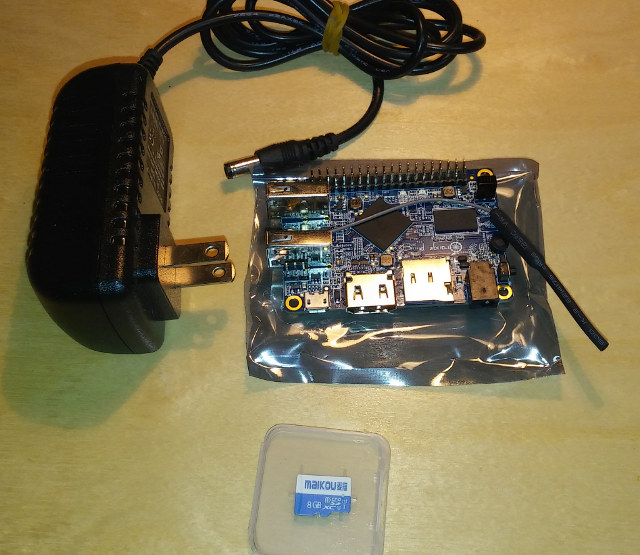
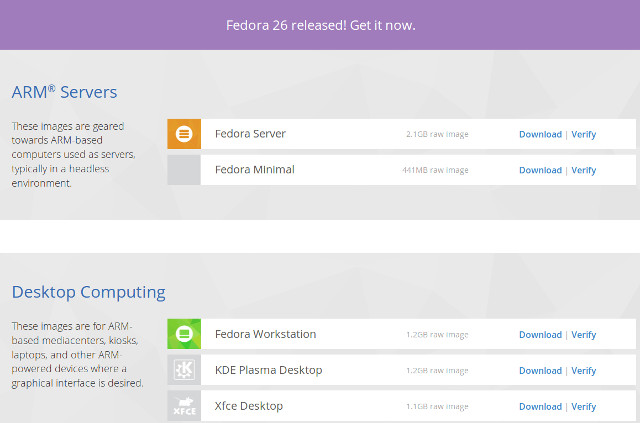
The decision to use device tree in Linux occurred several years ago, after Linus Torvalds complained that Linux on ARM was a mess, with the ultimate goal of providing a unified ARM kernel for all hardware. Most machine specific board files in arch/arm/mach-xxx/ are now gone from the Linux kernel, being replaced by device tree files, and in many case you simply need to replace the DTB (Device Tree Binary) file from an operating system to run on different hardware platforms. However, this is not always that easy as U-boot still often differ between boards / devices, so it’s quite frequent to distribute different firmware / OS images per board. Fedora has taken another approach, as the developers are instead distributing a single Fedora 26 OS ARMv7 image, together with an installation script. Images for 64-bit ARM (Aarch64) are a little different since they are designed for SBSA compliant servers, so […]
ROCK64 Board Review – Part 2: Quick Start Guide with Ubuntu 16.04.3 MATE, Multimedia Features, Some Benchmarks
Pine64 ROCK64 is the first maker board based on Rockchip RK3328 processor, and is potentially interesting for various applications including network storage thanks to USB 3.0 and Gigabit Ethernet, multimedia applications with 4K HDR video support, as well as other applications requiring I/Os. I’ve already tested Rock64 board with Android 7.1 operating system, so today I’ll report by finding and experience with Ubuntu 16.04.3 with MATE desktop. Selecting and Flashing a Linux Image You’ll find several operating systems in the Wiki, but you’ll also find more cutting edge images in ayufan’s github. But first let me explain some vocabulary used for Pine64 firmware files: Engineering version – Becomes with release build based on the stock build develop by Pine64 and the SoC vendor. It’s supposed to be more stable, but get less updates Community versions (currently managed via ayufan) are more frequently updates, and comes with more recent features. You’ll find […]
How to Setup an Orange Pi Zero DIY Smart Speaker with Google Assistant SDK
A preview release of Google Assistant SDK working with Raspberry Pi 3 and other ARMv7 boards was released in May, and soon after, AIY Projects Voice Kit was offered for free with Raspberry Pi Magazine in order to a complete smart speaker kit working with RPi 3. I wanted to try it on one of FriendlyELEC or Shenzhen Xunlong Allwinner board, since all we need is audio input and output, and an Internet connection. Earlier this month, I came across Orange Pi Zero Set 6 Kit that had all I needed: Orange Pi Zero ARM Linux board, an expansion board with built-in microphone and audio output jack, and a cute and small case to neatly put everything together. Orange Pi Zero Set 6 Kit Unboxing and Assembly Shenzhen Xunlong sent me the kit so that I can try it out. The package includes two Orange Pi packages, the plastic case, […]
Running Ubuntu 16.04 on MeLE PCG03 Apo Mini PC
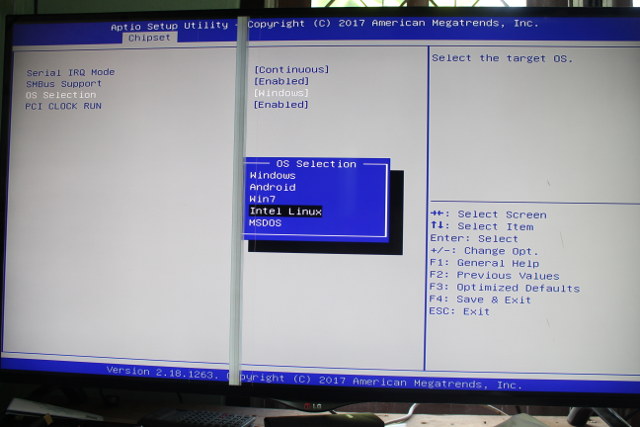
I completed my review of MeLE PCG03 Apo mini PC with Windows 10 about two weeks ago, and at the time when I tried Ubuntu, all I got was a black screen. MeLE said they would release an Ubuntu image for the board soon, so I did not investigate further. The company has now released Ubuntu 16.04 Desktop ISO via a link on Twitter together with (partial) instructions, and the company told me another company had worked on the image. I sent the link to Linuxium, as in the past MeLE or that other company used his work without asking. I turns out the ISO was identical to Ubuntu 16.04 Desktop ISO released in April last year.
|
1 2 |
linuxium@LINUXIUMONE:~/Downloads$ cmp -l ubuntu-16.04-desktop-amd64.iso.mele ubuntu-16.04-desktop-amd64.iso.canonical linuxium@LINUXIUMONE:~/Downloads$ |
Anyway, I still got the black screen issue using that image, and that’s because I first failed to find the option in the BIOS to change boot to Linux. When the mini […]
Getting Started with MediaTek X20 Android Development Board
Thanks to CNX for helping me get a hand on the 96Boards compliant Mediatek X20 board that was generously donated by Seeed Studio. In this article, I will walk through the steps to get the board up and running and also compile Android from the source code. The current Android is version 6. Unboxing the Beast First Boot Up The board boots up from the eMMC, and the first time you boot up you will get Android screen as shown in Figure-9. This is the default Android image from the factory, which surprisingly looks like it was setup for a phone screen mode, which is not sufficient for a HDMI monitor. It would be better to install the images that are made available at Linaro website or build your own. See the other section to flash the board with different images. Switching to Fastboot Mode Flashing image files are done […]
Tevo Tarantula 3D Printer’s Large Dual Extruder Auto Bed Level Sensor Firmware Upgrade
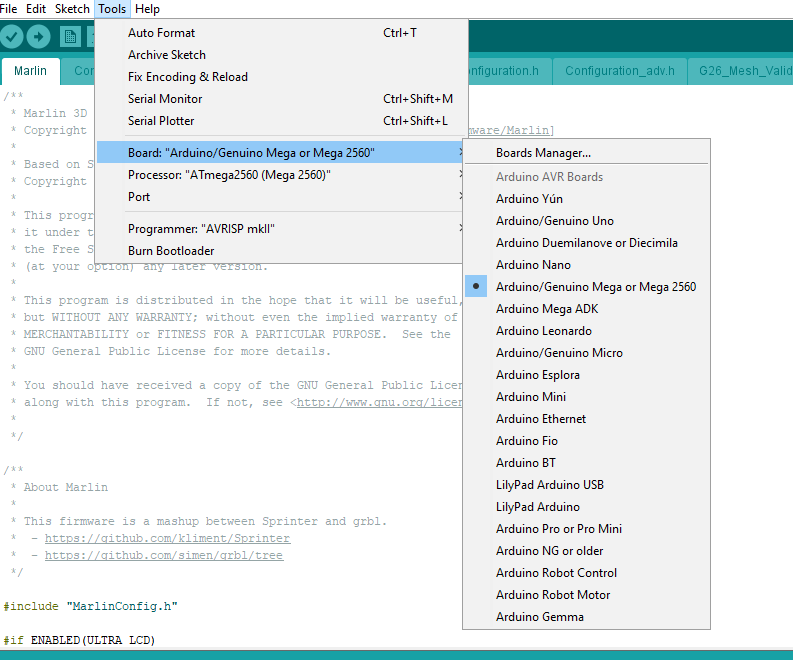
What a title. Just a quick update on the Tevo I am reviewing. I didn’t want to upgrade the firmware, but I read so many posts on Facebook about it I took the plunge. I didn’t like was the firmware that came with it. It only did a 3 point level, and seemed to go outside the build plate dimensions. The first 2 printers I have reviewed were Marlin, so it was what I am most familiar with. I used Jim Brown’s Marlin fork as a base. It was missing dual extruder and auto level sensor in the pre-configured profiles. It took a while, but I was able to add the extra features. The auto bed level sensor connects to where the normal Z end stop sensor is connected. I would like to warn you to warm your bed for 5 minutes for the best reproducible results. I tested several […]
How to Use Octoprint on Orange Pi Lite Board, Amlogic S905X and S912 TV Boxes
Karl here. This was article originally going to be how to setup Octoprint 3D printer server on an Orange Pi Lite. But after looking and running through the instructions it seemed like it would be too much so I created an img to simplify things. I also explored running Octoprint on an Amlogic S905x or S912 device and it turned out to be an even better solution. You get a case, power supply, and eMMC flash storage. What is Octoprint? I use Octoprint mainly for its ability to start and stop prints without having to use an sd card. Time lapse is also a nice feature. And one last thing is that I setup a pushbullet notification when it is complete. For a full list of features check out http://octoprint.org/. What is needed? Orange Pi Lite board provided by GearBest for the article, or an Amlogic S905X or S912 Android […]
How to Install RKMC “Kodi for Rockchip” App in your TV Box
I’ve started playing with Vorke Z3, an Android 6.0 TV box based on Rockchip RK3399 , and saying that Kodi 17.3 – installed from the Google Play Store – is not working so well is an understatement. The other Rockchip TV boxes I’ve recently reviewed with Android 6.0.1 such as Yundoo Y8 and A95X R2 are all using TVMC, a fork of Kodi 16.1 specifically designed for Rockchip devices. However, there’s no source code for that app, but a Rockchip engineer is maintaining his own fork of Kodi, with the code and some binaries libraries released on Github. The project is called RKMC. I did install the app, but I misunderstood part of the instructions at first, and the device would not boot anymore. I lost many hours of work, as I had to reflash the firmware. So I’ll show how I installed it in Vorke Z3 TV box. You […]