Koogeek BP2 is an FDA approved smart blood pressure monitor that connects over Bluetooth to your Android or iOS smartphone, or WiFi to the cloud. The company sent me a sample for evaluation, so let’s get started right away. Koogeek BP2 Unboxing The device is sent in a cardboard package with Koogeek brand… and some more derails about the specifications on the bottom of the package. I asked the company to confirm about FDA approval, and they told me to look for K134029 on the FDA website, which lead me to this document testing Shenzhen Belter Health Management and Analysis ePA-46B, and comparing it to the results of Omron HEM-7200-Z (BP742) with the conclusion being that: The Belter Blood pressure meter (ePA-46B) is substantially equivalent to the predicate devices. Koogeek BP2 is the same as Belter ePA-46B, but just rebranded, and with a different mobile app. In the package will find […]
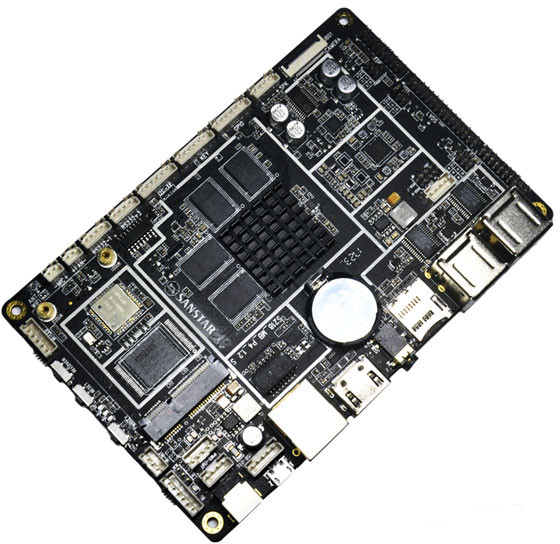
SanStar WS-3A Medical Board Runs Android 5.1 on Rockchip RK3288 SoC
Warp United, a “Chinese Health 2.0″/point-of-Care medical technology company based in Shenzhen, launched Warp 3 medical recorder – an Android powered handheld device supporting various vital signs and ultrasound medical modules – earlier this year, and the company has now just introduced SanStar WS-3A motherboard powered by Rockchip RK3288 quad core Cortex-A17 SoC, and running Android 5.1 in order to allow engineers to develop and connect their own medical modules via the various interfaces of the board, and create their own medical products. SanStar WS-3A medical motherboard specifications: SoC – Rockchip RK3288 quad core Cortex-A17 processor @ 1.8GHz with an ARM Mali-T764 GPU with support for OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0 /3.0, OpenVG1.1, OpenCL, Directx11 System Memory – 2GB or 4GB DDR3 Storage – 8GB, 16GB, or 32GB eMMC flash, micro SD slot up to 32GB Video Output / Display I/F HDMI 2.0 up to 3840 x 2160 pixel embedded DisplayPort (eDP) […]
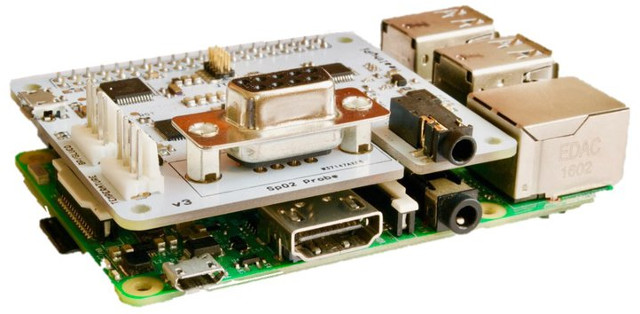
HealthyPi Raspberry Pi HAT Measures ECG, Body Temperature, and Oxygen Saturation (Crowdfunding)
Bangalore based ProtonCentral has launched the third version of Healthy Pi, a vital sign monitor using the Raspberry Pi as its computing and display platform, and capable of measuring body temperature, oxygen saturation, and ECG/respiratory data. Healthy Piv3 board specifications: MCU – Atmel ATSAMD21 ARM Cortex M0 MCU, compatible with Arduino Zero Vital Signs Chips ECG and respiration front-end – TI ADS1292R 24-bit analog front-end with SNR of 107 dB Pulse oximetry – TI AFE4490 Pulse Oximetry front-end with integrated LED driver and 22-bit ADC Temperature – Maxim MAX30205 digital body temperature sensor for skin temperature sensing Expansions Headers and Ports 1x 40-pin header to connect to Raspberry Pi 2x 3-pin connectors for temperature and BP/GLUCO DB9 connector for finger-clip Spo2 probe 3.5mm jack for ECG cable and probes 1x UART connector for an external blood pressure module USB – 1x micro USB port for power and programming Debugging – […]
Samsung S-Patch3 Wearable Health Tracker Based on Samsung Bio-Processor Hits the FCC
At the end of 2015, Samsung unveiled their S3FBP5A Bio-Processor comprised of an ARM Cortex-M4 MCU, a DSP, and sensors for PPG, ECG (electrocardiography), Skin temperature, BIA, and GSR to have a single package to design tracker able to monitor your health condition. The company demonstrated an early prototype called S-Patch at CES 2016 (See embedded video at the end of this post), and now S-Patch3 wearable health monitoring system has just hit the FCC. The system has two round shapes case connected via a cable, with one for the battery compartment, and the other containing the Bio Processors, and meant to be placed on your chest. The device can then synchronize the data with your smartphone in real-time over Bluetooth. People with heart conditions may benefit from the system, as if they wish to do so, they could share the data with their doctor. Few documents are publicly available […]
$100 Xiaomi “90 Minutes Ultra Smart Running Shoes” are Equipped with Intel Curie Module
If you’ve ever used a fitness tracker on a wristband, you must know that although it gives an indication of your level of activity, it’s usually not really accurate to count steps. Xiaomi’s “90 Minutes ultra smart running shoes” fixes the issue as the fitness tracker powered by Intel Curie module is placed right inside the shoes. Most of the information is in Chinese, and I could only find limited specifications for the shoes: Size – 39 to 45 Intel Curie Module based on Quark SE SoC with 6-axis accelerometer and gyroscope, Bluetooth 4.0 LE connectivity Battery – Good for 60 days on a charge Material Shoe sole – Rubber Shoe vamp – Fabric + Synthetic leather Shoe insole – Antibacterial removable air cushions The small device based on Intel Curie module resides inside the sole, stores fitness data such steps, distance covered, speed, (estimated) calories burnt, etc… It’s unclear […]
Open Surgery Initiative Aims to Build DIY Surgical Robots
Medical equipments can be really expensive because of the R&D involved and resulting patents, low manufacturing volume, government regulations, and so on. Developed countries can normally afford those higher costs, but for many it may just be prohibitively expensive. The Open Surgery initiative aims to mitigate the costs by “investigating whether building DIY surgical robots, outside the scope of healthcare regulations, could plausibly provide an accessible alternative to the costly professional healthcare services worldwide”. The project is composed of member from the medical, software, hardware, and 3D printing communities, is not intended for (commercial) application, and currently serves only academic purposes. Commercial surgical robots can cost up to $2,000,000, but brings benefits like smaller incisions, reduced risks of complications and readmissions, and shorter hospital stays thanks to a faster recovery process. There have already been several attempts within the robotics community to come up with cheaper and more portable surgical […]
Omron Project Zero 2.0 is a Thinner Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor & Smartwatch
Omron Project Zero BP6000 blood pressure monitor & smartwatch / fitness tracker was unveiled at CES 2016. The device was due to be released at the end of 2016 pending FDA approval, but the launch has now been delayed to spring 2017, and it will be sold under the name “HEARTVUE”. The company has however showcased a new version at CES 2017, for now just called Omron Project Zero 2.0 that has the same functions but is more compact and lightweight. The watch will also work with Omron Connect US mobile app, and can record accurate blood pressure, as well as the usual data you’d get from fitness trackers including activity (e.g. steps) and sleep, as well as smartphone notifications. Blood pressure measurement can be activated by the user by pressing a button and raising his/her wrist to the height of the chest. The goal is the same as the […]
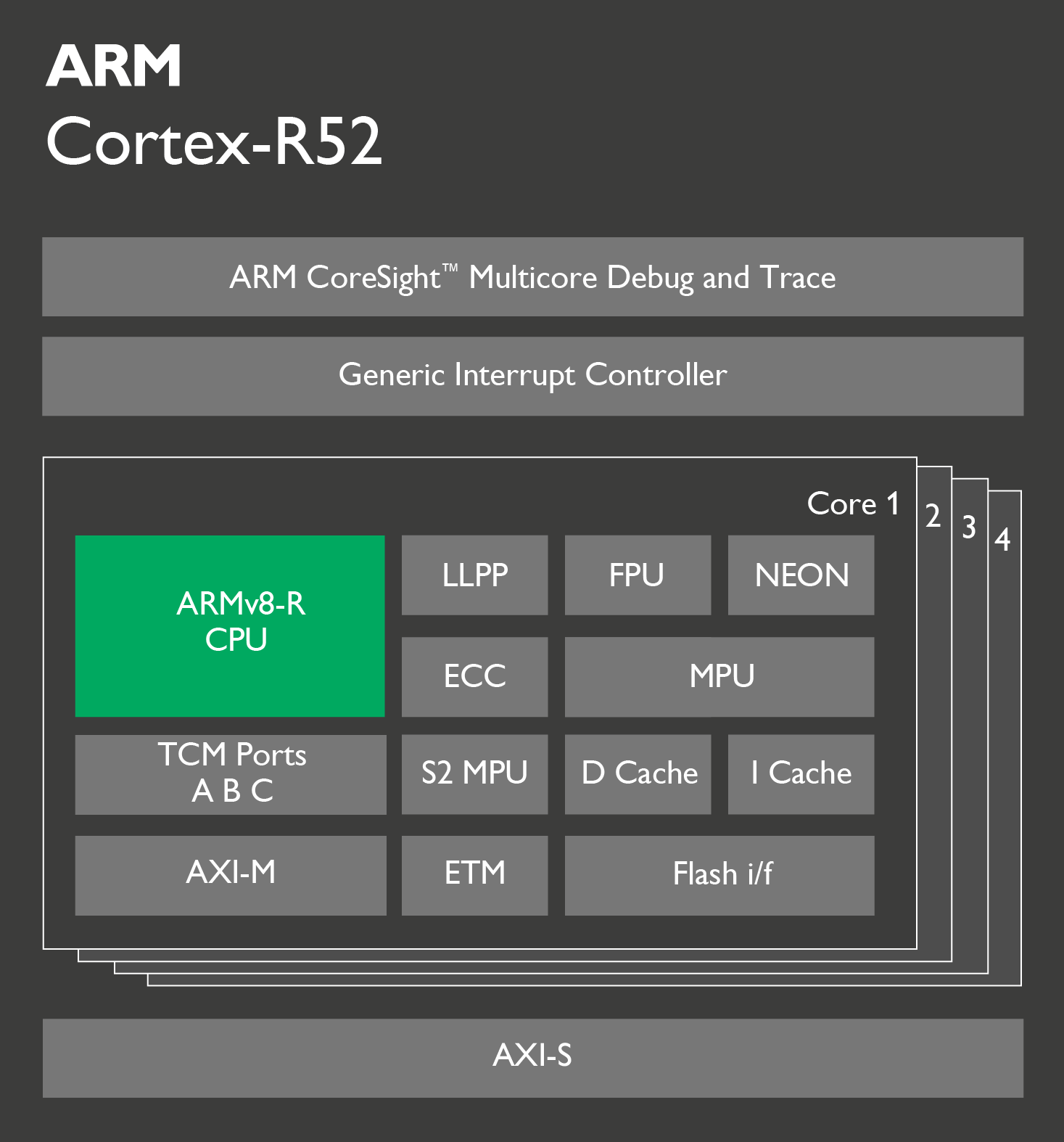
ARM Unveils Cortex-R52 ARMv8-R CPU Core for Safety-Critical Systems
ARM has introduced their very first ARMv8-R real-time 32-bit CPU core with Cortex-R52 designed for safety-critical applications in the automotive, industrial and health-care markets. It has been designed to address higher workloads with increased performance (up to 35%) compared to Cortex-R5 processor. The processor should be used in systems capable of fulfilling IEC 61508 SIL 3 and ISO 26262 ASIL D functional safety requirements. ARM explains the new processor address both random errors for example bit flipping from radiation, and systemic errors more related to software or design faults. The latter can be addresses with the right development processes, including following aforementioned functional safety standards, but random errors require some extra hardware features such as ECC memory, or dual core lock step processors, where instructions are run on two processors simultaneously and results compared. Normally, the whole software stack must be validated and certified on safety-critical systems, even for part […]