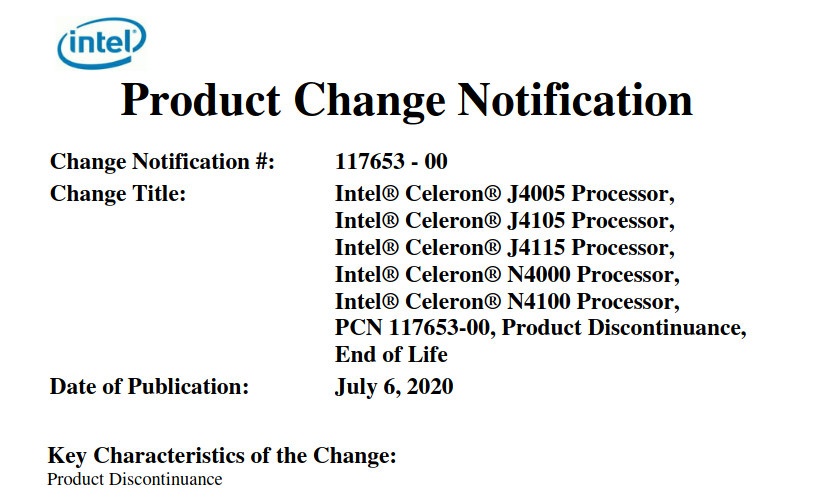
Intel Gemini Lake low power processors based on Goldmont Plus architecture were announced in 2017 as successors of Apollo Lake family with the official launch in 2018 fairly quickly followed by a supply shortage… But the processors have still been used in plenty of sub-$250 mini PCs, and some SBCs like ODROID-H2 or ODYSSEY-X86J4105, as well as a few laptops. More recently, the company announced Gemini Lake Refresh family, but to my surprise, Intel has already issued several product discontinuance notices for the several Gemini Lake (Refresh) processors. Affected Gemini Lake processors include: PCN117653-00 Intel Celeron J4005, J4105, J4115 Intel Celeron N4000, N4100 PCN117657-00 Intel Celeron Processor N4000C Intel Pentium Silver J5005, Intel Pentium Silver N5000 Intel has two end-of-life notifications because the schedule is slightly different: PCN117653-00 Product Discontinuance Program Support Begins: July 6, 2020 Product Discontinuance Demand To Local Intel Representative: October 9, 2020 Last Corporate Assurance Product […]
Intel Launches Core i3/i5 Penta-Core Lakefield Hybrid Processors
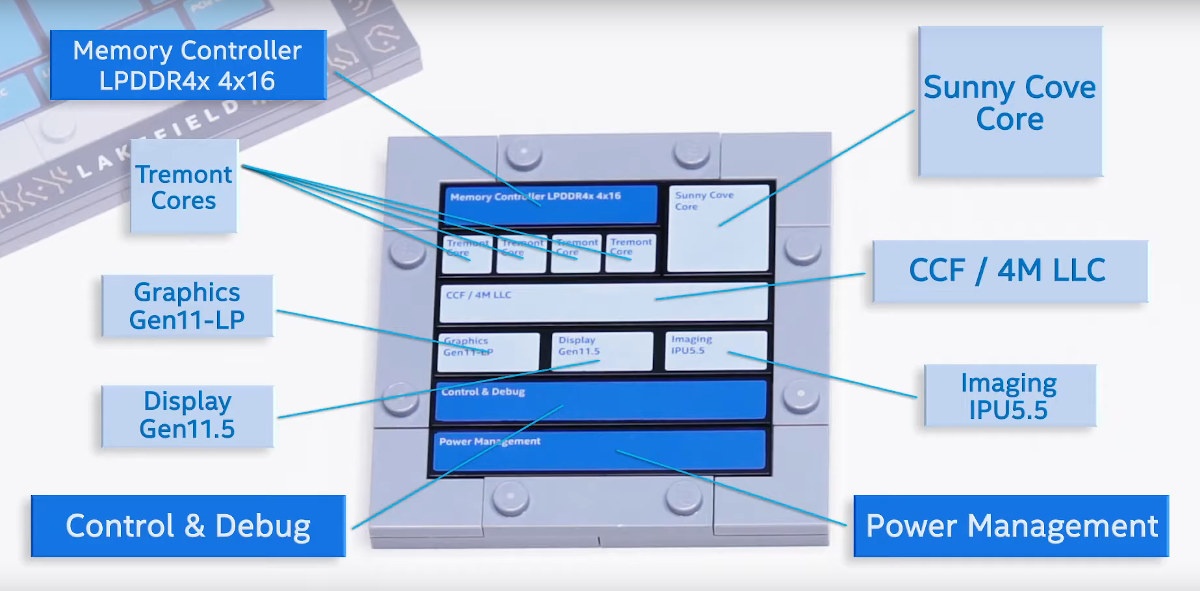
Intel unveiled plans for Lakefield Hybrid processors last year which combined a high-performance Sunny Cove core with four low-power Atom cores using Foveros 3D stacking technology and offering high peak single-thread performance and low power consumption for most tasks in a similar way to Arm’s big.LITTLE or DynamIQ technology. The company has now launched the first two penta-core Lakefield hybrid processors with Core i5-L16G7 and Core i3-L13G4 processors both with a 7W SDP (Scenario Design Power), but no TDP number which makes sense considering the Hybrid nature of the processor. Main features and specifications of the processors: Intel Core i3-L13G4 CPU – 1x high-performance Sunny Cove core @ 800 MHz / 2.8 GHz (Boost), 4x low-power Atom Tremont cores; All-core turbo boost: 1.3 GHz 4 MB Cache GPU – 48EU Intel UHD Graphics Gen11-LP @ 200 / 500 MHz with DX12, OpenGL4.5 API, and up to 4x independent displays Intel […]
Intel Launches Atom Denverton “Refresh” and “Low Power” Server Processors
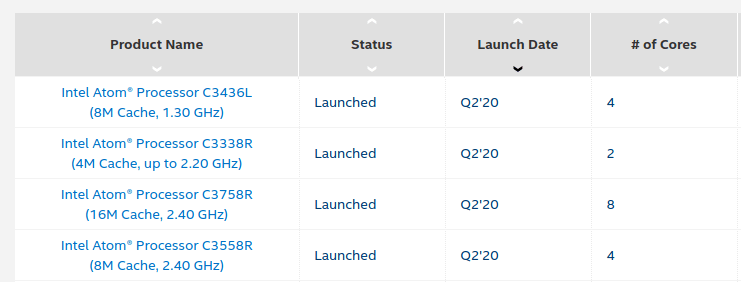
Intel Atom C3000 “Denverton” processors were first unveiled in 2016 for low power servers, and are now found in fanless network appliances and server motherboards. Intel has now quietly launched three new Atom Denverton “Refresh” and one “Low Power” processors, namely Intel Atom C3436L, C3338R, C3758R, and C3558R. Highlights for the “refreshed” and current processors: Intel Atom C3436L quad-core processor @ 1.3 GHz with 8MB cache, 10.75W TDP Intel Atom C3338R dual-core processor @ 1.8 GHz / 2.2 GHz (Turbo) with 4MB cache, 10.5W TDP Intel Atom C3558R quad-core processor @ 2.4 GHz with 8MB cache, 17W TDP Intel Atom C3758R octa-core processor @ 2.4 GHz with 16MB cache, 26W TDP Intel Atom C3338 dual-core processor @ 1.5 GHz . 2.2 GHz (Turbo) with 4MB cache, 8.5W TDP Intel Atom C3558 quad-core processor @ 2.2 GHz with 8MB cache, 16W TDP Intel Atom C3758 octa-core processor @ 2.2 GHz with […]
Updated x86/x64 Software Optimization Manual Reveals More Intel Tremont Details
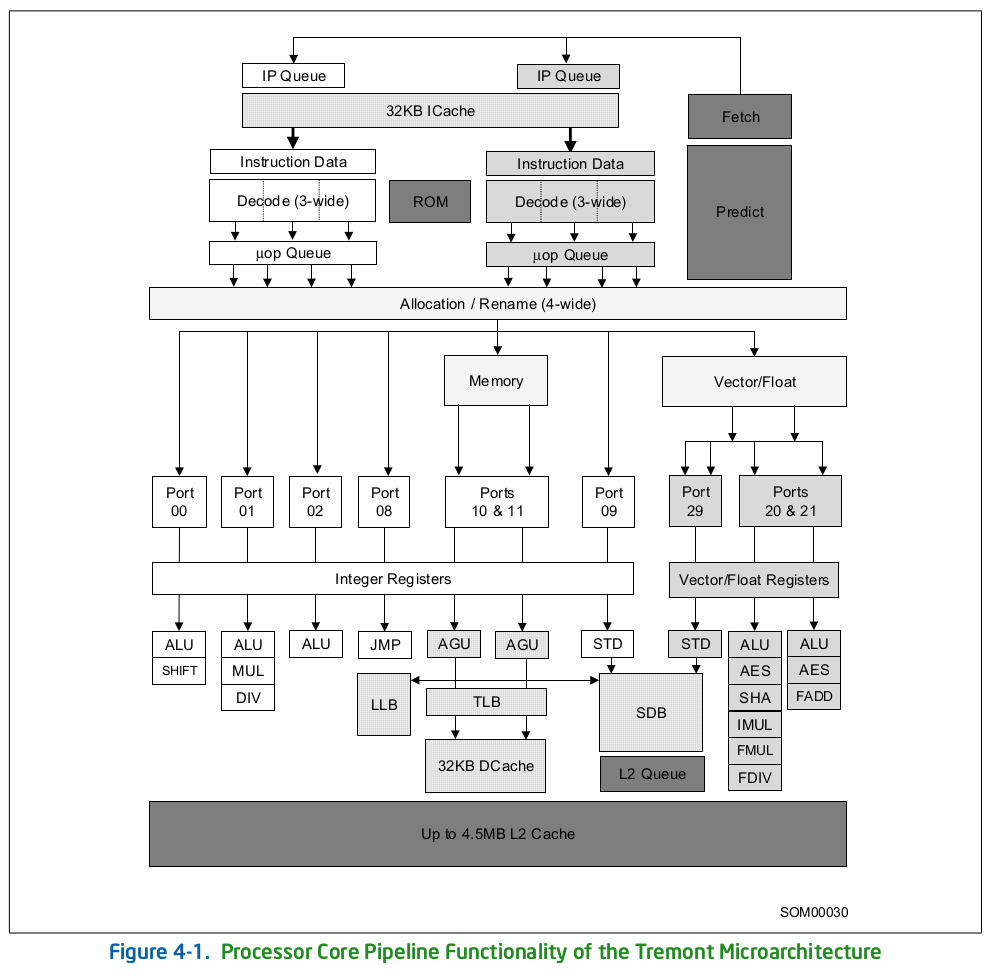
We first found out about Tremont microarchitecture in April 2018 in some Intel documents and Linux mainline source showing it was likely meant to be Goldmont Plus successor. Last year, Intel formally announced Tremont architecture providing some of the details with a block diagram and key features. But this morning, we were informed by email of a new revision of the x86/x64 Software Optimization Manual (PDF) with even further details about Tremont architecture. If you want to know all the details, jump to 4.1 Tremont Architecture section of the document, but here are some of the highlights / improvements over Golmond Plus microarchitecture: Enhanced branch prediction unit. Increased capacity with improved path-based conditional and indirect prediction. New committed Return Stack Buffer. Clustered 6-wide out-of-order front-end fetch and decode pipeline. Banked ICache with dual 16B reads. Two 3-wide decode clusters enabling up to 6 instructions per cycle. Deeper back-end out-of-order windows. […]
Intel Launches 15W to 125W Comet Lake VPro Processors for Enterprise Customers
Last week, we covered AMD Ryzen PRO 4000 processors with 15W TDP targeting ultra-thin business laptops with PRO features such as security, manageability, reliability, and longevity which are needed by enterprise customers. AMD compared the performance of their new processors to Intel Comet Lake processors without PRO features, but Intel has now just announced several Comet Lake processors with Intel VPro, including three 15W parts aims at the same markets as AMD Ryzen PRO 4000 processors. Liliputing has the full list of the about 40 parts that range from 15W to 125W Comet Lake Core VPro SoCs for mobile and desktop use to Comet Lake Xeon processors for workstations, but I’ll focus on the three 15W processors here: Core i5-10310U quad-core/octa-thread processor @ 1.7 GHz / 4.4 GHz (Turbo) with 6MB cache, 24EU Intel UHD Graphics; TPD down: 10W, TDP up: 25W Core i7-10610U quad-core/octa-thread processor @ 1.8 GHz / […]
Intel Atom P5900 “Snow Ridge” Processor to Power 5G Base Stations
Intel may have given up on developing 5G modems for mobile devices, but the company will still be participating in the ramping up of 5G technology by focusing on 5G infrastructure instead. So the company has just introduced the Atom P5900 “Snow Rigde” processor family designed for 5G wireless base stations requiring “high throughput, low latency processing for high-density network edge and security solutions”. The 10nm chips are offered with 8 to 24 cores based on the Tremont micro-architecture. There are four Atom P5900 “Snow Ridge” processors so far: Intel Atom P5921B 8-core processor @ 2.20 GHz with 9MB cache Intel Atom P5931B 12-core processor @ 2.20 GHz with 13.5MB cache Intel Atom P5942B 16-core processor @ 2.20 GHz with 18MB cache Intel Atom P5962B 24-core processor @ 2.20 GHz with 27MB cache P5912B supports up to 64GB ECC DDR4 memory, and other parts can handle up to 128GB RAM. […]
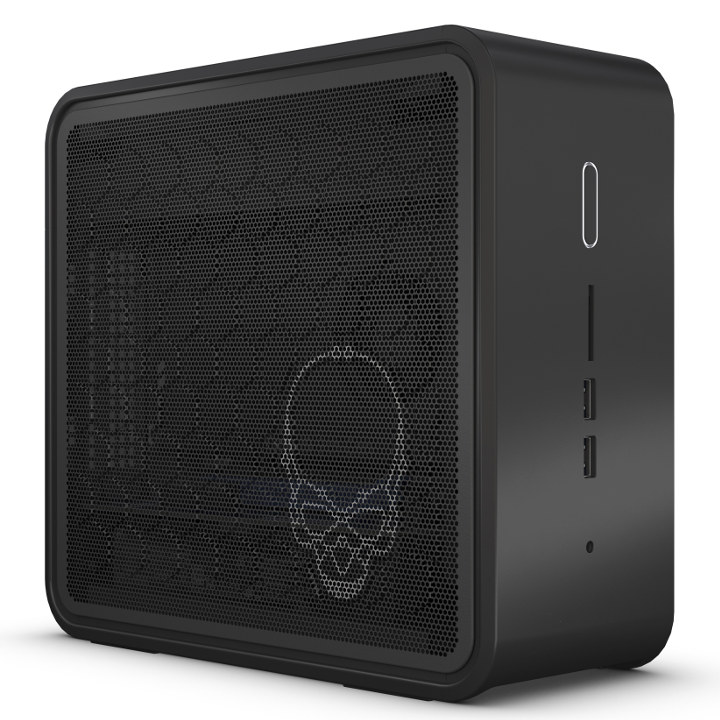
Introducing the Intel NUC 9 Compute Elements, Mini PC Kits, and 3rd-Party Ecosystem
Intel’s NUC mini PC range is familiar to anyone who has looked for a very small compact and functional PC. But they, and similarly sized mini PCs in general, have a notable limitation when compared to desktops and also many high-end laptops in that the graphics performance is somewhat restricted because it is typically provided by the processor’s integrated graphics. Whilst these integrated graphics are suitable for browsing, video playback, and the office style applications that the devices have been marketed towards, they are normally insufficient for gaming as only low framerates are obtainable. Intel initially tried to address this gaming shortfall through the introduction of the Intel Skull Canyon (NUC6i7KYK) NUC which came with a 6th-gen Skylake Core i7-6770HQ that included Iris Pro Graphics 580 and at the time with their 72 EUs (Executions Units) was Intel’s most powerful integrated GPU. Additionally, the Skull Canyon also featured a (USB-C) […]
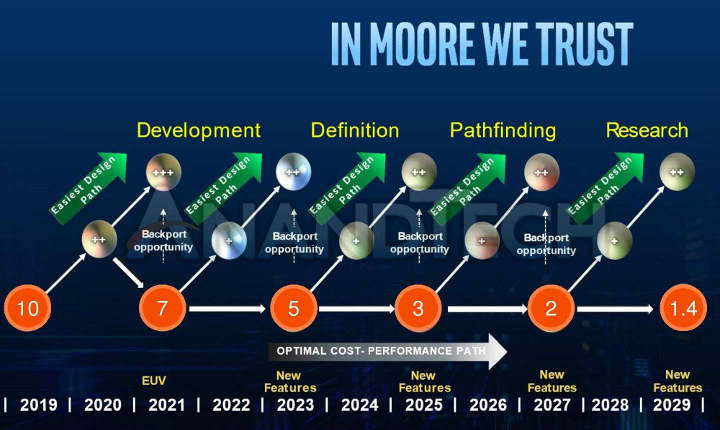
Intel Roadmap 2019-2029 – 1.4 nm Processors Expected within 10 Years
A roadmap from a slide by ASML presented at the IEDM conference recently shared on Anandtech shows Intel Roadmap for the next ten years with 7nm manufacturing process expected in 2021, 5nm in 2023, 3nm in 2025, 2nm in 2027, and 1.4nm in 2029. Intel did however contact Anandtech to explain the slide from ASML is a modified version of the Intel slide shown below that does not show actual process nodes, only the dates. I suppose Intel does not want to make any commitments seeing how their 10nm technology suffered delays after delays, and in any case the actual dimensions of the process may vary by that time frame depending on difficulties or new discoveries made. Both slides mention +, ++, and backport opportunities for all new processes. + and ++ are just iterative improvements for the current process, while back- porting is the option to port a process […]