In a recent article about Sonoff TH10/TH16 WiFi relays with sensor probes support, we also saw that ITEAD Studio started to have a nice family of home automation products. The company has now added one more item to the Sonoff family with Sonoff Pow support up to 16A/3500W input, and the first to also include power consumption measurements. Sonoff Pow specifications: SoC – Espressif ESP8266 Tensila L106 32-bit MCU up to 80/160 MHz with WiFi Connectivity – 802.11 b/g/n WiFi with WPA/WPA2 support Relay – HF152F-T relay with 90 to 250 VAC input, up to 16A (3500 Watts) Terminals – 6 terminal for mains and load’s ground, live and neutral signals. Programming – Unpopulated 4-pin header for flashing external firmware Misc – LEDs for power and WiFi status, power consumption circuitry with 1% accuracy. Dimensions – 114 x 52 x 32mm Temperature range – -40 ℃ to 125 ℃ The […]
Broadlink MP1 is a $20 WiFi Power Strip with 4 Independent Sockets
There are plenty of WiFi sockets going around such as Broadlink SP2 or Kankun KK-SP3, but in some cases it might be both more convenient and cheaper to get a WiFi power strip, and Broadlink MP1 offers just that with 4 sockets that can be controlled and programmed (timer) independently, and sold for just $19.88 on Banggood. Broadlink MP1 specifications: Connectivity – 802.11b/g/n WiFi, controllable over 3G/4G with smartphone 4 multi-standard (EU/US/AU, but not UK) sockets Power input – 10A/250V (max) Power output – 10A/250V (max) Rated power – 2000W Total Misc – Power button Dimensions – 254mm x 60mm x 32mm; 50cm sockets spacing; cord Length – 1.5m with AU plug (Adapter provided for other countries) Weight – 450g The power strip can be controlled via Broadlink ihc (Intelligent Hone Control) app available for Android and iOS, which lets you independently manually turn on or off or set timers […]
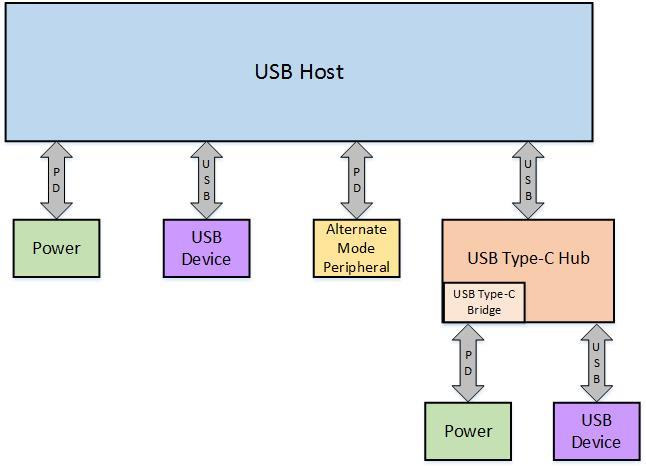
The USB Type-C Authentication Specification Aims to Prevent Damage from Non-Compliant Cables and Adapters
The new USB Type-C standard is great, as cables are reversible so it does not matter if you connect them up or down, it can handle USB 3.1 data speed, as well as carrying video and up to 100W power thanks to USB-C power delivery. In theory all is great, but in practice, many USB-C cables are not compliant, and Benson Leung, a Google employee, has found that many USB-C cable sold on Amazon were not compliant, with even one damaging his Pixel 2 laptop and two USB PD analyzers. His reviews on Amazon, as well as customer complaints, probably lead the company to ban the sale of non-compliant cable or adapter, but to really mitigate the issue, a technical solution was needed, and that’s why the USB 3.0 Promoter Group has defined the Authentication Protocol for USB Type-C as part of the USB Power Delivery 3.0 specifications. Key […]
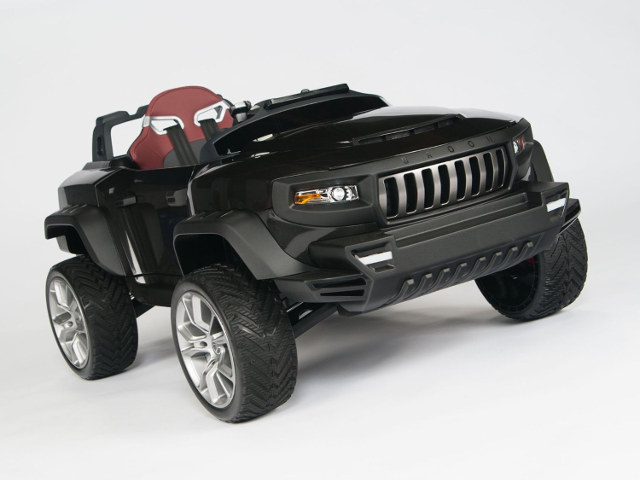
Henes Broon T870 is a Kids’ Electric Car Controlled by an Android Tablet
If you ever wanted to played around with an electric car that’s a bit better than an RC toy, but don’t quite have the cash for a full-size Tesla model, Henes has designed an electric card for you your younger kids that’s controlled by an Android tablet and allows both manual and remote driving. Henes Broon T870 specifications: Tablet – 7″ Android 4.4.2 tablet PC smart system with HD resolution display, micro SD, HDMI and audio output ARM Cortex-M3 based main control system Bluetooth remote control Built-in stereo speakers Functioning hood & doors 4 wheel drive with high density urethane tires Spring suspension & shock absorbers Leather bucket seat and seat belt Foot pedal accelerator Bright Headlight / Aux Light / Turn Signal Light / Tail/Brake/BackUp Lights Motors – Dual 24V driving motors Battery – Rechargeable 24V 7Ah battery pack for a little over 2 hours drive, or up to […]
BayLibre ACME Cape for BeagleBone Black Measures Power and Temperature with Sigrok
Sigrok open source signal analysis software suite had a major release last week-end with libsigrok 0.4.0, libsigrokdecode 0.4.0, sigrok-cli 0.6.0, and PulseView 0.3.0. The new version added numerous bug fixes for supported hardware such as UNI-T UT61E digital multimeter or USBee AX Pro logic analyzer, and added support for several logic analyzers, oscilloscopes, multimeters, programmable power supplies, an electronic load, an LCR meter, a scale, and one BeagleBone Black cape, namely BayLibre ACME. The ACME initiative was launched in order to get rid of the limitations of proprietary solutions, and provide an open source hardware and software multi-channel power and temperature measurements solution to the community. BayLibre ACME cape supports up to 8 probes to measure VBUS (0 to +36V), VSHUNT ( 2.5uV up to 81.92mV), CURRENT AND POWER. Three current / power probes have been developed with all featuring TI INA226 for the ADC conversion: ACME HE10 Power Probe […]
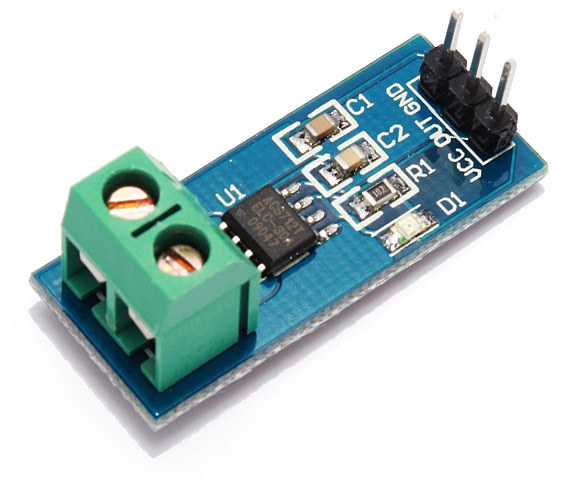
ACS712 Module Measures Currents up to 30A for as Low as $1 Shipped
Usually, if I buy a high power electric appliance, I like to double check it power consumption either with a Kill-a-watt when possible, and when not, e.g. cable directly hooked to the device or current intensity is too high, I use a digital electric clamp meter. Both methods are quite convenient as you don’t need to cut any wire to measure the current and determine the power consumption, but they don’t allow for data gathering since they don’t connect to the network. Earlier this week, I’ve come across a projects using ESP8266 for a mains energy monitor for a solar panel setup, and measuring mains current, electric meter, and gas meter. They use a photosensor to measure power consumption on their electric meter, which works, but may be problematic if the meter is on the street, and iSnail current sensor, using hall effect just like clamp meter, but instead of […]
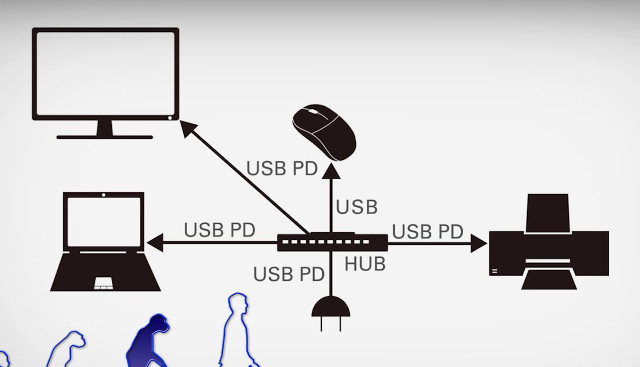
USB Power Delivery Advantages Explained (Video)
USB 3.0 and greater specifications not only promise higher speeds, up to 10Gbps for USB 3.1, but also the ability to deliver up to 100W over USB to power your laptop, display, and printer via equipment, usually a USB hub, that supports USB Power Delivery, or USB PD, via a USB Type C connector. So far very few products appear to support it, and I could only find the Macbook and ChromeBook Pixel, and a few USB PD chargers on Amazon. So basically in the future, the need for power supplies should decrease sharply, simplifying connections, and decreasing the cost of products and shipping since devices will only need a USB port that’s compatible with USB PD, meaning your computer, printer, and display won’t need an extra power supply as long as they consume less than 100 watts combined. The reasons I’m writing about this today, is that completely forgot […]
Multi-function Power Banks Can Jump Start Your Car Beside Charging Your Phone
Many people carry a USB power bank with them to make sure their smartphone does not run out of battery, but based on my experience failing to start your car because of a depleted or dead battery will bring ever more anxiety. Interestingly/funnily enough, while this happened to my neighbors last week-end, today I was informed that TM08 multi-function power bank was designed to both charge your phone or laptop, and help start your car. TM08 specifications: Input – 12V/1A Output – 5V-2A via USB and 12V jump starter for car with 200A starting current, and 400A peak current Battery Capacity – 12000mah Charging Time – 3 to 4 hours Life cycle – Over 1,000 cycles Dimensions – 130x70x25 mm Weight – 311 grams Operating Temperature – -20℃-85℃ The kit comes with adapters to charge your phone or other devices, as well as cables to connect to your car’s battery. […]