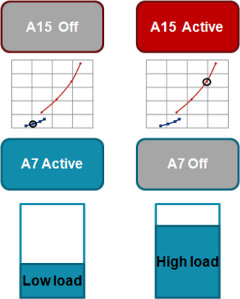
There was a big,LITTLE mini-summit during Linaro Connect Europe 2012, where an update was given on current big.LITTLE implementations and the results of measurement of power vs performance. Big.LITTLE Processing Implementations Overview As briefly mentioned in “Versatile Express TC2 (2xA15, 3xA7) Development Board at ARM Techcon 2012“, there are 2 big.LITTLE implementations: In-kernel switcher (IKS) This implementation is already available through Linaro and only required minimal changed to the kernel as it mainly an augmentation to DVFS (Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling) except instead of only adjusting voltage and frequency depending on the load, it will also move the load to different cores. The main drawback is that this implementation only uses half the cores. For example, on a 2x Cortex A15 / 2x Cortex A7 system, it can only use 2 cores at the same time (either A15 or A7 cores), as the load is managed between one type […]
AMLogic Releases U-Boot and Updated Linux Kernel Source Code
AMLogic released kernel 3.0.8 source code for AML8726-MX a few months ago, and yesterday they provided an updated tarballs with the kernel, and for the first time, AFAIK, released the source code for U-Boot. There are 4 new files apparently generated from the (internal) git repository in AMLogic: common-2012-11-20-git-b687495906.tar.gz (108M) – This is the same kernel 3.0.8 release has last time, but with updated code. m1-kernel-android-2012-11-20-git-5d0f6b8e93.tar.gz (103M) – This looks like an older kernel 2.6 for AML8726-M1 only. uboot-master-2012-11-20-git-9b50e9a295.tar.gz (16M) – U-Boot 2010.06 possibly to use with the older 2.6 kernel. Only for M1 & M3 platforms. uboot-next-2012-11-20-git-b0e532795a.tar.gz (40M) – U-Boot 2011.03 for use with M3 and M6 platforms. I’ve already explained how to build the kernel in the previous post, so I’ll focus on U-Boot this time. Ubuntu 12.04 arm-linux-gnueabi- toolchain fails to build U-Boot (uboot-next), so you’ll have to install Sourcery toolchain instead: wget http://openlinux.amlogic.com/download/linux/ARM/gnutools/arm-2010q1-188-arm-none-eabi-i686-pc-linux-gnu.tar.bz2 tar xjvf arm-2010q1-188-arm-none-eabi-i686-pc-linux-gnu.tar.bz2 […]
TQ Group TQMa6X Embedded Modules based on Freescale i.MX6 Processors
TQ Group has recently unveiled several TQMa6X embedded CPU modules that feature Freescale i.MX6 Solo, Dual and Quad processors, targeting screen, multi-touch, and multi-display applications as well as conventional controlling tasks. 3 modules are available: TQMa6S-AA – Single Cortex A9 / 1,2 GHz, 2 GB eMMC Flash, 512 MB DDR3, 64 kB EEPROM, -25°C…+85°C TQMa6D – Dual Cortex A9 / 1,2 GHz, 2 GB eMMC Flash, 512 MB DDR3, 64 kB EEPROM, -25°C…+85°C TQMa6Q – Quad Cortex A9 / 1,2 GHz, 2 GB eMMC Flash, 1 GB DDR3, 64 kB EEPROM, -25°C…+85°C TQMa6X modules share the following specifications: Processor – Freescale MCIMX6 Single/Dual/Quad Cortex A9 up to 1,2 GHz System Memory – Up to 2 GB DDR3 SDRAM Storage – Up to 64 GByte eMMC Flash, EEPROM: 0 / 64 kbit and up to 128 MB NOR-Flash. System interfaces: CAN – 2x FlexCAN ESAI (Enhanced Serial Audio Interface) Ethernet – 1x 10/100/1000 Mbit (IEEE […]
Freescale i.MX6 Resources: Development Boards, Documentation, Source Code and Tools
Reader “Mark” recently left a comment saying the NDA on Freescale i.MX6 resources was lifted and documentation and source code were now available for the platform. So it’s time for me to look into it, and provide an overview of Freescale i.MX6 features, list available development platforms, and have a closer look at the documentation, source code and tools for the platform. Freescale i.MX6 Processors In 2011, Freescale initially announced 3 processors in the i.MX6 series for consumer, industrial and automotive markets, but added 2 lite SoC in 2012, and there are now 5 members in the family: Freescale i.MX6SoloLite – Single Cortex A9 processor up to 1 GHz with 256KB L2 Cache, 32-bit DDR3 and LPDDR2 memory support, and 2D graphics accelerator (Vivante GC355 + GC320) Freescale i.MX6Solo – Single Cortex A9 core up to 1 GHz with 512KB L2 Cache, 32-bit DDR3 and LPDDR2 memory support, and 2D & […]
$199 GIZMO EXPLORER KIT – Embedded Development Kit Based on AMD G-Series G-T40E APU
I’ve just stumbled upon a low cost and open source embedded development kit featuring AMD G-Series G-T40E dual core APU that comes with the following: The Gizmo Board – A compact (10×10 cm) development board for powered by an AMD G-Series APU. The Explorer Board – An expansion I/O board providing an alpha-numeric keypad, a micro-display, and a breadboard area for prototyping and customization. Sage SmartProbe JTAG Development Tool – The kit includes the SmartProbe hardware and 20 hours of trial time use. Ethernet & USB Cables – The USB cable lets you connect the SmartProbe to your PC. The Ethernet cable is for networking connectivity, which can be used to access the SmartProbe as well. USB wall charger Power Supplyand Cable – A universal power supply for the Gizmo board, with a U.S.-standard cord. 6x standoffs with nuts Alpha-numeric keypad – To connect to the explorer board Installation DVD […]
Kontron ULP-COM-sAMX6i – Freescale i.MX6 Solo, Dual and Quad Computers on Module
Freescale i.MX6 series was first announced in January 2011, and there have been delays due to problem with the silicon, but now the i.MX6 processors are finally in mass production, and lots of different products are using this SoC. The latest product I found is ULP-COM-sAMX6i by Kontron which is a series of computers on module based on ULP-COM (Ultra Low Power) standard featuring Freescale i.MX6 solo, dual and quad processors. Those commercial and industrial grade modules target markets such as transportation, medical and military. Here are the technical specifications of the modules: CPU – Freescale i.MX 6 Single, Dual and Quad Core ARM Cortex-A9 @ 800 MHz (Industrial grade), 1 GHz and 1.2 GHz System Memory – Up to 2 GB DDR3 Storage – Optional onBoard NAND/eMMC up to 64GB Graphics / Video – Dual Display, HD 1080p Decode/Encode and 2D/3D acceleration Video Output Resolution Parallel LCD 18/24 bit […]
Learn How to Write a Driver for Linux 3.x With The Linux Driver Template
A Linux Driver Template (LDT) has been published to help new Linux kernel developers writing hardware device drivers. Constantine Shulyupin posted the Linux Driver Template (LDT) on the Linux mailing list in order to merge it into the mainline Linux kernel. The code can be used as as a starting point for new drivers, and shows how to use several Linux facilities such as module, platform driver, file operations (read/write, mmap, ioctl, blocking and nonblocking mode, polling), kfifo, completion, interrupt, tasklet, work, kthread, timer, simple misc device, multiple char devices, Device Model, configfs, UART, hardware loopback, software loopback and ftracer. This sample has been added to other device drivers samples in eLinux.org. And if you want to learn further there’s always the Linux driver bible: “Linux Device Drivers, Third Edition” which can be downloaded for free as PDF, although it’s for 2.6.10 kernel and many parts may not be up-to […]
XBMC for Linux on AllWinner A10 Devices? It Works! (Sort of)
Following the lack of support by AllWinner for the video engine libraries (CedarX), I had more or less given up on hope XBMC for Linux would ever run properly on AllWinner A10/A13 hardware. But recently, I found out some progress had been made using existing libs, and saw the Pengpod Tablet video showing XBMC running in Linux fairly smoothly. So I decided to cross-compile XBMC by following the instructions available at http://linux-sunxi.org/XBMC and trying to run it in Linaro ALIP 12.04 rootfs in my Mele A1000. Finally, I managed to cross-compile XBMC, but the performance was very poor in the GUI (6 to 12 fps) and I was unable to play videos and my serial console was flooded with messages like:
|
1 |
[DISP] not supported image0 pixel sequence:216 in img_sw_para_to_reg |
[Update: I managed to have XBMC Linux running & playing videos on Mele A1000 by using j1nx image (rootfs + kernel). I would first exhibit the exact same […]