I bought ThL W200 last year as my main (and only) phone, and my review was rather positive, because after testing the phone for a week or so I did not encounter some of the issues. After a short while I found GPS was not working very reliably, so I had to find instructions to fix GPS on Mediatek phones, then the first battery died after about 8 months, maybe that’s normal for my usage, but I was expecting it to last longer. Finally, after a while both front and rear cameras started to have issues such as green screen, color lines, or simply refusing to work with the message: “can’t connect to camera”. In all of this the good news (for me) was I was not alone, and I saw some instructions saying, you had to terminate the camera app, clear all data, and restart the phones. It seemed […]
How to Upgrade Allwinner A80 OptimusBoard Firmware
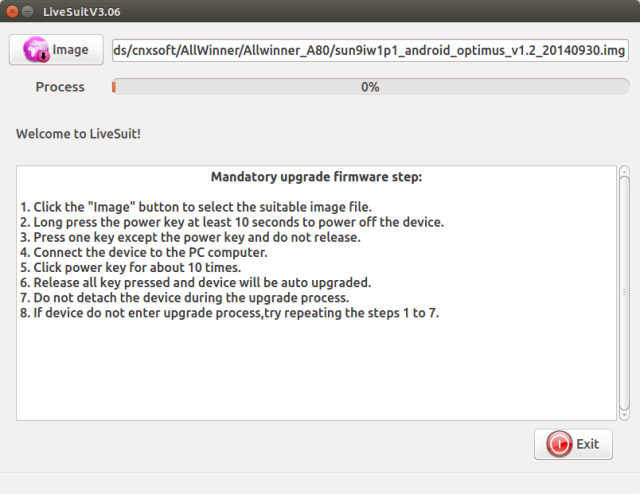
After informing Allwinner I had some rather slow write speed (3MB/s) to the NTFS partition of my USB drive on my A80 OptimusBoard, they kindly provided a new compressed Android firmware image (sun9iw1p1_android_optimus_v1.2_20140930.img.7z) with some NTFS optimizations that can be downloaded from baidu (password: x2tz), mega.co.nz or simos.info (please only use this link, if the other two do not work as it’s a private website and monthly bandwidth may be limited). I vaguely remember tools like LiveSuit (Linux) or PhoenixSuite (Windows), and I ended up on sunxi-linux Livesuit wiki as I’m running Ubuntu 14.04 on my PC, but you should be able to flash the firmware with PhoenixSuite if you run Windows. The instructions below can also be used for other Allwinner based devices. First you need to install LiveSuit, and build Allwinner USB drivers as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
sudo apt-get install dkms git build-essential git clone https://github.com/linux-sunxi/sunxi-livesuite.git cd sunxi-livesuite/awusb make sudo cp awusb.ko /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/ sudo depmod -a sudo modprobe awusb cd.. |
In order to use LiveSuit as a normal user, you also have […]
Test Your 4K Device True Resolution With a 4K UHD / 2160p Video Test Pattern
Now many products are sold on the market advertising 4K video output, but how to test and check if it just a lie with only part of the system support 4K (e.g. physical video output), but the rest of the system makes you lose quality? When I worked on DVD players, we had some special DVDs with video pattern allowing us to test different video quality. You can read about different video test patterns in “AVSHD 709 DVD document“. There are also some expensive equipments such as DVDO AVLab TPG – 4K Test Pattern Generator that generate test patterns to calibrate video equipments, but if all we want to do is to check the resolution has not been tempered with there must be a cheaper and easier way. After having a discussion about this issue on Google+, Dan Car decided to create a 2160p (3840×2160) test pattern image with some […]
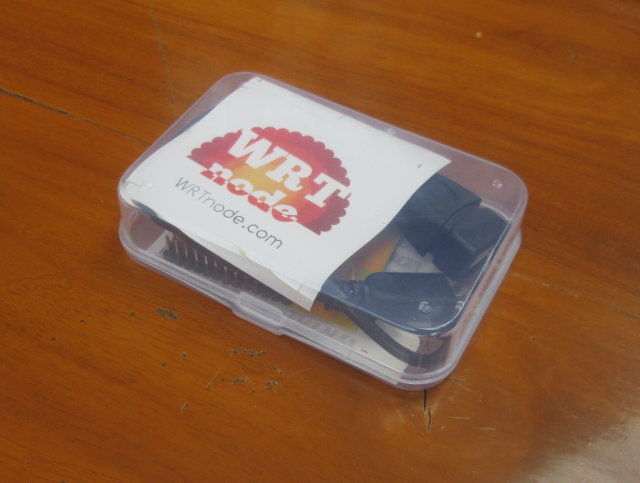
Getting Started with WRTnode OpenWRT Development Board
Seeed Studio sent me two nice little boards that can be used for IoT development: WRTNode and LinkIt ONE. Today, I’ll show pictures of WRTNode and accessories, and go through the “starting guide“, and will test LinkIt ONE board a few days later. WRTnode Unboxing I’ve received WRTnode by Fedex, and the board is stored in a plastic box. Inside the box, you’ll find the board, a “special” USB used to power the board and as an OTG adapter, a piece of paper with useful links (Wiki), and some WRTnode stickers. Any micro USB to USB cable can be used to power the board, but this cable is useless to connect USB devices such as flash drives, webcams (OpenCV is supported), Bluetooth dongles, and so on. You could even connect a USB hub to connect multiple USB devices as shown below. I’ve also taken a picture of both sides of […]
Creating and Flashing an Android Image from Rockchip RK3288 SDK
Following up on my post explaining how to build Android for RK3288 TV box, I’ve generated a firmware image, and flashed it to Tronsmart Orion R28 Meta TV box to see if it could boot properly. There’s basically no information in the Andoird SDK explaining how to do basic things like building from source, and generating and flashing the resulting image, so I’d like to thanks Linuxium, Droidmote and Naobsd for their various tips. Since I’ve built everything from source, I’m using a Linux machine, but you should be able to create and flash the Android image in Windows using tools in RKTools/windows folder. First let’s copy the required, and freshly built, files to create the firmware:
|
1 2 3 4 |
cp rockdev/Image-rk3288/* RKTools/linux/Linux_Upgrade_Tool_v1.2/rockdev/Image/ cp RKTools/rk3288-3.10-uboot-data1G.parameter.txt RKTools/linux/Linux_Upgrade_Tool_v1.2/rockdev/parameter cp RKTools/bootloader/uboot-emmc/RK3288Loader_uboot_Apr212014_134842.bin RKTools/linux/Linux_Upgrade_Tool_v1.2/rockdev/ cd RKTools/linux/Linux_Upgrade_Tool_v1.2/rockdev/ |
We’ll also need to edit package-file follows (I only had to change the bootloader field):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# NAME Relative path # #HWDEF HWDEF package-file package-file bootloader RK3288Loader_uboot_Apr212014_134842.bin parameter parameter misc Image/misc.img kernel Image/kernel.img boot Image/boot.img recovery Image/recovery.img system Image/system.img backup RESERVED #update-script update-script #recover-script recover-script |
And now create the firmware file:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
./mkupdate start to make update.img... Android Firmware Package Tool v1.0 ------ PACKAGE ------ Add file: ./package-file Add file: ./RK3288Loader_uboot_Apr212014_134842.bin Add file: ./parameter Add file: ./Image/misc.img Add file: ./Image/kernel.img Add file: ./Image/boot.img Add file: ./Image/recovery.img Add file: ./Image/system.img Add CRC... Make firmware OK! ------ OK ------ ********RKImageMaker ver 1.61******** Generating new image, please wait... Writing head info... Writing boot file... Writing firmware... Generating MD5 data... MD5 data generated successfully! New image generated successfully! Making update.img OK. Press any key to quit: |
The firmware file update.img can be flashed with upgrade_tool […]
How to Build Android 4.4 for Rockchip RK3288 Devices (Tronsmart Orion R28)
After blowing up my ATX power supply, and learning such things as “FULL” power supplies do exists, I finally managed to build Android for Tronsmart Orion R28 using the provided SDK. I haven’t tried to load it on the device yet, but the build could complete successfully after following the steps below in Ubuntu 14.04. The SDK is probably not specific to one device, so it might just also work on other RK3288 TV boxes and tablets. First download Android 4.4 SDK for RK3288, or use the one in the micro SD card provided with the Beta version of R28 Pro and Meta. Install some dependencies:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
sudo apt-get install git-core gnupg flex bison gperf libsdl1.2-dev libesd0-dev libwxgtk2.8-dev \ squashfs-tools build-essential zip curl libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev pngcrush schedtool libxml2 \ libxml2-utils xsltproc lzop libc6-dev schedtool g++-multilib lib32z1-dev lib32ncurses5-dev \ lib32readline-gplv2-dev gcc-multilib libswitch-perl gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi lzop libncurses5-dev \ libssl1.0.0 libssl-dev |
Extract the SDK:
|
1 |
tar xvf Orion_R28_SDK_doc.tar.gz |
And build the kernel first: Enter the kernel directory:
|
1 |
cd RK3288_R-BOX_ANDROID4.4.2-SDK_V1.0.0/kernel/ |
Change arch/arm/boot/dts/Makefile to use RK3288 device tree file instead of an RK3188 (may not be needed, but the build failed for me without that change…):
|
1 |
dtb-$(CONFIG_ARCH_ROCKCHIP) += rk3288-box.dtb |
It’s also quite […]
Rockchip RK3288 Android 4.4.2 SDK and Schematics Released for Firefly Board
Firefly-RK3288 development board was first announced in July. I still don’t have news about availability nor pricing, but the T-Firefly website launched yesterday. They seem do have a nice Wiki, but unfortunately everything is currently in Chinese, except when you go to the download page. You’ll find firmware upgrade_tool for Linux and Windows, the USB drivers for rooting and firmware update, firmware images (Android 4.4.2, Ubuntu 14.04, and dual boot), the board schematics (PDF), and Android KitKat 4.4.2 SDK with U-Boot, Linux, and Android source code, some documentation, XBMC apk (no source) with H.265 hardware decode support for MP4, MOV and MKV container formats. The SDK is available on Bitbucket. I planned to test it, but unfortunately my network connection is very slow (and unstable) to this server, and I failed to retrieve it with git clone. The company also posted the build instructions in Chinese in their website, but […]
Linux (Enlightenment and Lubuntu) in WeTek Play Amlogic TV Box
Last week I reviewed WeTek Play, a TV box with two DVB-S2 tuners, powered by Amlogic AML8726-MX dual core ARM Cortex A9 processor, and running Android 4.2, but the company also released several Linux based images including one with Enlightenment window manager, and another, temporary one, with Ubuntu core which allows you to install Lubuntu or Xubuntu with apt-get. There are also working on OpenELEC, but have not released the binary yet. Today, I’ll try the Enlightenment image because it also supports hardware video decoding via Gplay (gstreamer), and show how to install Lubuntu. The instructions below have been done in a computer running Ubuntu 14.04, but a Windows computer can also be used. Download Wetek-Linux.img.bz2 Connect a micro SD card to your computer, extract and flash Wetek-Linux.img: In Linux using a terminal window:
|
1 2 3 |
bzip2 -d Wetek-LInux.img.bz2 sudo dd if=Wetek-Linux.img of=/dev/sdd bs=1M sync |
In Windows, extract the image, and use Win32DiskImager to copy the image to your micro SD […]