The Embedded Linux Conference & IoT summit 2017 took place in the US earlier this year in February, but there will soon be a similar event with the Embedded Linux Conference *& Open Source Summit Europe 2017 to take up in Europe on October 23 – 25 in Prague, Czech Republic, and the Linux Foundation has just published the schedule. It’s always useful to find out what is being discussed during such events, even if you are not going to attend, so I went through the different sessions, and compose my own virtual schedule with some of the ones I find the most interesting. Monday, October 23 11:15 – 11:55 – An Introduction to SPI-NOR Subsystem – Vignesh Raghavendra, Texas Instruments India Modern day embedded systems have dedicated SPI controllers to support NOR flashes. They have many hardware level features to increase the ease and efficiency of accessing SPI NOR […]
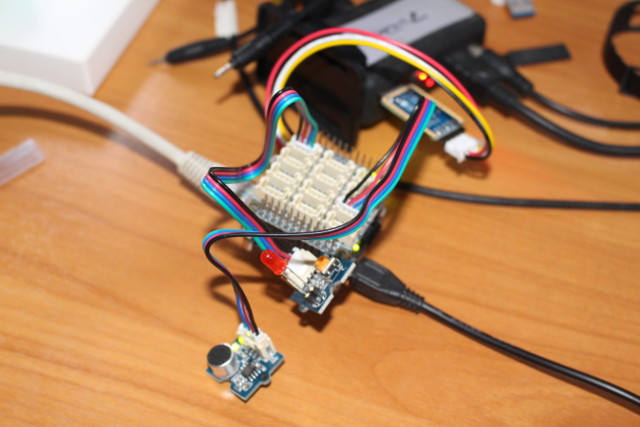
Using GPIOs on NanoPi NEO 2 Board with BakeBit Starter Kit
NanoPi NEO 2 is a tiny 64-bit ARM development board powered by Allwinner H5 processor. FriendlyELEC sent me a couple of NEO 2 samples together with their BakeBit Start Kit with a NanoHat and various modules via GPIOs, analog input or I2C. I’ve already tested both Armbian with Linux 4.11 and Ubuntu Core Qt with Linux 3.10, and ran a few benchmarks on NanoPi NEO 2. You would normally prefer to use the Armbian image with Linux mainline since it provided better performance, but at the time I was told GPIO support was not there. Configuring NanoPi NEO 2 board with BakeBit library So this week-end, when I decided to test GPIO support and BakeBit Starter Kit, I decided to follow this advice, especially nanopi-neo2-ubuntu-core-qte-sd4g-20170329.img.zip image is still the recommended one in the Wiki. So I went with that image. I’ll use Python examples from Bakebit library, but if you […]
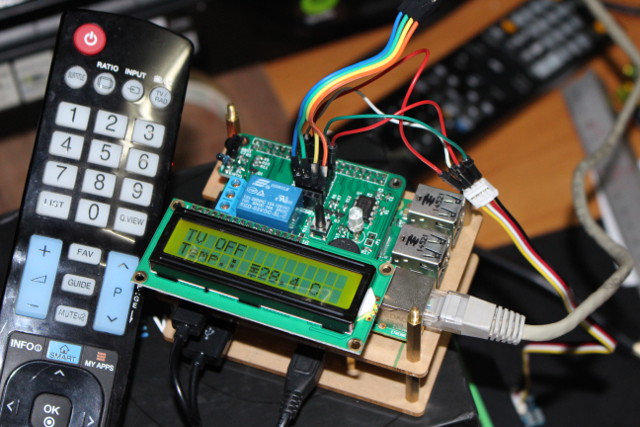
Getting Started with RabbitMax Flex IoT and Automation Hat for Raspberry Pi
At the beginning of the month I showed how to assemble RabbitMax Flex, a Raspberry Pi HAT compliant add-on board for Raspberry Pi boards with 40-pin header, that targets IoT and home automation project with its relay, IR transmitter and receiver, I2C headers for sensors, buzzer, RGB LED, and more. Since I’ve already described the hardware, I’ve spend some time this week-end following the user’s guide to play around with the board using a Raspberry Pi 2 board, and try various features. The user’s manual explains that you need the latest version of Raspbian, but I’d not played with my Raspberry Pi 2 board for a while, so the kernel and firmware were quite old:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
uname -a Linux raspberrypi 4.1.7-v7+ #817 SMP PREEMPT Sat Sep 19 15:32:00 BST 2015 armv7l GNU/Linux pi@raspberrypi ~ $ /opt/vc/bin/vcgencmd version Sep 23 2015 12:12:01 Copyright (c) 2012 Broadcom version c156d00b148c30a3ba28ec376c9c01e95a77d6d5 (clean) (release) |
So the first thing I had to do was to upgrade Raspbian. There are basically two options to upgrade, either downloading and dumping the latest Raspbian firmware image to your micro SD card, and […]
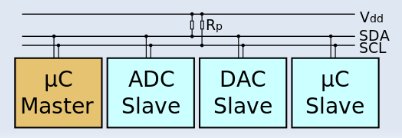
Board Bringup: You, Me, and I2C – ELCE 2012
David Anders, embedded systems developer at Texas Instruments, explains how to work with I2C in Linux based embedded systems at ELCE 2012. Abstract: Board bring up is one of the most under documented aspects of embedded development. I2C is such a powerful, low-cost, and ubiquitous method of communication, that a basic understanding of it’s usage is essential to the embedded linux developer to quickly bring up and debug embedded designs. This presentation will look at the various software and hardware aspects of working with I2C using simple case studies highlighting the implementation of an EEPROM and a GPIO Expander. Most embedded Linux developers at some point in their career will be handed a piece of hardware that is untested. This presentation intends to provide some information about core tools and methods for bring up of I2C interfaces and assorted I2C based peripheral devices. David Anders has previously presented at Embedded […]