Sailfish OS is a new mobile operating system based on the Qt platform that will soon end-up in mobile phone near you. Until now it was possible to build the SDK yourself, but it was pretty challenging since the documentation was lacking, as Jolla, the company behind Sailfish OS, focused on development. The good news is that you don’t need to build the SDK yourself anymore, since Jolla has just released Sailfish SDK Alpha for Linux 32-bit & 64-bit, and Windows & Mac OS versions will come later. You’ll need a computer that meet the following requirements: A host machine running a Linux operating system Oracle’s VirtualBox version 4.1.18 or higher pre-installed on the host machine. About 5GB of free disk space 4GB of RAM or more is recommended You can get started in two steps: Install the SDK – Download the 32 bit or 64 bit Linux installer. (~650 […]
ISEE Introduces IGEP COM CYGNUS & AQUILA Powered by TI Sitara AM335x Processor
ISEE will officially launch and showcase 2 new computers-on-module at Embedded World 2013 on February 26-28, in Nuremberg, Germany: IGEP COM CYGNUS and IGEP COM AQUILA. Both CoM shares the same characteristics except the former is powered by TI Sitara AM3352 (Cortex A8, no GPU) and the later by TI Sitara AM3354 (Cortex A8 + PowerVR GPU). This makes the CYGNUS suited for cost sensitive applications such as industrial control, home automation, and test and measurement devices, and the AQUILA for applications that requires more advanced graphics and multimedia capabilities such as gaming, auto infotainment and navigation devices. The key specifications of the 2 modules are as follows: Processor – Texas instruments Sitara AM3352 Cortex A8 @ 720 Mhz (CYGNUS) and AM3354 Cortex A8 @ 720 Mhz + PowerVR SGX GPU (AQUALIA) System memory – 256 MB DDR3 SDRAM, 303 MHz, 16-bit Storage – 128 MB SLC NAND FLASH + […]
Final Release of Fedora 18 for AllWinner A10 & A13 Powered Devices
A few months ago, Hans de Goede, currently working at Red Hat and a Fedora contributor, started to show up on linux-sunxi mailing list, and sent a lot of kernel patches for linux-sunxi kernel. Last week-end, he announced “Fedora 18 Final for Allwinner A10 and A13 based devices” on linux-sunxi community mailing list. To install it, first download the image:
|
1 |
wget http://scotland.proximity.on.ca/contrib-images/hansg/Fedora-18-a10-armhfp-r1.img.xz |
And write it to an SD card (all data will be wiped out):
|
1 |
xzcat Fedora-18-a10-armhfp-r1.img.xz > /dev/mmcblk0 |
You may have to replace “/dev/mmcblk0” by your own SD card device, e.g. “/dev/sdc”. AllWinner based devices can share the same kernel, but u-boot is board/products specific, so you’ll have to install u-boot for your board. First remove the SD card, re-insert it in order to automatically mount the FAT partition, and run:
|
1 |
sh <uboot-part-mount>/select-board.sh |
This will show the list of supported boards and products. Then run the command again for your device. For example:
|
1 |
sudo sh <uboot-part-mount>/select-board.sh mk802 |
[…]
Phytec India Unveils “Open Board-AM335x” Development Kit
PHYTEC has launched the Open Board-AM335x development kit in order to support Linux and Android development on Texas Instruments AM335x Sitara ARM Processors in India. The Open Board-AM335x is comprised of a baseboard and phyCORE-AM335x SoM, and comes with 512 MB DDR3 SDRAM, 512 MB NAND Flash, and optionally, 8 MB SPI Flash. The baseboard is open source hardware as schematics and Gerber/BOM are freely available. Here are the key features of Phytec Open Board-AM335x: SoM – PhyCore-AM335x with ARM Cortex-A8 processors @ 720 MHz (AM3352, AM3354, AM3356, AM3357, AM3358 and AM3359) System Memory – 512 MB DDR3 RAM Storage – 512 MB NAND + SD Card slot + 8 MB SPI NOR Flash (Optional) + 32 KB EEPROM (Optional) Serial – 1x UART (RS232) + 4x UART (TTL) USB – 1x USB Host + 1x USB OTG Connectivity – 1x 10/100/1G Ethernet Audio – WM8974 Codec Display Interfaces – 24 bpp TTL […]
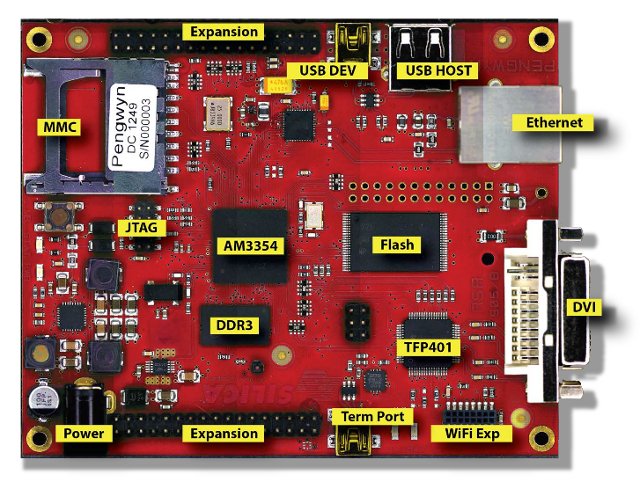
SILICA Pengwyn Low Cost Open Industrial Development Platform Powered by Sitara AM3354 Processor
At the end of January, SILICA, an Avnet subsidiary, announced the Pengwyn, a single board computer based on Texas Instruments Sitara AM3354 Cortex A8 processor. The board targets industrial customers, and the company promotes it as “an open platform to develop applications under Linux or Windows Embedded operating systems”. Here are the specifications of the Pengwyn board: Texas Instruments Sitara AM 3354 ARM Cortex-A8 MCU @ 720 MHz System Memory – 256 MB DDR3 Storage – 1 GB Nand Flash, 32 MB SPI Flash Memory, and microSD slot (if not used with Wi-Fi/Bt modules) Connectivity and expandability USB Host and Device Ports RJ-45 Ethernet Port Connector for optional 1 GB Ethernet Port 2x connectors for generic expansions modules SDIO/MMC Port (can be used for optional WI-FI/bluetooth modules) DVI Display Port Silica will provide Linux (Arago Project, an OpenEmbedded based Distribution) and Windows Embedded Compact 7 BSP and images, as well as […]
$59 pcDuino – AllWinner A10 Board with Arduino Compatible Headers
pcDuino is a new development board based on AllWinner A10 Cortex A8 SoC that comes with 1GB RAM and 2GB NAND Flash, HDMI output, as well as USB and Ethernet RJ45 ports, and is said to feature 2.54mm pin headers compatible with Arduino boards. Here are the pcDuino specifications: SoC – AllWinner A10 ARM Cortex A8 CPU @ 1GHz + Mali-400 GPU System Memory – 1GB DRAM Storage – 2GB Flash + SD card slot for up to 32GB Video Output – HDMI USB – 2x USB 2.0 Host Connectivity: Ethernet – 10/100 Mbps (RJ45) Wi-Fi – Via USB Wi-Fi dongle (not included with the board) Headers – 2.54mm pin headers: 1x UART, 6x ADCs, 2x PWMs up to 24MHz, 14x GPIOs, 1x I2C and 1x SPI. Power Supply – 5V/2A Dimensions – 125mm x 52mm The board comes preloaded with Ubuntu 12.10, but it also supports Android 4.0 ICS. […]
Canonical Unveils Ubuntu on Tablets
Yesterday, Ubuntu.com displayed a time counter for an announcement reading “Tic Toc Tablet Time” that ended being about Ubuntu on Tablets, and not an HTC Tablet running Ubuntu as some blogs speculated, as both companies had a timer counter set to expire at the same time for separate, and unrelated, announcements. The interface looks very much like Ubuntu for Phones with a similar “Welcome Screen”, except multiple users are supported, no icons (except for apps), and you can swipe around the 4 edges to access the dash, opened applications, notifications, and more. Canonical highlights 5 key features for Ubuntu on Tablets: Real multitasking – Run mobile and tablet apps at the same time on the same screen Secure multi-user Voice controlled HUD productivity Edge magic for cleaner apps – As I said previously no buttons, you control eveything from the edges. Content focus – Messages and media are easily accessible […]
Linux 3.8 Release
Linus Torvalds has announced the release of Linux Kernel 3.8: The release got delayed a couple of days because I was waiting for confirmation of a small patch, but hey, we could also say that it was all intentional, and that this is the special “Presidents’ Day Release”. It sounds more planned that way, no? Anyway, the really good news is that things calmed down a lot on the last week. There are noticeably fewer commits, and they are also all quite small. The few commits with more than just a couple of lines tend to be due to a couple of reverts, and two architecture patches where some identifiers got renamed (tile), or some defines got moved from the uapi file to a private header (x86). And there’s one radeon patch that uses a helper function instead of reading bytes directly. And even those “bigger” patches weren’t really that […]