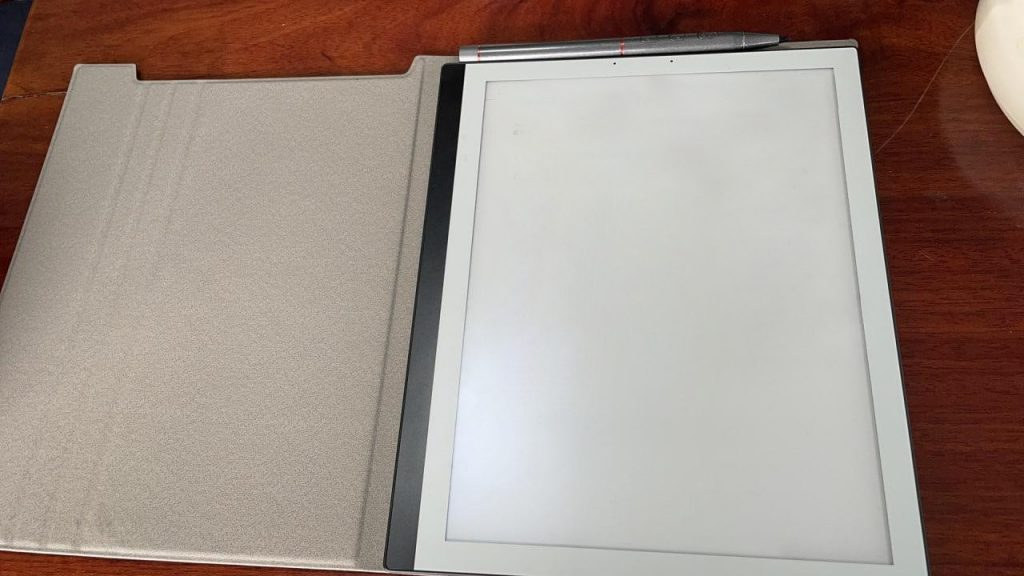
We’ve covered several e-readers in the past, but the PineNote 10.3-inch e-reader will be a bit different, as the hardware & software will be entirely developed by the community like other Pine64 platforms such as Pinebook Pro, PineCone, Rock64 single board computer, etc… Based on the Rockchip RK3566 quad-core Cortex-A55 processor, PineNote will be one of the fastest e-readers on the market, and leverage the code already written for Quartz64 single board computer, including mainline Linux support. PineNote (preliminary) specifications: SoC – Rockchip RK3566 quad-core A55 processor with Mali-G52 EE GPU, 0.8 TOPS NPU (AI accelerator) System Memory – 4GB of LPDDR4 RAM Storage – 128GB eMMC flash Display – 10.3-inch panel with 1404×1872 resolution (227 DPI), 16 levels of grayscale, front light with cool (white) to warm (amber) light adjustment, capacitive glass layer for finger touch-based input, and a Wacom electromagnetic resonance layer (EMR) for EMR pen input. There’s […]
Debian 11 “BullsEye” released with Panfrost & Lima GPU drivers, exFAT support, driverless printing
Debian 11 “BullsEye” has been released with Panfrost & Lima open-source drivers for Arm GPUs, in-kernel exFAT file system, driverless printing, and many more updates, plus a 5-year support window. Debian’s release is significant as the Linux operating system serves as the base for Ubuntu and derivatives, Raspberry Pi OS, and together with Ubuntu, is one of the operating systems supported by Armbian which offers images for a range of Arm-based single board computers. Arm Mali GPU support in Debian 11 I remember a few years ago 3D graphics acceleration on Arm boards was news, as it was quite a challenge to get it working due to binary blobs. But Debian 11 now comes with Mesa 20.3 framework which includes Panfrost and Lima open-source Mali GPU drivers by default, as well as the Vulkan 1.0 conformant V3DV driver for Raspberry Pi 4. As noted in the documentation that means the […]
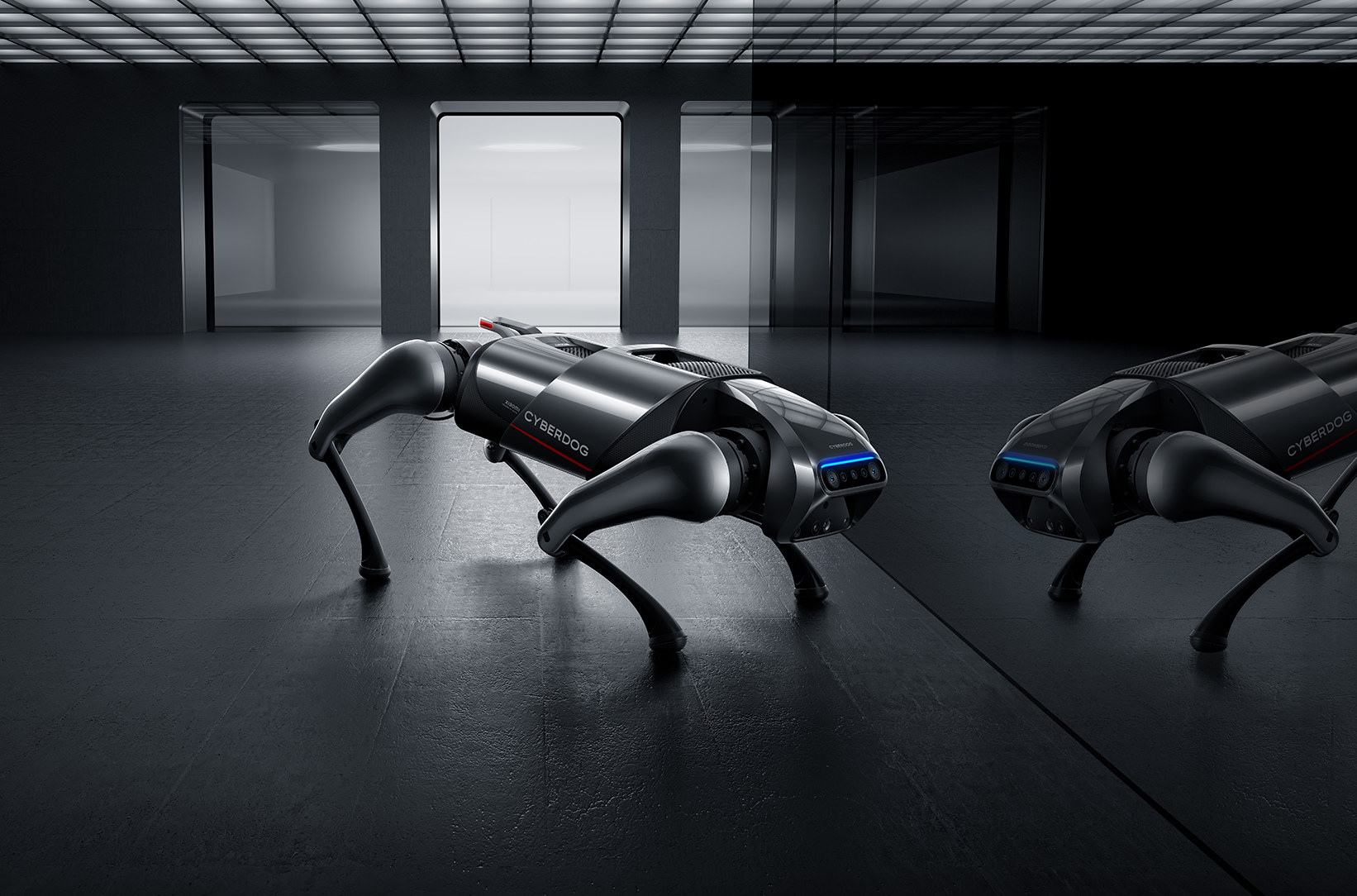
Xiaomi CyberDog quadruped robot is based on NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX
We’ve previously written about consumer-grade smart robotic dogs selling for several hundred dollars with Petoi Bittle equipped with Arduino & Raspberry Pi, as well as XGO Mini Pro with Kendryte K210/K510 AI processor. Xiaomi has now launched its own quadruped robot that looks like a dog with the Xiaomi CyberDog equipped with a more powerful NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX system-on-module (SoM), a larger and heavier body than competing consumer models, and a price tag of a little over $1,500. Xiaomi CyberDog specifications and key features: SoM – NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NXwith an hexa-core NVIDIA Carmel 64-bit Arm processor, a 384-core NVIDIA Volta GPU with 48 Tensor Cores, 2x NVDLA deep learning accelerators delivering a total of 21 TOPS at 15 Watts, 8GB RAM. Storage – 128GB “near” industrial-grade SSD Xiaomi’s in-house developed servo motors offering Maximum torque – Up to 32N·m Rotation speed – Up to 220Rpm Maximum speed – […]
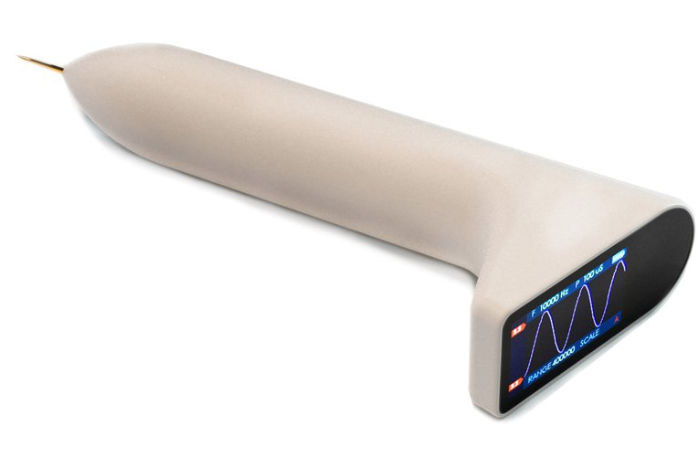
Arduino programmable wireless multitool offers color display, touch controls (Crowdfunding)
QUARK may look like the perfect weapon to hijack a plane, but instead, it’s an open-source, Arduino-based wireless multitool for hardware engineers equipped with a full-color screen and touch-based controls. Based on ESP32 WiFI & Bluetooth wireless SoC, Mulin Group’s QUARK is an ultra-portable multimeter, signal generator and oscilloscope, a bit like IkaScope WiFi Pen-Oscilloscope, except having a laptop or phone to visualize measurements is only optional. The company also compares it to DT71 smart tweezers which do not have an oscilloscope function due to the tiny display. QUARK features & specifications: WiSoC – ESP32 dual-core processor with WiFI & Bluetooth connectivity Display – 240 x 134 IPS display Measurements Voltage – 0 to 26 V Current – 0 to 3.2 A Resistance from 0 to 2 MΩ Capacitance from 2 pf to 1000 uF Inductance up to 1 H Sampling rate for oscilloscope function – 400 ksps Features – […]
TTGO T-Motion USB adapter offers LoRa and GPS for under $30
USB adapters are one of the easiest ways to add new features to existing hardware, and if you’d like to add LoRa connectivity and GPS tracking to any device or board with a USB board TTGO T-Motion USB adapter offers just that. Manufactured by LilyGO, the USB dongle is based on AcSiP S76G system-in-package that integrates an STM32 MCU with a Semtech SX1276 LoRa transceiver and GPS into a single. The GPS antenna is placed on the board inside the enclosure, while the external LoRa antenna is connected through an SMA connector. TTGO T-motion specifications: SiP – AcSiP S76G system-in-package with STMicro STM32L073x Arm Cortex M0+ MCU with up to 192 KB of Flash memory and 20 KB of RAM, Semtech SX1276 supporting global 868 MHz or 915 MHz ISM-Bands, Sony CXD5603GF GNSS receiver. Antenna Internal GPS antenna External LoRa antenna Host interface – USB 2.0 male port Misc – […]
Mali-G78 GPU’s Valhall instruction set documentation released after reverse-engineering work
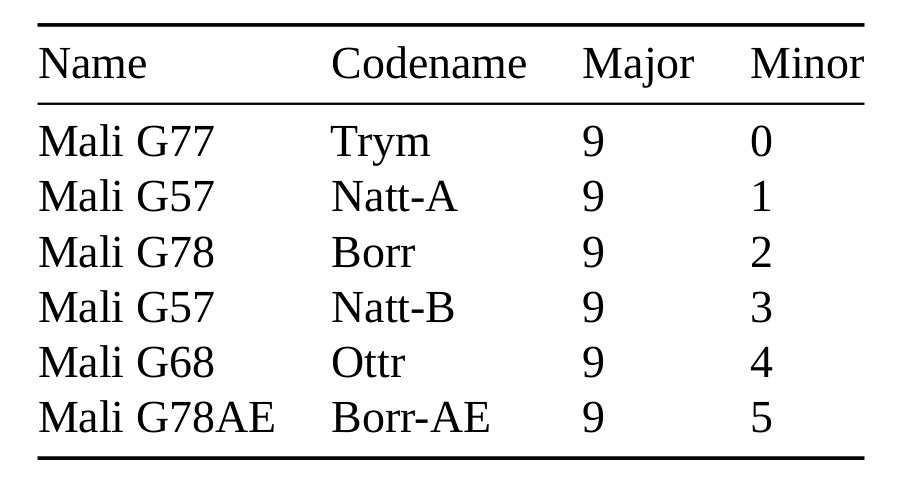
Collabora has been working on Panfrost open-source GPU driver for Arm Mali Bifrost and Midgard GPU for several years, and even getting official support from Arm. But apparently, that support does not include documentation for Mali-G78 GPU and other recent Arm Valhall Mali GPUs, as the company recently reverse-engineered Mali-G78 for about a month before releasing the documentation on the Valhall instruction set (PDF). Other results from the reverse-engineering include an XML architecture description that can be parsed by programs, as well as a Valhall assembler and disassembler that were used as a reverse-engineering aid. Besides Mali-G78 “Borr” GPU, the work will be useful for other Valhall GPUs include Mali-G77 “TryM’, Mali-G57 “Natt-A/B”, Mali-G68 “Ottr”, and Mali-G78AE “Borr-AE” for automotive & industrial applications. Alyssa Rosenzweig explains Collabora’s work that was based on the International edition of the Samsung Galaxy S21 phone powered by Samsung Exynos 2100 system-on-chip with a Mali-G78 […]
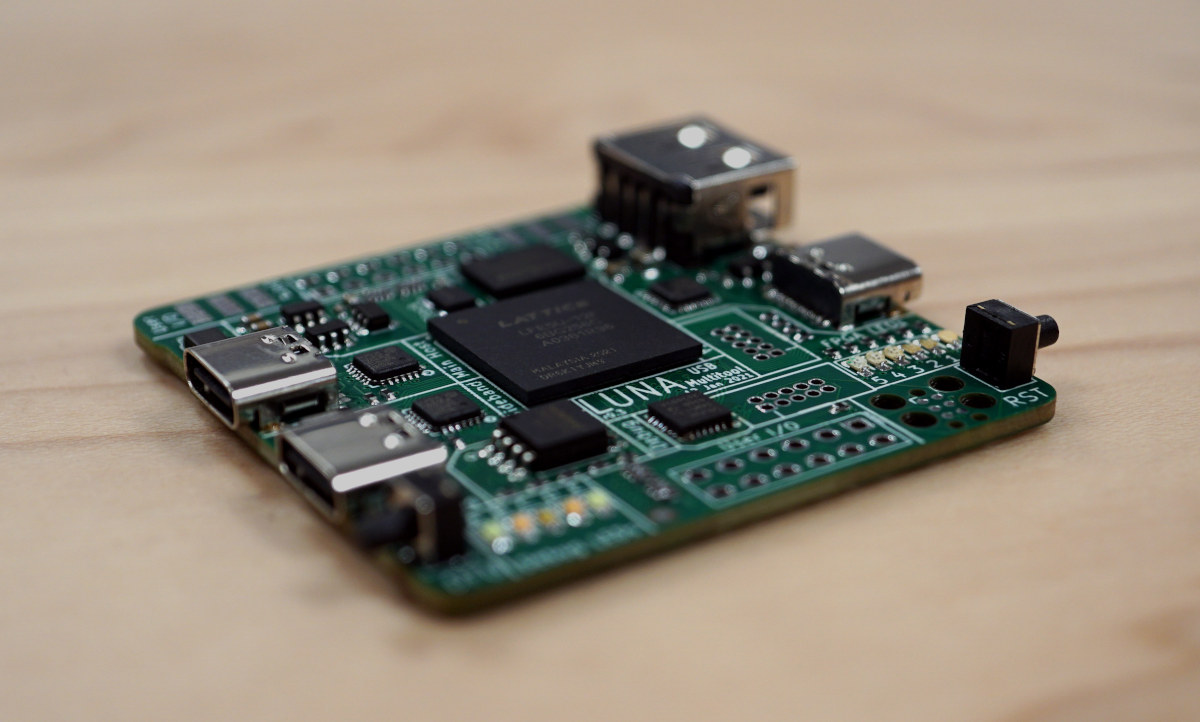
Cynthion board enables USB Hacking through Lattice ECP5 FPGA (Crowdfunding)
Update 16/02/2023: The LUNA board has been renamed to Cynthion, but the gateware framework continues to be called LUNA. Several USB hacking/debugging boards were launched in 2020 either based on microcontrollers or FPGA with the likes of Tigard (FTDI FT2232HQ), Ollie (STM32F042), Glasgow Interface explorer (Lattice Semiconductor iCE40), or Protocol Droid (STM32). All those were launched on Crowd Supply, and there’s now another one with LUNA “multi-tool for building, analyzing, and hacking USB devices” based on a Lattice Semiconductor LFE5U-12F ECP5 FPGA that raised over $100,000 in a few days. Cynthion hardware specifications: FPGA- Lattice Semiconductor LFE5U-12F ECP5 FPGA with 12K LUTs System Memory – 64 Mbit (8 MiB) RAM for buffering USB traffic or for user applications Storage – 32 Mbit (4 MiB) SPI flash for PC-less FPGA configuration USB – 3x High-Speed USB interfaces, each connected to a USB3343 PHY capable of operating at up to 480 Mbps. […]
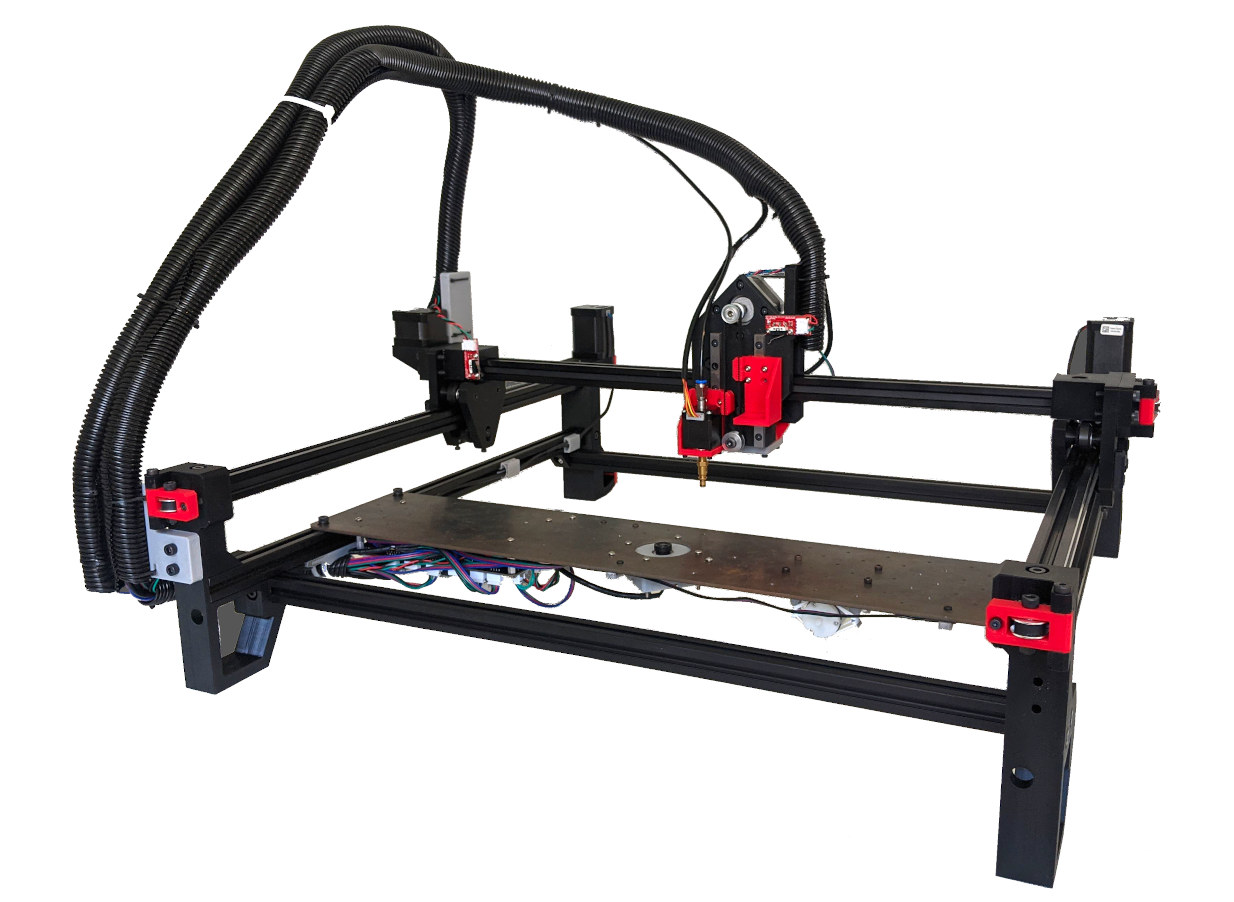
Index PnP – An open-source pick-and-place machine for mid-scale manufacturing
We’ve previously written about one open-source pick-and-place machine, SimplePNP aiming to provide a low-cost solution for several hundred dollars and relying on OpenPnP open-source control software. But Stephen Hawes found out this type of solution did not cut it for mid-scale manufacturing (100 to 5000 units per year), so he decided to build his own. Meet Index PnP, an open-source pick-and-place machine designed for mass-production volumes typical of crowdfunding projects. The project was introduced launched with the following requirements Automated – no human interaction necessary from attaching the paste-applied board to the machine to having a board ready for reflow Capable of picking and placing components down to 0603 passives Integrated up and down vision for fiducial scanning and on-nozzle component alignment Automatic nozzle tip changer to support a wide range of component sizes Frame and motherboard design capable of future upgrades Mechanical and Electrical support for conveyor belt module […]