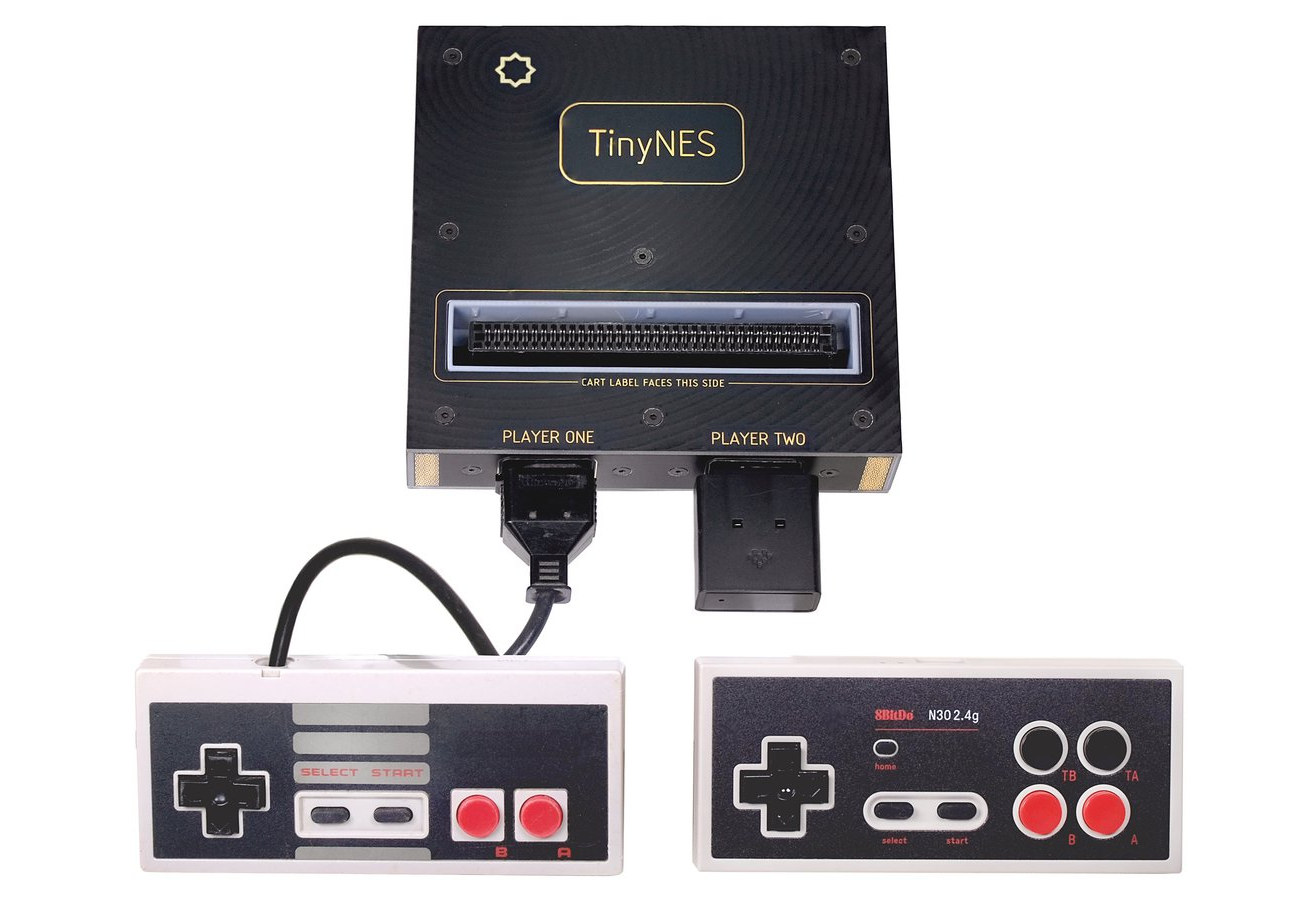
Tall Dog Electronics’ TinyNES (Tiny Nostalgia Evocation Square) is an open-source hardware game console compatible with NES cartridges and featuring the original MOS 6502-based Ricoh RP2A03 CPU (central processing unit) and the Ricoh RP2C02 PPU (picture processing unit) found in the Nintendo NES, although clones may be also used in the future due to the lack of availability. Designed to offer the same experience as the original Nintendo NES, the console comes with two NES controller ports, a cartridge slot, RCA video composite and mono audio outputs, and all electronics is housed in an FR-4 enclosure, the same material used for most PCBs. TinyNES specifications: CPU – MOS 6502-based Ricoh RP2A03 central processing unit, or UMC UA6527 clone PPU – Ricoh RP2C02 picture processing unit, or UMC UA6528 clone Cartridge slot for NES cartridges Controller ports – 2 original NES-style 7-pin controller ports Video – NTSC composite (CVBS) analog […]
Linux 5.16 Release – Main Changes, Arm, RISC-V and MIPS architectures
Linus Torvalds has just announced the release of Linux 5.16: Not a lot here since -rc8, which is not unexpected. We had that extra week due to the holidays, and it’s not like we had lots of last-minute things that needed to be sorted out. So this mainly contains some driver fixes (mainly networking and rdma), a cgroup credential use fix, a few core networking fixes, a couple of last-minute reverts, and some other random noise. The appended shortlog is so small that you might as well scroll through it. This obviously means that the merge window for 5.17 opens tomorrow, and I’m happy to say I already have several pending early pull requests. I wish I had even more, because this merge window is going to be somewhat painful due to unfortunate travel for family reasons. So I’ll be doing most of it on the road on a laptop […]
OS and Memory Impact on Mini PC Gaming Performance
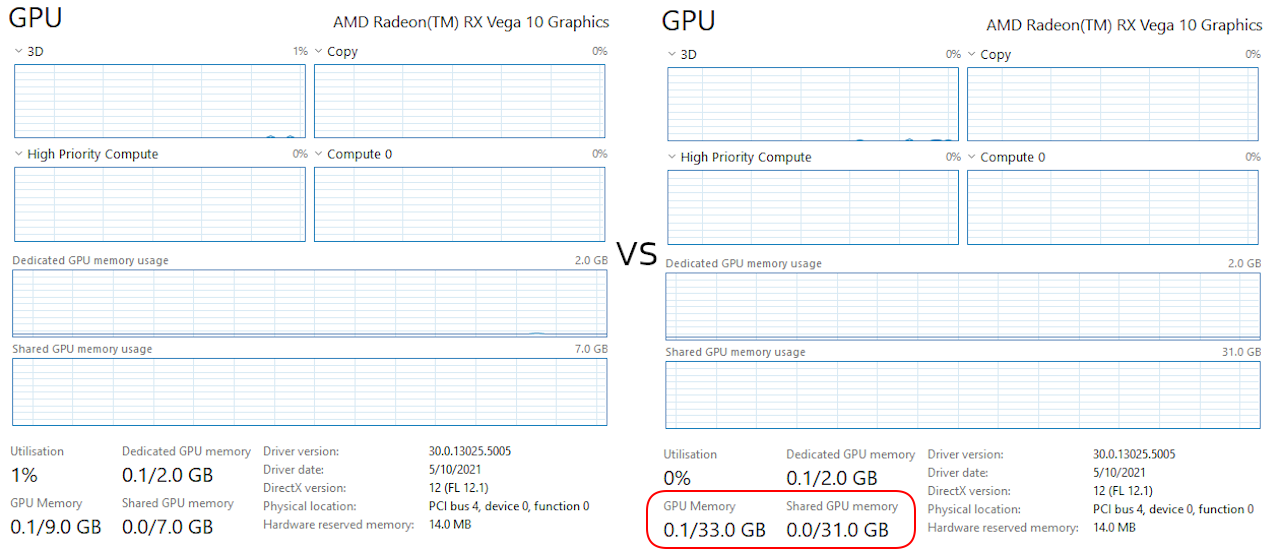
This article looks at what the effect of running a different operating system or having more memory has on similarly spec’d Intel and AMD mini PCs when gaming. Note: This article has been updated and corrected as a result of reader feedback and additional testing. It was inspired by having built and tested a pseudo ‘Steamdeck’ running Manjaro on an AMD-based mini PC with 16GB of memory, which made me wonder what the performance would be like using Windows 11. Initial results were surprising because Windows appeared much slower. As I’d previously heard of performance improvements when using 64GB of memory I swapped out the currently installed 16GB memory and immediately saw improved results. As I’d never observed such a dramatic performance increase on Intel mini PCs just through increasing the memory I decided to explore further by testing gaming performance on similar Intel and AMD mini PCs when using […]
Beelink GTi11 review – Part 2: Ubuntu 20.04 on an Intel Core i5-1135G7 mini PC
Previously I reviewed Beelink’s new GTi11 Intel Tiger Lake mini PC running Windows 11, so in this part, I will cover Ubuntu 20.04. Hardware Recap The GTi11 is a 168 x 120 x 39mm (6.61 x 4.72 x 1.54 inches) actively cooled mini PC and the review model has an i5-1135G7 Intel Tiger Lake quad-core 8-thread 2.50 GHz Core processor boosting to 4.20 GHz with Intel’s Xe Graphics. The review model also includes a 500GB M.2 2280 NVMe PCIe Gen 3.0 SSD drive initially with Windows 10 Pro installed but now successfully upgraded to Windows 11 Pro, two sticks of 8GB DDR4 3200 MHz memory, a soldered WiFi 6 (or 802.11ax) Intel AX201 chip and dual 2.5Gb Ethernet ports. The specifications list four of the USB ports as 3.0 so I retested them on Ubuntu using a Samsung 980 PRO PCle 4.0 NVMe M.2 SSD housed in an ‘USB to […]
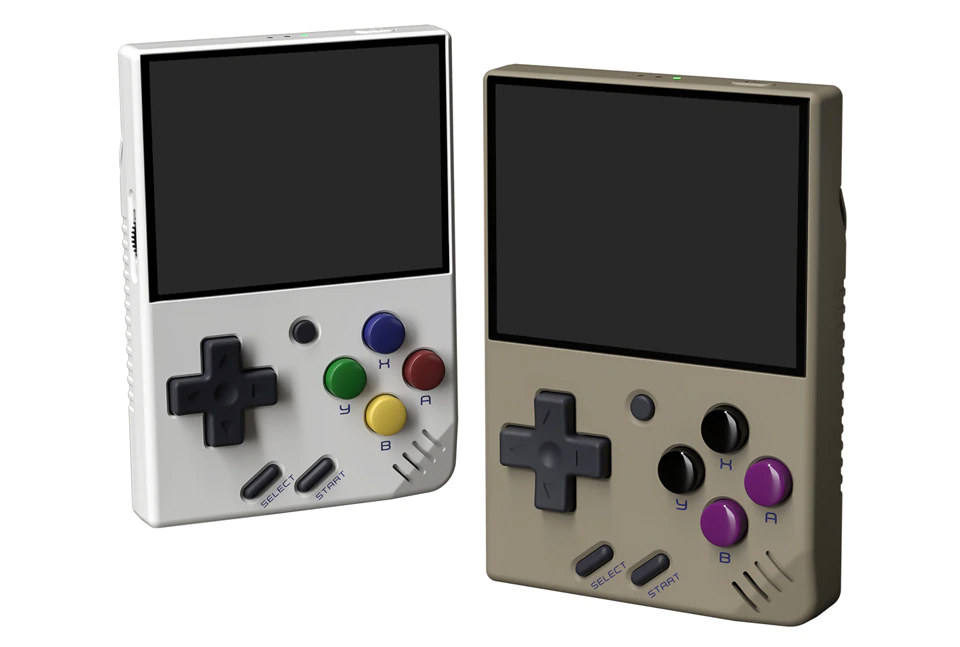
Portable game console runs RetroArch on SigmaStar SSD202D processor
SigmaStar SSD202D “Smart Display” dual-core Cortex-A7 processor has found its way into the MIYOO mini portable game console compatible with RetroArch Linux distribution. Initially designed for industrial smart displays or other HMI applications, we’ve already seen the low-cost Arm Linux processor with 64MB (SSD201) or 128MB (SSD202D) memory has been integrated into a gateway, a single board computer, and M5Stack UnitV2 AI camera devkit, but somehow, it’s now gone into a consumer device. MIYOO mini portable game console specifications: SoC – SigmaStar SSD202D dual-core Cortex-A7 processor @ 1.2 GHz with 2D GPU, 128MB DDR3 (Note: no GPU) Storage – 32GB MicroSD card Display – 2.8-inch IPS screen with 640×480 resolution Audio – 3.5mm audio jack User input – D-PAD, Menu, Select and Start buttons, ABXY buttons, R/R2 and L/L2 buttons at the back USB – 1x USB-C port Misc – Power button, Vibration motor, LEDs Battery – 3.7V/1,900mAh battery good […]
AMD Ryzen V1000/R1000 Mini-ITX board is made for game arcades, slot machines
Axiomtek GMB140 is a compact Mini-ITX motherboard powered by AMD Ryzen Embedded V1000/R1000 processor and mostly designed for gaming applications, as well as medical imaging, interactive kiosks, control rooms, and video surveillance. But when we’re not talking about your kids playing games at home here, but instead slot machines, arcade systems, and electronic gaming machines (EGM) powered by the GMB140 board with a PCIe interface for gaming I/O modules, and optional support for a 9-bit serial port for the SAS 6.02 protocol. Axiomtek GMB140 mini-ITX board specifications: SoC – AMD Ryzen Embedded V1000/R1000 quad-/dual-core “Zen” processor with Radeon Vega graphics either: AMD Ryzen Embedded V1807 w/ VEGA 11 graphics AMD Ryzen Embedded V1756 w/ VEGA 8 graphics AMD Ryzen Embedded V1605 w/ VEGA 8 graphics AMD Ryzen Embedded V1202 w/ VEGA 3 graphics AMD Ryzen Embedded R1606 w/ VEGA 3 graphics AMD Ryzen Embedded R1505 w/ VEGA 3 graphics System […]
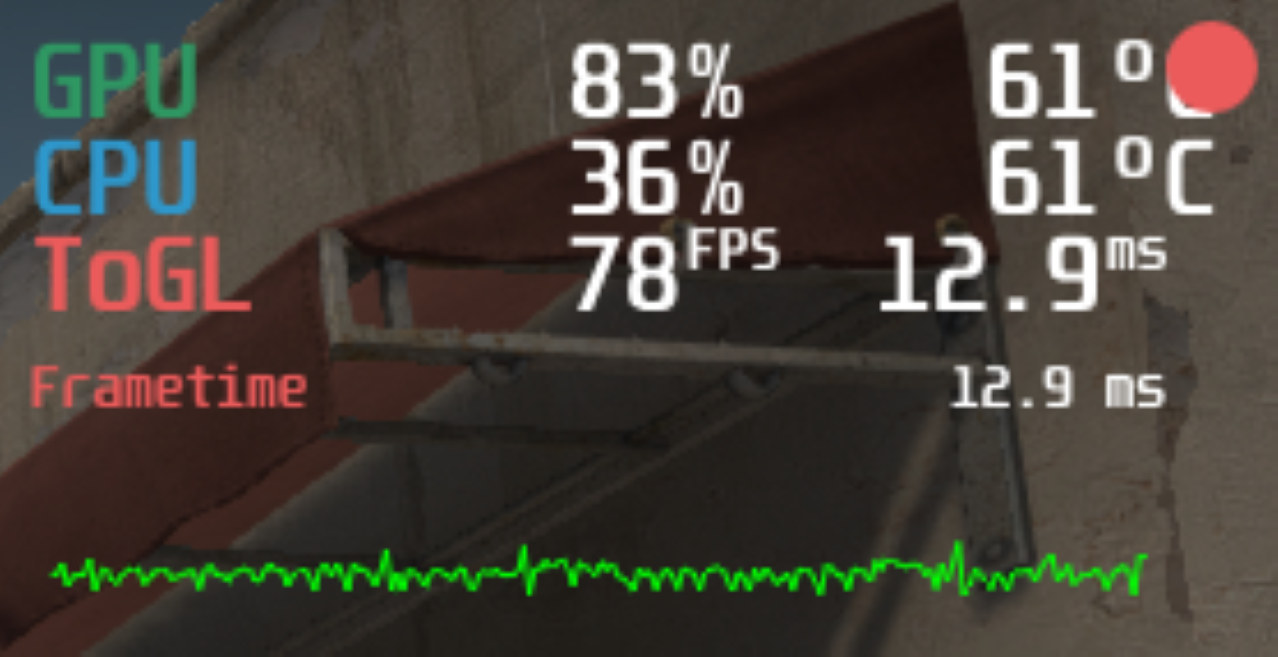
Using MangoHud to check FPS, CPU & GPU usage on a ‘hackendeck’
Previously I followed Valve’s documentation to build a ‘hackendeck’ using a mini PC to emulate their highly anticipated Steam Deck. Interestingly the ‘hackendeck’ uses a Linux OS, specifically Manjaro, as whilst Valve based their earlier version of Steam OS on Debian, they have now switched to being based on Arch. If the ‘hackendeck’ had just been Steam on Windows then to review gaming performance I’d just use MSI Afterburner. Until now, however, for Linux, I’ve always had to estimate the average FPS as I’ve not been aware of a good reliable equivalent. Fortunately several ‘commenters’ recommended using MangoHud, a Linux open-source Vulkan/OpenGL overlay for monitoring FPS, CPU/GPU usage, and temperatures similar to MSI Afterburner. So now I’ve been able to capture the average frame rate for the games I previously tested and I’ll present them below. MangoHud Installation and configuration The installation of MangoHud was extremely simple. First I installed […]
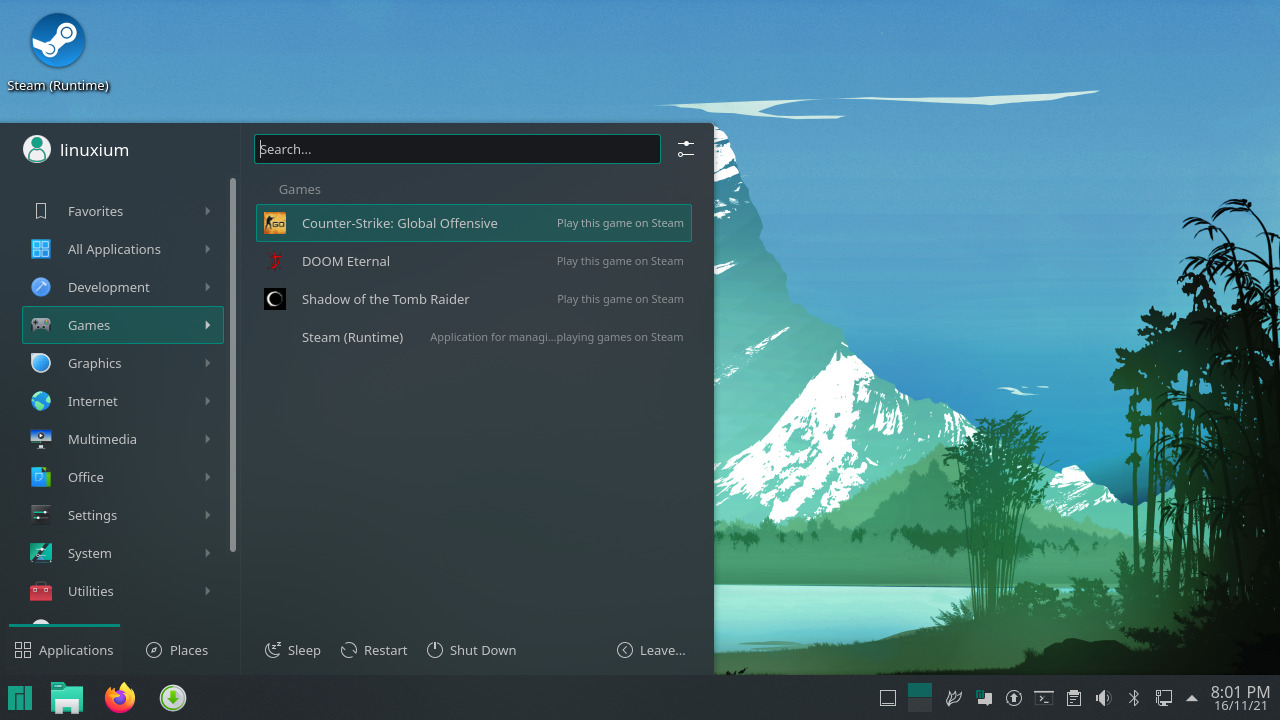
Experiences of configuring and using a ‘hackendeck’ homemade Steam Deck
Valve recently released information about developing for the Steam Deck if you didn’t have a Dev-Kit which is an engineering verification test build (EV2) version of their device. Included in the documentation is a suggestion to build your own Steam Deck, or ‘hackendeck’ using a mini PC. Whilst I didn’t have the exact brand they picture in the article I did have a mini PC with the required specifications so I set about following the instructions to see how it performed. Hardware Overview Valve’s documentation under ‘Performance’ states that ‘if you are really interested in finding a PC for testing that will perform similarly to a Steam Deck … there are a few options out there and then goes on to suggest a mini PC with the following ‘roughly similar specifications to a Steam Deck’: AMD Ryzen 7 3750H Radeon RX Vega 10 Graphics 16GB of DDR4 RAM This exactly […]