During an investor conference, Qualcomm announced eight new Snapdragon S4 mobile processors: MSM8660A, MSM8260A, MSM8630, MSM8230, MSM8627, MSM8227, APQ8060A and APQ8030. All are using Qualcomm’s Krait CPU architecture. Here’s an excerpt of the press release: NEW YORK – November 16, 2011 – Qualcomm Incorporated announced today the expansion of its Snapdragon S4 class of next-generation mobile processors… The addition of new Snapdragon S4 processors, which are aimed at lowering design, engineering and inventory costs while bringing leading-edge 3G and 4G Internet connection speeds, will allow OEMs to introduce S4-based devices with next-generation mobile architecture throughout their respective device roadmaps-from basic smartphones to high-end smartphones and tablets. The enhanced S4 processors are also optimized for use with a suite of software solutions available from Qualcomm that help enable OEMs to deliver industry-leading feature sets for multimedia, connectivity, camera, display, security, power management, browsing and natural user interface design. The Krait CPU […]
Qualcomm Snapdragon S4: MSM8960
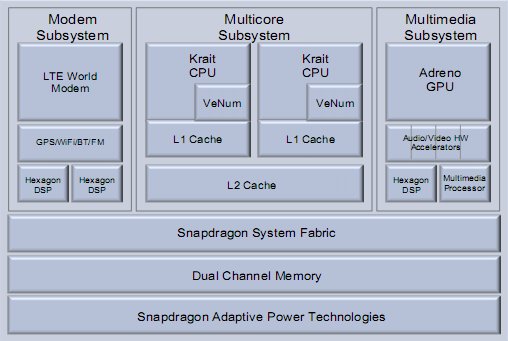
Qualcomm initially announced the Snapdragon S4 is a blog post back in August. They have now released a white paper providing further information on this processor. The Qualcomm Snapdragon S4 (MSM8960) is composed of two Krait CPUs clocked between 1.2 and 1.5 Ghz, an Adreno 225 GPU and a modem subsystem with LTE, GPS, Wifi, Bluetooth and FM support. It will be manufactured using 28nm technology and provide much lower power consumption compared to previous generations. Key features and improvements: New CPU micro-architecture: The Krait CPU offer a 60% performance improvement compared to the scorpion CPU used in previous generations. SIMD/VFP performance: Multimedia instructions (SIMD) and floating point operations have also been improved, but no metrics have been provided. Optimized memory subsystem: Krait includes dual-channel memory. Dual-channel memory is critical in order for the processor to being able to handle the large bandwidth requirements in multicore systems. 25/40% power improvement: […]