. The chipset comes with eight Kryo 360 cores, a Snapdragon X12 LTE modem for download speeds up to 600 Mbps, as well as Qualcomm AI engine and Hexagon 685 DSP for accelerating artificial intelligence workloads. The Qualcomm Spectra 250 ISP found in the SoC is said to enable most of the premium camera features found in professional cameras including noise reduction, image stabilization, and active depth sensing. Snapdragon 670 specifications: CPU – Octa-core processor with a cluster of 2x Kryo 360 performance cores @ up to 2.0 GHz, and a cluster of 6x Kryo 360 efficiency cores @ up to 1.7 GHz Visual Processing System (aka GPU) – Adreno 615 GPU with support for Open GL ES 3.2, Open CL 2.0, Vulkan, DirectX 12, H.264/H.265/VP9 Ultra HD video playback, DisplayPort over USB Type-C DSP – Hexagon 685 DSP […]
Snapdragon Wear 2500 Launched for the 4G LTE Kid Watch Market
Qualcomm has made several announcements at Mobile World Congress Shanghai 2018. We’ve already covered Snapdragon 632, 639, and 629 processors for mid- and high-tier smartphones, but the company has also finally announced a new SoC for wearables succeeding Snapdragon Wear 2100. Meet Snapdragon Wear 2500, specifically targeting 4G children watches. Qualcomm is usually not the best company when it comes to releasing technical details about their processors, but here what Snapdragon Wear 2500 specifications should look like: Processor – 4x Arm Cortex A7 GPU – Adreno-class GPU Connectivity – Fifth generation 4G LTE modem with RF front-end (RFFE), location engine, “Bluetooth streaming architecture”, NXP NFC solution Camera I/F – 5MP Ultra-low power sensor hub working with InvenSense sensors Power – Wearable PMIC reducing Rock Bottom Sleep Current (RBSC) by percent, charger, fuel gauge Compact package Snapdragon Wear 2500 is designed for low power with up to 14 percent longer battery […]
Qualcomm Introduces Snapdragon 632, 439 and 429 Mobile Platforms
Qualcomm has announced three new snapdragon mobile platforms for high- and mid-tiers mobile devices with Snapdragon 429, Snapdragon 439, and Snapdragon 632 processors. The new chips will bring higher performance, better battery life, more efficient designs, improved graphics and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities into these classes of devices. Snapdragon 429 & 439 Designed for mid-range smartphones, both Snapdragon 439 and Snapdragon 429 processors are pin-to-pin compatible, equipped with artificial intelligence capabilities, X6 LTE modem, and deliver up to 25% performance increase over previous generation processor, respectively Snapdragon 430 and Snapdragon 425 that enhance the camera, voice, and security experience. Snapdragon 439 however features an octa-core Cortex A53 processor clocked at up to 1.95 GHz coupled with an Adreno 505 GPU delivering up to 20% faster graphics rendering compared to SDM430, while the Snapdragon 429 comes with a quad core Cortex A53 processor and an Adreno 504 GPU yielding up to […]
Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 is Designed for Windows 10 Mobile PCs
As you all probably know, Qualcomm and Microsoft worked together and launched always-on, always-connected Windows 10 mobile PCs powered by Qualcomm Snapdragon 835 Arm processor earlier this year. Battery life is spectacular, but considering the fairly high price of such devices, many were disappointed by performance which in many cases is not much better than much cheaper Intel Apollo Lake laptops. But performance of future Qualcomm based Arm laptops will improve significantly thanks to Snapdragon 850 Mobile Compute Platform featuring eight Kryo 385 cores clocked to close to 3 GHz, and other enhancements. Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 “Mobile Compute Platform” specifications: CPU – 8x Kryo 385 Arm cores clocked @ up to 2.96 GHz GPU – Adreno 630 Visual Processing Subsystem with Open GL ES 3.2, Open CL 2.0, Vulkan, DirectX 12 Ultra HD Premium video playback and encoding @ 4K (3840×2160) 30fps, Slow motion HEVC video encoding of FHD (1080p) […]
Qualcomm Snapdragon XR1 is a Dedicated eXtended reality (XR) platform For XR / VR Headset
Qualcomm has unveiled its first Snapdragon XR platform specifically designed for extended / augmented / virtual reality headsets during a launch event leading up to the Augmented World Expo (AWE). Snapdragon XR1 features the usual Arm based Kryo cores, Adreno GPU, Hexagon DSP, ISP, and so on, but for whatever reason, the company did not disclose details specifications about the platform / SoC. XR1 also provides Qualcomm AI Engine for on-device processing, as well as an advanced XR software service layer, machine learning, the Snapdragon XR Software Development Kit (SDK) and Qualcomm Technologies connectivity and security technologies. Advanced vision processing capabilities of the SoC enabled technologies such as Visual Inertial Odometry (VIO) The XR1 platform will be for higher headsets with 3 to 6 degrees of freedom (3DoF, 6DoF), support ultra high-definition 4K video resolution at up to 60 frames per second, and offer reduced unwanted noise using its Spectra […]