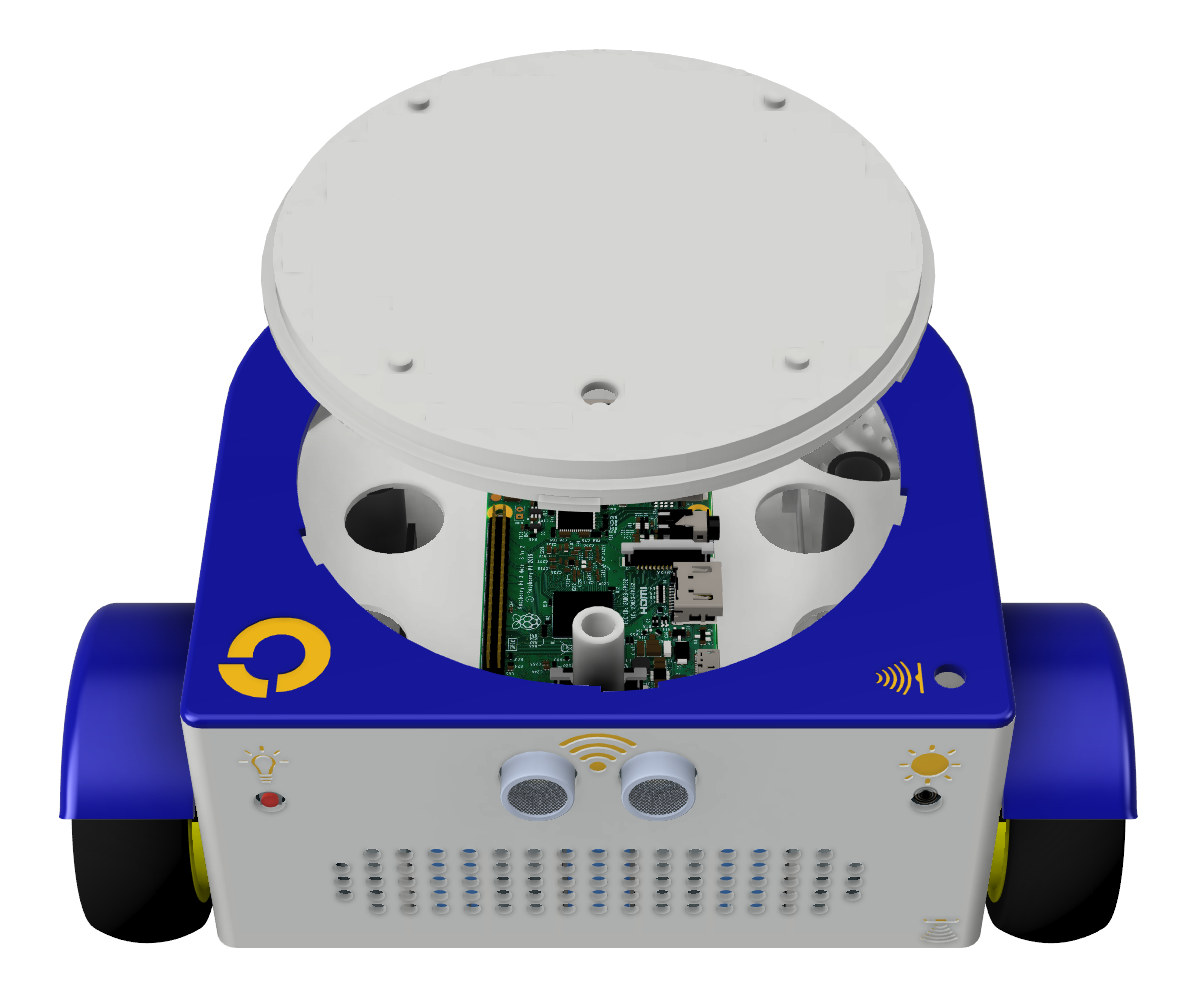
FOSSBot is an “open design” 3D printed educational robot comprised of a Raspberry Pi SBC and various off-the-shelf modules, as well as open-source software that can be used for education purposes. The FOSSBot DIY robot has been developed by the Harokopio University of Athens and the Greek Free and Open Source Software (GFOSS) community, and builds upon the “GSOC 2019 – A DIY robot kit for educators” with the main goal being to have a platform to “familiarize teachers with modern education models based on the S.T.E.A.M approach. (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics)”. FOSSbot key components: SBC – Raspberry Pi Zero W, Raspberry Pi 3, or Raspberry Pi 4. Mechanically and electrically compatible Raspberry Pi alternatives could be an option too although part of the software would have to be modified Storage – 32GB MicroSD card Expansion board – Adafruit Perma-Proto HAT for Pi – No EEPROM to connect sensors […]
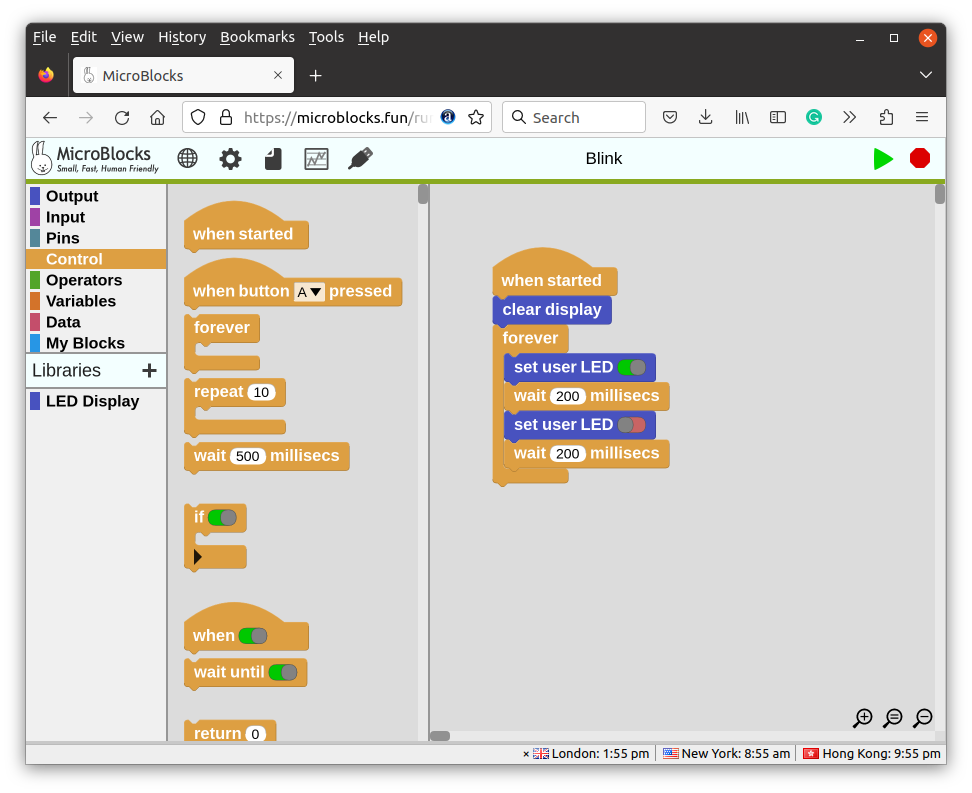
MicroBlocks is a visual programming IDE for 32-bit microcontrollers
MicroBlocks is a visual programming IDE for 32-bit microcontrollers currently supporting the BBC Micro:bit V1/V2, Calliope mini (aka the German Micro:bit), Adafruit Circuit Playground Express and Bluefruit, Raspberry Pi Pico and Pico W, and various other boards including ESP32 and ESP8266-based boards. I discovered MicroBlocks in the list of talks for FOSDEM 2023, and although it did not make it to my virtual schedule, I thought it was interesting to look into and write about it. In their upcoming FOSDEM talk, Bernat Romagosa and Kathy Giori refer to MicroBlocks as small, fast, and human-friendly with development guided by four guiding principles: liveness, parallelism, portability, and autonomy. The IDE is inspired by Scratch, and as such, looks very similar to other visual programming interfaces I have used over the years. You can launch MicroBlocks from Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge on a PC (not a mobile device) without having to install […]
FOSDEM 2023 schedule – Open-source Embedded, Mobile, IoT, Arm, RISC-V, etc… projects
After two years of taking place exclusively online, FOSDEM 2023 is back in Brussels, Belgium with thousands expected to attend the 2023 version of the “Free and Open Source Developers’ European Meeting” both onsite and online. FOSDEM 2023 will take place on February 4-5 with 776 speakers, 762 events, and 63 tracks. As usual, I’ve made my own little virtual schedule below mostly with sessions from the Embedded, Mobile and Automotive devroom, but also other devrooms including “Open Media”, “FOSS Educational Programming Languages devroom”, “RISC-V”, and others. FOSDEM Day 1 – Saturday February 4, 2023 10:30 – 10:55 – GStreamer State of the Union 2023 by Olivier Crête GStreamer is a popular multimedia framework making it possible to create a large variety of applications dealing with audio and video. Since the last FOSDEM, it has received a lot of new features: its RTP & WebRTC stack has greatly improved, Rust […]
ESP32 OpenMQTTGateway smart plug acts as an BLE MQTT gateway and a power meter
The Theengs Plug ESP32 smart plug runs OpenMQTTGateway firmware to serve as a BLE MQTT gateway and power meter compatible with Home Assistant, Homebridge, OpenHAB, DomoticZ, FHEM, Jeedom, NodeRed, AWS, and any MQTT-compatible IoT or Smart Home system. While the Matter standard should improve interoperability between Smart Home frameworks over time, there are still millions of devices already produced that are not Matter compatible, and the Theengs Plug aims to at least partially address this issue by helping users reduce the number of hubs required and have only one that supports different ecosystems. Theengs Plug hardware specifications: Microcontroller – ESP32 dual-core wireless MCU with 2.4 GHz WiFi and Bluetooth LE connectivity Network Protocol – MQTT Power Supply – 100-120VAC, 60Hz, up to 15A Dimensions – 103 x 61 x 34.6mm Temperature Range – Operating: 0ºC ~ 40ºC; storage: -10°C ~ 50°C Humidity – 0%~95% (no condensation) Certification – UL Some […]
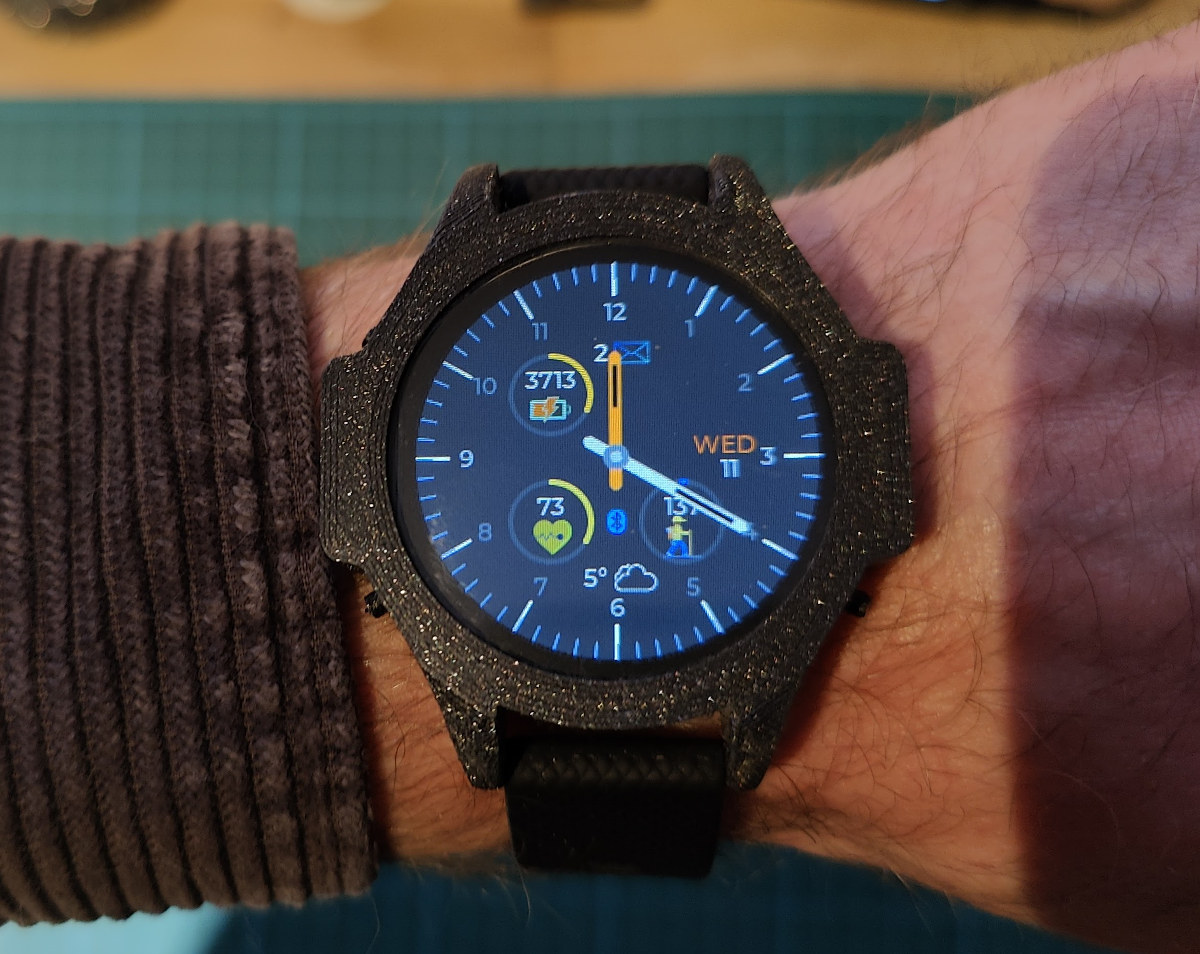
ZSWatch open-source hardware nRF52833 smartwatch runs Zephyr RTOS
ZSWatch is an open-source hardware smartwatch based on an u-Blox ANNA-B402 module with Nordic Semi nRF52833 Bluetooth 5.1 SoC and running Zephyr real-time operating systems. We’ve seen several open-source hardware smartwatches over the years, as well as open-source firmware projects such as AsteroidOS or InfiniTime with the latter used in the PineTime smartwatch, and the ZSWatch adds to the list of interesting open-source wearables with all source files made public. ZSWatch specifications: Wireless module – u-blox ANNA-B402 based on Nordic Semi nRF52833 Arm Cortex-M4F microcontroller with Bluetooth LE 5.1 and direction finding support Storage – 8MB flash (MX25R6435FZNIL0) Display – 1.28-inch 240×240 IPS TFT circular display with GC9A01 driver; covered with Sapphire Crystal Glass. Sensors Accelerometer (LIS2DS12TR) for step counting, etc… MAX30101EFD for pulse oximetry and heart rate monitoring Misc 3x buttons for navigation (prev, next, enter) Vibration motor (DRV2603RUNT) with haptics driver to give better vibration control. Power Management […]
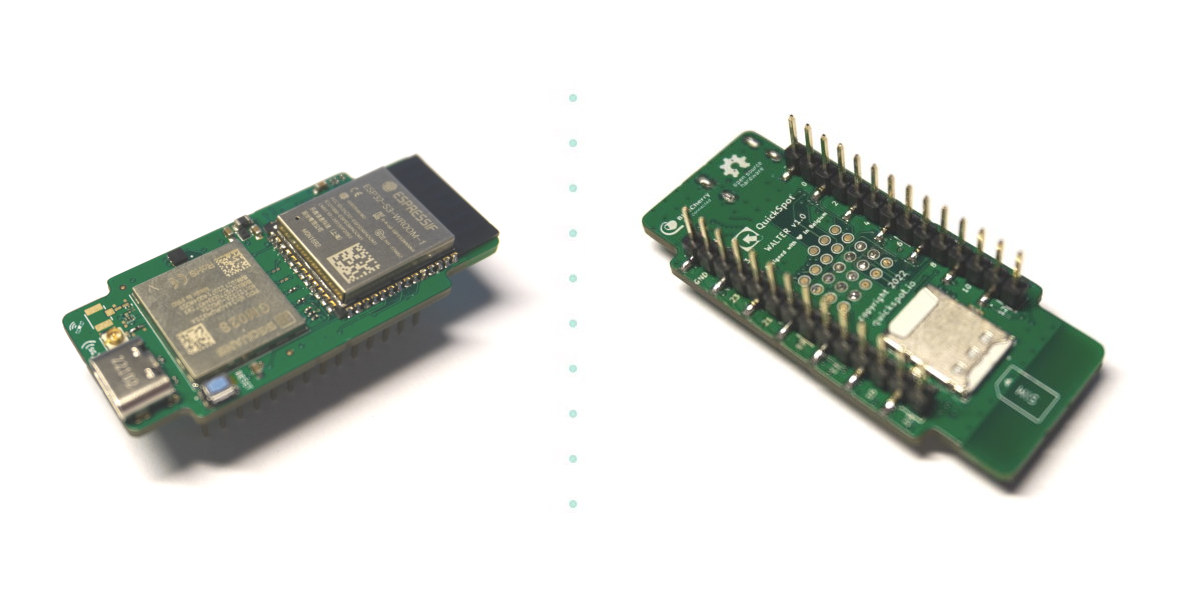
Walter ESP32-S3 board supports NB-IoT, LTE-M, and GPS
QuickSpot Walter is an ESP32-S3 development board with built-in WiFi 4 and Bluetooth LE/Mesh connectivity, as well as NB-IoT, LTE-M, and GNSS support through a Sequans GM02SP 5G IoT modem that appears to be a variant of the Sequans Monarch 2 GM02S with GNSS support. Walter specifications: Wireless modules ESP32-S3-WROOM-1-N16R2 module ESP32-S3 dual-core LX7 microcontroller 2MB QSPI PSRAM 16MB QSPI flash 802.11 b/g/n WiFi 4 up to 150 Mbps with on-board antenna Bluetooth 5 LE up to 2Mbps, Bluetooth Mesh Sequans GM02SP modem LTE Cat M1 (LTE-M) and NB1/NB2 (NB-IoT) GNSS and assisted GNSS using GPS and Galileo constellations NanoSIM for cellular connectivity I/Os 2x 14-pin headers with up to 24x GPIO, UART, VIN, 3.3V, and GND 23x test points 3.3V I/O voltage Power Supply 5V (3.0 to 5.5V) DC via VIN pin 5V via USB Type-C port Dimensions – 55 x 24.8 mm Temperature Range – -40°C to +85°C […]
Merlot is an open-source hardware tricolor wireless E-paper display
paperd.ink Merlot is a tricolor E-paper display with an open-source hardware control board based on ESP32 wireless SoC that is programmable with Arduino, MicroPython, or the ESP-IDF framework. We first wrote about the paperd.ink 4.2-inch ESP32-based monochrome e-Paper display last year, but the company has now refined its design with the “paperd.ink Classic” replacing the 3D printed enclosure with a vacuum cast enclosure and adding a 1,900 mAh battery. They also launched a new model, the Merlot, based on the same design but with a display supporting three colors: black, white, and red. Merlot specifications: Wireless module – ESP32-WROOM-32 module with ESP32 dual-core processor, 4 MB SPI flash, 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 & Bluetooth LE connectivity Storage – MicroSD card slot for storing images, files, etc Display – 4.2″ tricolor e-Paper display with 400 x 300 resolution; full refresh: ~ 17 seconds; partial update: also 17 seconds… USB – 1x […]
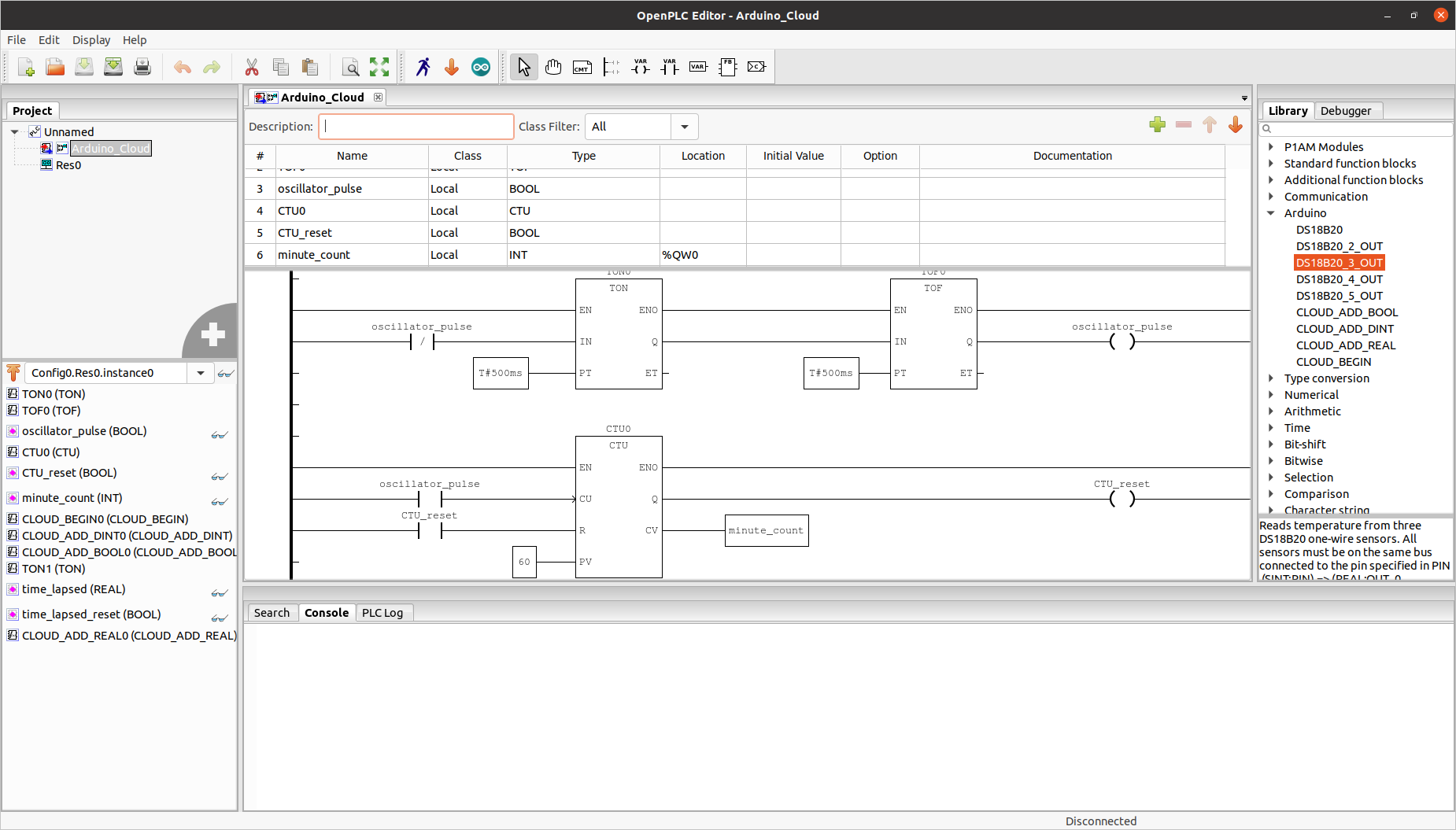
OpenPLC open-source Programmable Logic Controller Suite works with Arduino, ESP8266/ESP32, Raspberry Pi, etc.
OpenPLC is an open-source, free-to-use Programmable Logic Controller Suite, compliant with the IEC 61131-3 standard, and working with a range of hardware platforms such as Arduino, ESP8266/ESP32, Raspberry Pi SBCs, as well as Windows and Linux machines. When Arduino unveiled the Arduino PLC IDE, we noted the languages defined by the IEC 61131-3 standard were licensed, and the PLC key for the Portenta Machine Control unit sold for $17.60. One reader complained about the high license cost per device, but Massimo Banzi, the co-founder of the Arduino project, replied it was cost-effective for smaller deployments: Actually it’s not that much money compared to the cost of other PLC software (thousands of dollars per seat!). This model helps small companies with not that many devices.. It’s possible to negotiate bulk licenses for companies. But there’s also another option with OpenPLC open-source PLC suite that does not require any license fee. That’s […]