At the end of last year, ARM announced ARMv8, the first ARM 64-bit ARM archtecture, and last week at ARM Techcon 2012, ARM announced the first ARMv8 cores: Cortex A53 and A57. But since there’s no silicon at the moment, what if you wanted to develop code running on ARMv8 before the hardware is available? The answer is: Fast Models, a Virtual Platform (VP) to accelerate software development. This is especially important for ARMv8 since hardware is not expected to be available for another year. In this post, I’ll first show how to run “Hello World!” in ARMv8 fast models, then we’ll run ARM Linux 64-Bit (Aarch64) in the virtual platform. ARMv8 Foundation Model In order allow the developer’s community to program for ARMv8 (Cortex A53/A57 cores), ARM has made ARMv8 Foundation Model, a virtual platform, available free of charge. This v8 Foundation model provides a basic ARMv8 platform environment […]
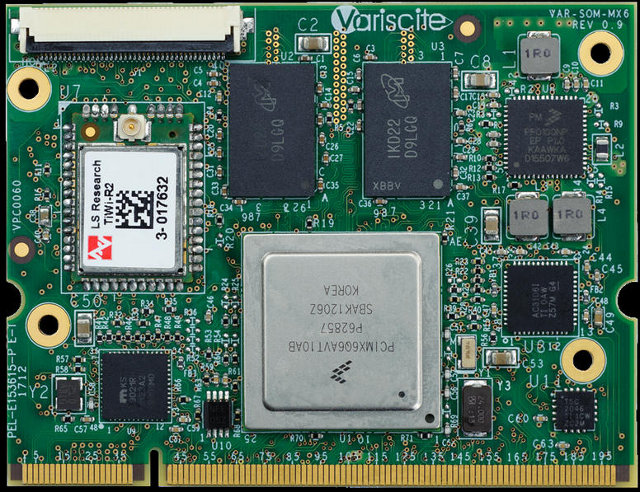
Variscite VAR-SOM-MX6 Freescale i.MX 6 Solo, Dual and Quad System on Modules Start at $59
Variscite has unveiled a new series of system on modules powered by Freescale i.MX6 Solo, Dual, DualLite and Quad processors with 512 to 2048 MB DDR3 RAM, and 128 to 1024MB SLC NAND Flash. Here are the modules key features: SoC – Freescale i.MX 6 series SoC (Single/Dual /Quad ARM® Cortex™-A9 Core, 1.2 Ghz) System Memory • Up to 16 Gb DDR3 RAM Storage – Up to 8 Gb NAND Flash for storage memory/boot Video Output: 2 x LVDS display interface HDMI V1.4 i nterface 1 x MIPI DSI Touch panel interface Camera – Parallel & serial camera interface (CSI) Connectivity On-board 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet PHY WLAN (802.11 b/g/n) Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR USB – 1 x USB 2.0 host, 1 x OTG Audio – Stereo line -In/out, digital & analog microphone, and S/PDIF In/Out Other interfaces: 2 x SD/MMC Serial interfaces ( SPI , I2C, UART, I2S,) 2x CAN […]
$100 Mele A1000G / A2000G Android Media Players with 1GB RAM and 8GB Flash
I’ve been asked by several people when there would be a Mele with 1GB RAM, well the time is now, with the Mele A1000G and Mele A2000G. Both appear to be based on the previous Mele A1000 and Mele A2000 set-top boxes, but feature 1 GB RAM and 8 GB Flash instead of 512 MB RAM and 4 GB Flash. Here are Mele A1000G & Mele A2000G Specifications: SoC – AllWinner A10 Cortex A8 processor @ 1GHz System Memory – 1 GB DDR3 Storage: 8GB NAND Flash SD card slot (up to 32 GB) Connectivity: Wi-Fi – 802.11 b/g 10/100 MB Ethernet USB – 3 USB Host ports SATA Interface for 2.5″ HDD Video Output – HDMI, composite and VGA. Audio Output – RCA stereo output and optical out (SPDIF) Audio Formats – MP3 / WMA / WAV / OGG / FLAC / MKA Video Formats – TS / M2TS […]
PengPod 700 & 1000 – Linux Tablets Based on AllWinner A10
There are plenty of tablet based on AllWinner A10 and A13 processors, but all of them run Android, and you are out of luck if you want to run Linux on your tablet, unless you hack this yourself. But this is about to change as PengPod will launch 2 tablets and 1 mini PC running Linux from NAND flash or micro SD card: PengPod 700 – 7″ tablet with Allwinner A10, 1GB RAM and 8GB Flash PengPod 1000 – 10″ tablet with AllWinner A10, 1GB RAM and 8GB Flash PengStick – AllWinner A10 mini PC with 1GB RAM and 4 GB Flash The table below gives more detailed specifications and comparison of the three devices. Device PengPod1000 PengPod700 PengStick Type Tablet Tablet TV Stick CPU Allwinner A10 AllWinner A10 AllWinner A10 Android 4 4 4 Linux 3.0.42 3.0.42 3.0.42 Screen 10” 7” External Resolution 1024×600 800×480 1080i Ram 1GB 1GB […]
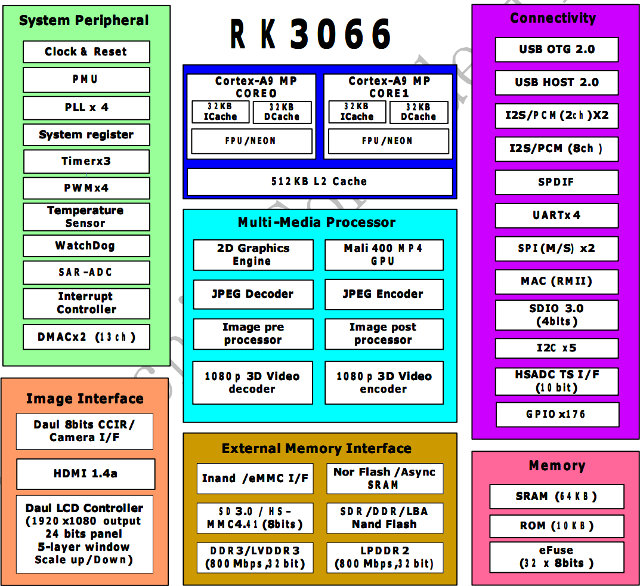
Rockchip RK3066/RK30xx Processors Documentation, Source Code and Tools
Rockchip RK3066 (part of RK30xx family) is a Chinese dual ARM Cortex A9 SoC targeting multimedia products such as tablets (e.g. Cube U30GT), mini PC (e.g UG802, MK808) and in theory set-top boxes, but I can’t find any products based on this Rockchip processor. It seems mini PCs/ HDMI TV sticks have taken over this market. RK3066 Processor The processor features two ARM Cortex A9 clocked at up to 1.6 Ghz with a quad core Mali-400MP GPU. It can support 1080p (3D) encoding/decoding, provides HDMI 1.4a, VGA, composite, component and LVDS video outputs (Dual display support), USB 2.0 Host and OTG ports, a MAC interface (Ethernet), and much more… Here are the key features of Rockchip RK3066 processor: Dual Core A9 + Quad Core Mali-400MP GPU 2 banks, 8/16 bit Nor flash / SRAM interface 8 banks, 8/16 bit async NAND flash, LBA NAND flash and 8-bit sync ONFI NAND […]
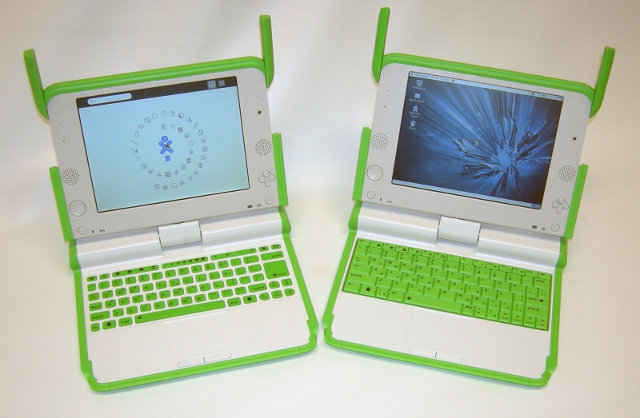
OLPC XO-4 Touch Laptop Powered by Marvell ARMADA PXA2128
Last year, OLPC (One Laptop Per Child) announced their first laptop powered by ARM, with OLPC X-1.75 powered by Marvell ARMADA 610 single core processor (And sold over 100,000 since Q1 2012). The 2 new models – OLPC XO-4 and OLPC XO-4 Touch – will be upgraded to ARMADA PXA2128 triple core processor (2 ARMv7 Core + 1 Hybrid LPM (Low Power Mode) ARMv7 core), which the OLPC XO-4 Touch offering multitouch support. OLPC XO-4 laptop will look exactly like the OLPC 1.75 laptop pictured below. OLPC XO-4 will have the following specifications: SoC – Marvell PXA2128 (ARMv7 compatible) @ 1 GHz with Vivante GC2000 GPU System memory – 1GB or 2GB DDR3 RAM (Depending on configuration) Mass storage: 4 GB or 8GB NAND flash (eMMC) Internal microSD card slot for repair/replacement Externally accessible SD card slot; Display – 7.5” dual-mode TFT display with touchscreen (2 simultaneous touch max) Audio […]
TI and AllGo Embedded Launch E-Tab Tablet Reference Design Powered by TI AM3354 Processor
Texas Instruments and Allgo Embedded jointly announced the availability of E-Tab, a tablet reference design based on Cortex A8 Sitara AM3354 processor that targets the healthcare, logistics, retail and education markets as well as hotels and restaurants. Here are the tablet reference designs specifications: Processor – TI’s AM3354 ARM Cortex-A8 microprocessor (up to 1 GHz) Operating System – Android ICS 4.0 System Memory – 512 MB DDR3 RAM Storage – 512 MB Nand Flash and 4GB Micro SD card Display – 7″ WVGA TFT LCD with 5-Touch Capacitive Touch panel Audio – Stereo Headphone, Internal MIC and Internal Mono Speaker Connectivity: WiFi 802.11 b/g/n + BT 2.1 Module Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR Ethernet 10/100Mbps (Optional) Camera – Internal USB Camera Module (Optional) USB Interfaces – USB High Speed Host Port and USB OTG (ADB and Debug purpose) Key/Button – Single Button for Back and Home screen, Reset Switch and Power […]
VIA ARTiGO A1250 Slim System Powered by Quad Core E-Series Processor
VIA Technologies announced the VIA ARTiGO A1250 slim system featuring a 1.0 GHz VIA QuadCore E-Series processor and VIA VX11H media system processor (MSP). The VIA ARTiGO A1250 is a low profile system targeted at home or office applications such as home server, home automation, hotel management, media streaming, digital signage, surveillance as well as medical and healthcare applications. Here are the key features of ARTIGO A1250: VIA QuadCore E-Series processor (U4650E) @ 1.0 GHz Up to 8GB of DDR3 1333 SDRAM SODIMM Supports one 2.5″ SATA HDD or Flash SSD installation Quiet, ultra slim profile design (3cm high) VIA VX11H media system processor with DirectX11 support 3D and HD video up to 1080p HDMI & VGA display ports with dual independent display support I/O: HDMI, VGA, 2x USB 3.0, 2x USB 2.0, GigaLAN, Audio-in/out/mic-in Average power consumption of 27W TDP Dimensions: 17.7cm x 12.5cm x 3.0cm I understand that inside […]