Last post about ELCE 2012 videos… David Stewart, manager of the Yocto Project team within the Open Source Technology Center at Intel, gives an introduction to the Yocto Project, as well as a status update at ELCE 2012. Abstract: The Yocto Project is a joint project to unify the world’s efforts around embedded Linux and to make Linux the best choice for embedded designs. The Yocto Project is an open source starting point for embedded Linux development which contains tools, templates, methods and actual working code to get started with an embedded device project. In addition, the Yocto Project includes Eclipse plug-ins to assist the developer. This talk gives a walk-through of the key parts of the Yocto Project for developing embedded Linux projects. In addition, features will be described from the latest release of the Yocto Project, v1.3. The talk will include demos of some of the key new […]
Video4Linux: Current Status and Future Work – ELCE 2012
Hans Verkuil, R&D software engineer at Cisco Systems Norway, talks about Video4Linux status, progress, and plans at the embedded Linux Conference in Barcelona, Spain, on November 7, 2012. Abstract: Video4Linux is a fast-changing subsystem where a lot of work is done to support the complex video hardware of embedded systems. This presentation will give an overview of the developments in the past year and the work that is planned for the near future. Hans covers SoC video devices support, core, control, and videobuf2 frameworks, HDTV timings & events API, video connector support, media controllers, codec & flash support, and more… You can also download the slides for this presentation. For further details about development, subscribe to linux-media mailing lists or chat on #v4l IRC channel on freenode. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting […]
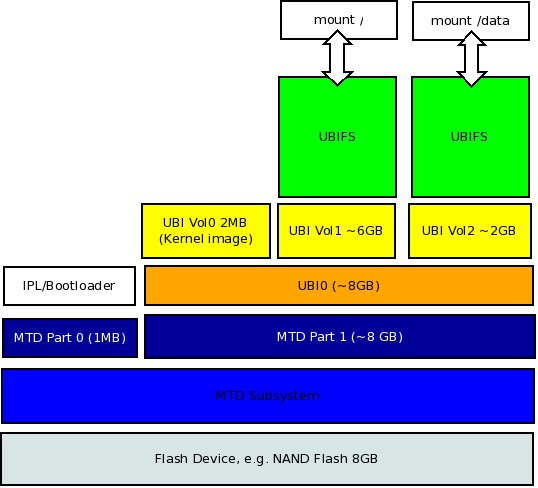
UBI Fastmap – ELCE 2012
Thomas Gleixner, Linux kernel programmer at Linutronix, talks about UBI flash management layer, and fastmap implementation to speed up boot times at the Embedded Linux Conference Europe, on November 7, 2012. Abstract: UBI is a flash management layer in the Linux kernel designed to handle especially the shortcomings of NAND flash. UBI itself has the requirement to scan the full flash at boot time. With flash sizes becoming larger and larger this can take quite some time. A recent development implemented fast mapping functionality which is designed to put an upper bound on the number of flash eraseblocks to scan. This allows faster boot times without sacrifying the robustness of UBI. This talk gives an overview of the UBI fastmap design and looks at costs and benefits. The talk provides an overview of UBI and its shortcomings, and explains UBI fastmap implementation in details showing it provides significant speedup proportional […]
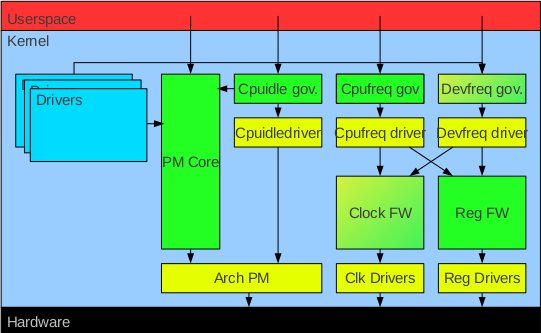
Debugging Embedded Linux (Kernel) Power Management – ELCE 2012
Tero Kristo, Linux kernel developer at Texas Instruments, explains how to debug power management in Embedded Linux at ELCE 2012. Abstract: The presentation will talk about debugging various problems a kernel developer can face when working with power management. These include hardware related issues (IC / HW layout bugs, bad documentation) and software related (kernel bugs, driver problems, adding new kernel features, bad userspace behavior.) Along with presenting some of these problems, I will discuss about ways to debug these… power management typically requires specific tools to be used. I will base the discussion on my first hand experience from working with Linux PM. Target audience is (kernel) software developers interested in power management. The presentation is divided into 3 sections: Debugging tools / methods for PM Disabling kernel features Stress testing Tracing (printk / low level UART) GPIO / LED trace Debugger Buffered traces / statistics with trace-cmd & […]
BoFs: Developer Tools and Methods: Tips & Tricks – ELCE 2012
Tim Bird, senior staff software engineer at Sony Network Entertainment, hosts a BoF session about tools & methods for embedded Linux developers at ELCE 2012. Abstract: In this Birds-of-a-Feather-session, Tim will share some of his favorite tips for developing embedded Linux software. This will include tips for using ‘git’, how he does multi-platform development, and tips for other tools that other developers might find useful. Prior to the event, Tim will do a survey and solicit ideas from other developers as well. Please come to this BoF prepared to share your own productivity tips for embedded Linux development. Tim talks is divided into the following key points: Git tips – How to finds info about commits (git log, git show), use aliases (e.g. for colored output), find a commit that caused problem (git bisect), and more Patch management – quilt patch managing tool, diffinfo, and splitpatch (to break patches apart) […]
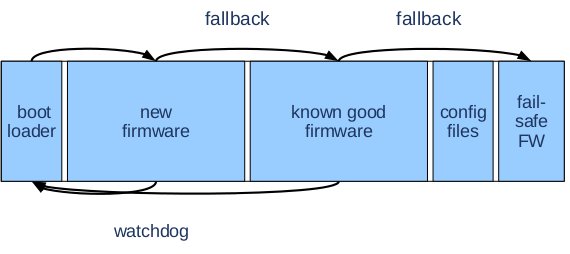
Upgrading Embedded Linux Without Bricking – ELCE 2012
Arnout Vandecappelle, senior embedded software architect at Essensium/Mind, talks about ways to greatly decrease the risk of bricking your board/device during upgrade thanks to gubies scripts and tools at the Embedded Linux Conference in Barcelona, Spain, on November 6, 2012. Abtract: Embedded systems are often modified remotely, e.g. to upgrade the firmware or change the configuration. This may however break the system and render it inaccessible, which is a major problem if the device is hard to reach physically. Unfortunately, no catch-all failsafe solution exists to make sure that the device stays accessible remotely even if a modification goes wrong. Instead, the possible failures have to be anticipated and covered. This talk discusses some of the frequently occurring failures, how they can be detected and handled. These include power failure, kernel crashes, network failure and data corruption. We include examples of concrete use cases. Finally, there is room for discussion about […]
The End of Embedded Linux (As We Know It) – ELCE 2012
Chris Simmonds, freelance consultant and trainer (2net ltd), discusses the future of embedded Linux now that storage and processing power are no longer an major issue, and try to find the best Linux platform for embedded systems at ELCE 2012. Abstract: Embedded Linux is at a cross roads where the combination of Moore’s law making devices more powerful and the mass production of consumer devices, especially mobile, making them cheaper means that the old ways no longer work. Only a few years ago we though in mega: MHz, MBytes, MBits/s. Now we have to think in giga. The days of the single core CPU are almost over, as are the days of the QVGA display. All this means that there is a need to re-think how embedded devices are programmed. Two obvious roads lie ahead: Android and Ubuntu (or other desktop operating system of your choice). This talk considers the […]
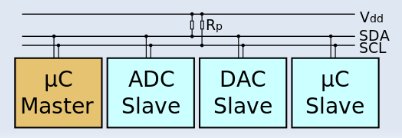
Board Bringup: You, Me, and I2C – ELCE 2012
David Anders, embedded systems developer at Texas Instruments, explains how to work with I2C in Linux based embedded systems at ELCE 2012. Abstract: Board bring up is one of the most under documented aspects of embedded development. I2C is such a powerful, low-cost, and ubiquitous method of communication, that a basic understanding of it’s usage is essential to the embedded linux developer to quickly bring up and debug embedded designs. This presentation will look at the various software and hardware aspects of working with I2C using simple case studies highlighting the implementation of an EEPROM and a GPIO Expander. Most embedded Linux developers at some point in their career will be handed a piece of hardware that is untested. This presentation intends to provide some information about core tools and methods for bring up of I2C interfaces and assorted I2C based peripheral devices. David Anders has previously presented at Embedded […]