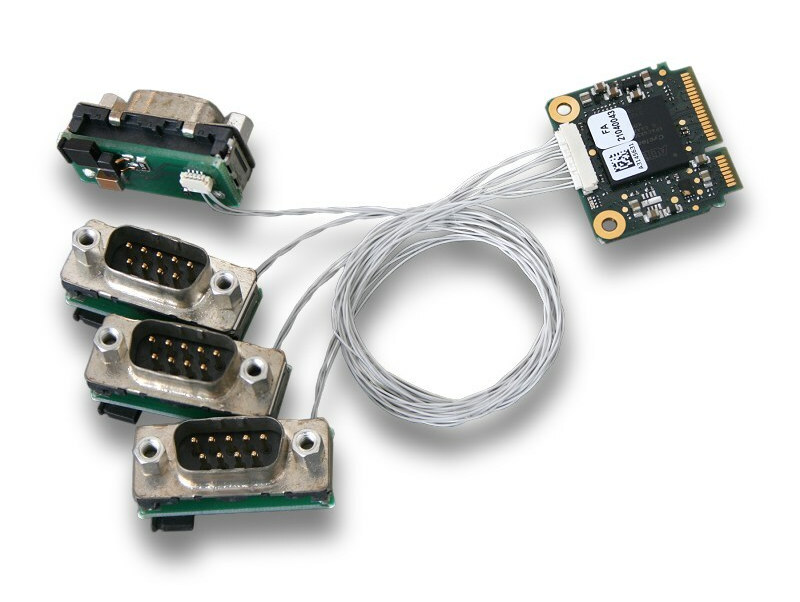
esd electronics CAN-PCIeMiniHS/402 is a half-size mini PCIe card with four CAN FD Interfaces designed for embedded systems with one model adding extended temperature range support from -40C to 85°C. The company also introduced the CAN-Mini/402-4-DSUB9-150mm adapter to more easily connect the four CAN network interfaces via DSUB9 connectors. It comes with four individual small adapter boards, each equipped with a DSUB9 plug and a jumper for selectable onboard CAN termination, as well as 150 mm long wires. CAN-PCIeMiniHS/402 highlights: 4x CAN FD interfaces according to ISO 11898-2, no galvanic isolation, bit rates from 10 Kbit/s up to 8 Mbit/s Bus mastering and local data management by FPGA (Intel Cyclone IV EP4CGX) PCIe Mini interface according to Mini Card Electromechanical Spec. R1.2 Supports MSI (Message Signaled Interrupts) HW-Timestamp capable Dimensions – 30 mm x 27 mm (Half-size mini PCIe form factor) Temperature Range Standard – 0°C … +75°C Extended range: […]
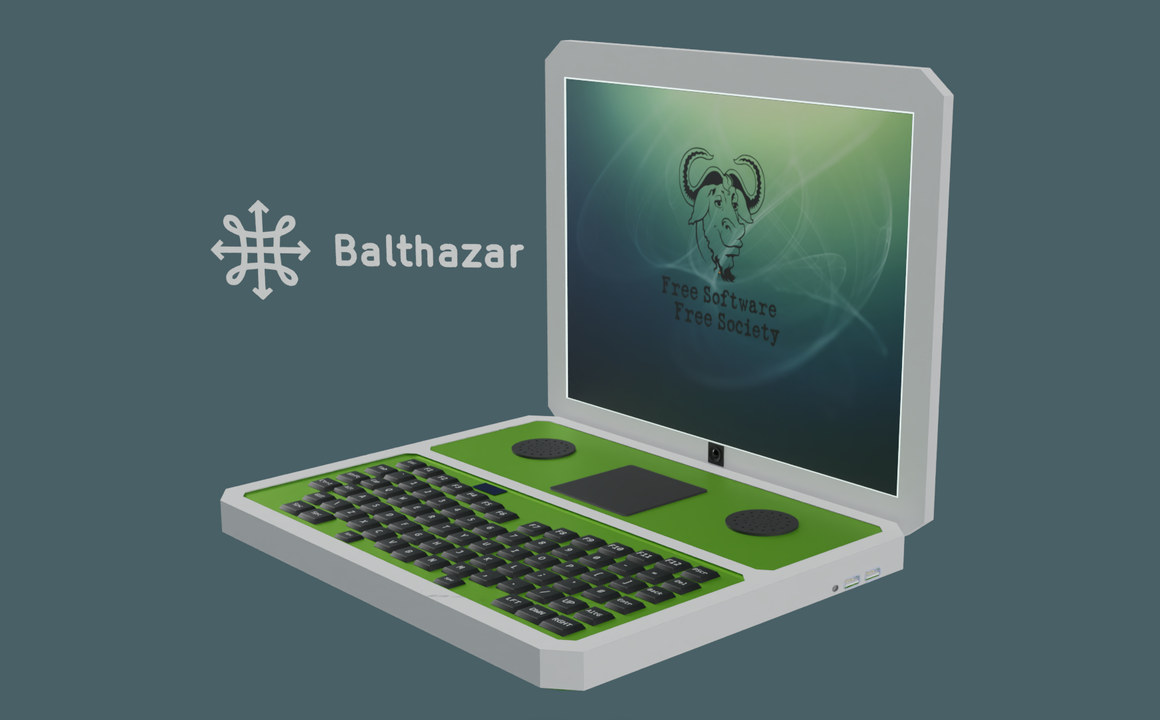
Balthazar – An open-source hardware modular RISC-V, Arm, or FPGA laptop
The Balthazar Personal Computing Device (BPCD) is an open-source hardware 13.3-inch laptop with a RISC-V, Arm, or FPGA module and designed to be upgradable, expandable, and sustainable. The developers say the laptop is based on a few concepts inspired by the EOMA68 project. The EOMA68 is a CPU module based on the PCMCIA form factor, and an Allwinner A20 EOMA68 module was showcased in a prototype of the Rhombus Tech 15.6-inch Libre Laptop but I don’t think the project was ever manufactured. Balthazar laptop features: SoM with RISC-V, FPGA, or Arm Cortex-A7x processor plus memory and flash Storage – SATA SSD, eSATA connector, microSD card socket Display – 13.3-inch non-glare display Video Output – HDMI Audio – Speakers, detachable microphone array Camera – Detachable webcam Connectivity – Ethernet, WiFi USB – 2x USB 3.0 ports, Micro USB OTG port, Micro USB port User input Waterproof keyboard with an illuminated track-point […]
FOSDEM 2023 schedule – Open-source Embedded, Mobile, IoT, Arm, RISC-V, etc… projects
After two years of taking place exclusively online, FOSDEM 2023 is back in Brussels, Belgium with thousands expected to attend the 2023 version of the “Free and Open Source Developers’ European Meeting” both onsite and online. FOSDEM 2023 will take place on February 4-5 with 776 speakers, 762 events, and 63 tracks. As usual, I’ve made my own little virtual schedule below mostly with sessions from the Embedded, Mobile and Automotive devroom, but also other devrooms including “Open Media”, “FOSS Educational Programming Languages devroom”, “RISC-V”, and others. FOSDEM Day 1 – Saturday February 4, 2023 10:30 – 10:55 – GStreamer State of the Union 2023 by Olivier Crête GStreamer is a popular multimedia framework making it possible to create a large variety of applications dealing with audio and video. Since the last FOSDEM, it has received a lot of new features: its RTP & WebRTC stack has greatly improved, Rust […]
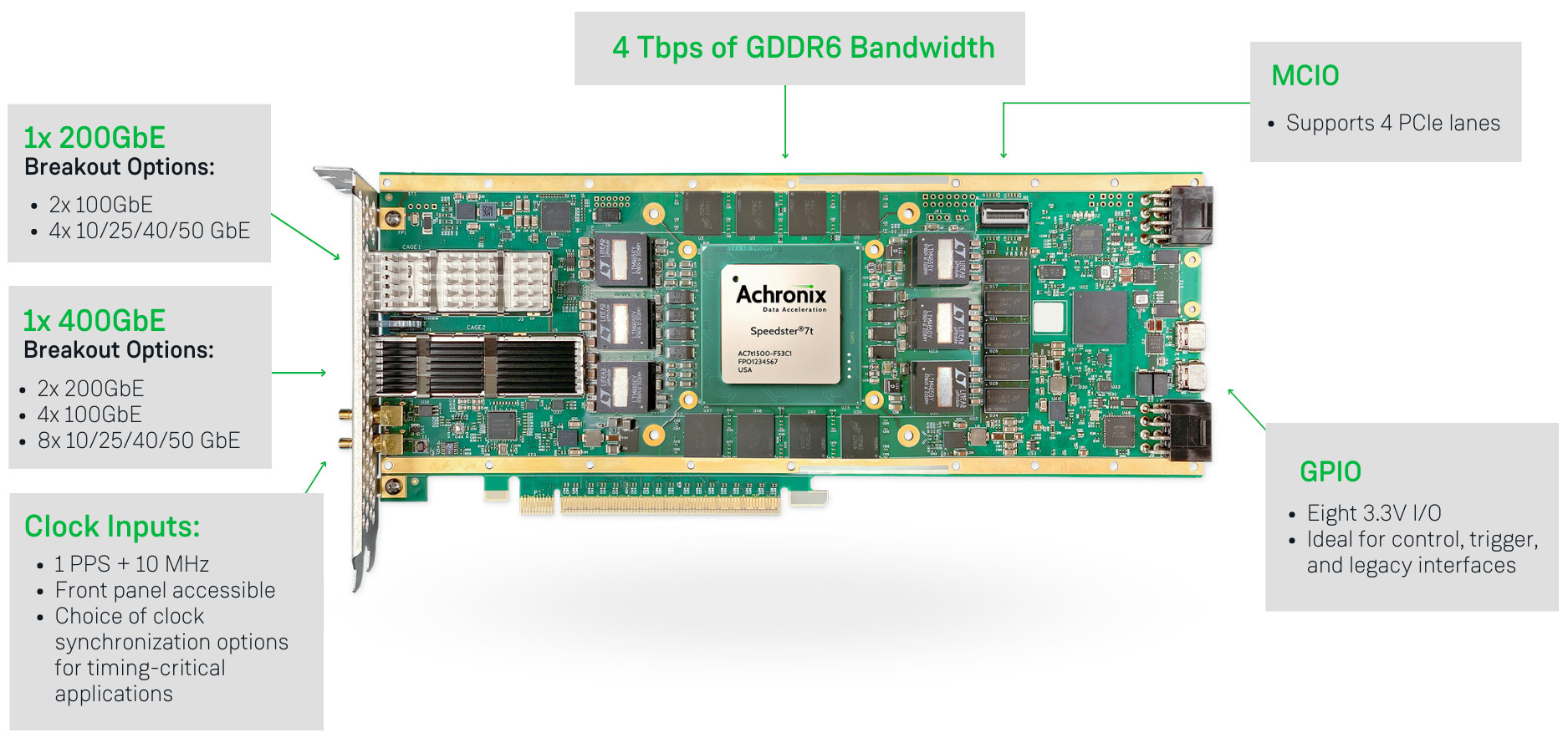
Achronix Speedster7t AC7t1500 FPGA is now available for high-bandwidth applications
Achronix Semiconductor has recently announced the general availability of the Speedster7t AC7t1500 FPGA designed for networking, storage, and compute (AI/ML) acceleration applications. The 7nm Speedster7t FPGA family offers PCIe Gen5 ports and GDRR6 and DDR5/DDR4 memory interfaces, delivers up to 400 Gbps on the Ethernet ports, and includes a 2D network on chip (2D NoC) that can handle 20 Tbps of total bandwidth. Achronix Speedster7t highlights: Two-dimensional network on chip (2D NoC) enabling high bandwidth data flow throughout and between the FPGA fabric and hard I/O and memory controllers and interfaces MLP (Machine Learning Processors) blocks with arrays of multipliers, adder trees, accumulators, and support for both fixed and floating-point operations, including direct support for Tensorflow’s bfloat16 format and block floating-point (BFP) format. Multiple PCIe Gen5 ports High-speed SerDes transceivers, supporting 112 Gbps PAM4 and 56 Gbps PAM4/NRZ modulation, as well as lower data rates Hard Ethernet MACs that support […]
Lattice Avant mid-range FPGA platform features up to 500K logic cells, 25 Gbps SERDES, Hard PCIe Gen4
Lattice Avant is a new low-power and small form factor mid-range FPGA platform, manufactured with a 16nm FinFET process, and equipped with 25 Gb/s SERDES, hardened PCI Express, external memory PHY interfaces, a high DSP count, and a security engine. Lattice Semi is better known for its entry-level FPGAs such as the iCE40 which is popular in the community thanks to low-cost hardware and support for open-source tools, but the Avant platform marks the company’s entry into the mid-range FPGA market, defined by chips with 100k to 500k logic cells (LCs). Lattice Avant highlights: FPGA fabric – 200K to 500K logic cells up to 350 MHz DSP – 700 to 1,8000 18×18 multipliers @ up to 650 MHz to support the latest AI algorithms Memory 14-36 Mbit embedded memory up to 650 MHz DDR3L/DDR4/LPDDR4 and DDR5 support I/Os 4x to 28x 25 Gbps multi-protocol SERDES Hard PCIe Gen4 200 to […]
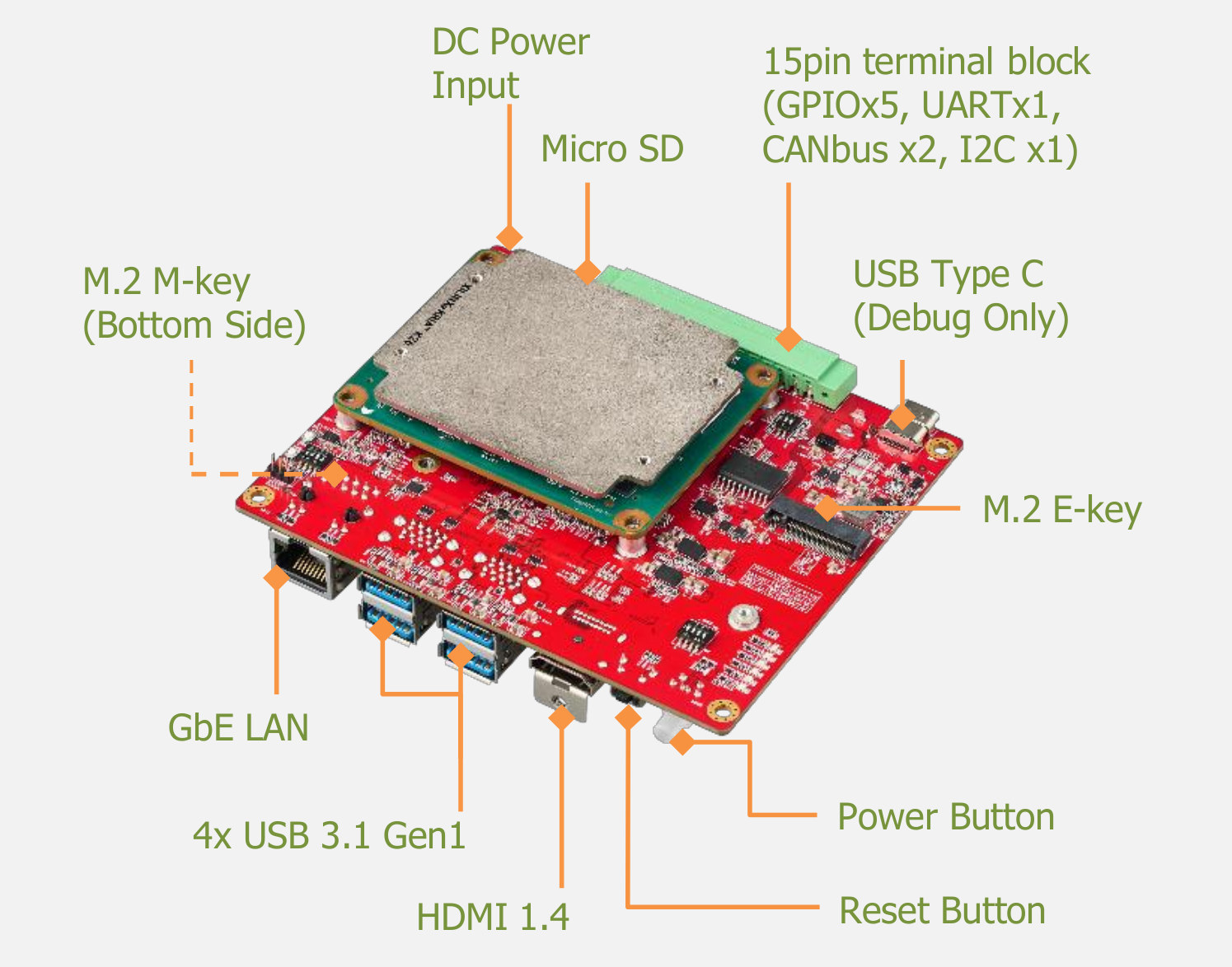
Innodisk EXMU-X261 FPGA Machine Vision Platform is based on AMD Xilinx Kria K26 SoM
Innodisk, better known for its embedded storage and memory chips, had announced its intention to turn to the AI market earlier and started with the launch of USB camera modules last month, but the company has gone a step (or two, or three) further with the introduction of the EXMU-X261 FPGA machine vision platform. The EXMU-X261 is powered by an AMD Xilink Kria K26 system-on-module and features HDMI 1.4 video output, Gigabit Ethernet, four USB 3.1 Gen 1 ports for the cameras and other peripherals, as well as two M.2 sockets and a terminal block for expansion. EXMU-X261 specifications: System-on-module – AMD Xilinx Kria K26 FPGA module powered by a Zynq UltraScale+ XCK26 FPGA MPSoC with a quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 processor, up to 250 thousand logic cells, and a H.264/265 video encoder/decoder Storage – MicroSD card socket Video Output – HDMI 1.4 port Networking – Gigabit Ethernet RJ45 port USB […]
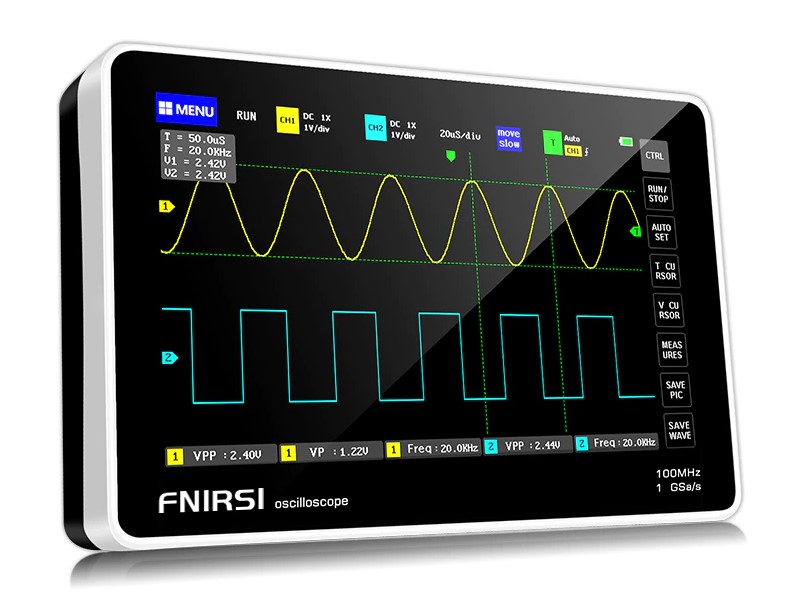
FNIRSI 1013D teardown and mini review – A portable oscilloscope based on Allwinner CPU & Anlogic FGPA
The FNIRSI 1013D is a dual-channel flat-panel oscilloscope with a rich set of features. It is cost-effective and useful to people in the maintenance and R&D industries. Although it has been on the market for a few years, I purchased one, and I decided to introduce it and disassemble it to check out the hardware design. FNIRSI describes its oscilloscope as “small and portable”, so I assume it should include a lithium battery, a TFT LCD screen, a processor to handle the display, and another chip to process the digital signals. Let’s take it apart first to find out. FNIRSI 1013D oscilloscope unboxing FNIRSI 1013D package content: 1x FNIRSI 1013D oscilloscope 2x 100MHz matching probes (1X and 10X) 1x USB cable 1x Charging adapter 1x Instruction manual The FNIRSI 1013D adopts a 7-inch 800 x 480 resolution color TFT LCD with a capacitive touch screen. There are two input channels […]
AMD unveils low-cost Artix UltraScale+ AU7P FPGA and Zynq UltraScale+ ZU3T MPSoC
AMD has added two new low-cost, low-power members to its UltraScale+ family with the Artix UltraScale+ AU7P FPGA and the Zynq UltraScale+ ZU3T MPSoC. Both devices are manufactured with the 16nm FinFET process and offer entry points to the transceiver-based UltraScale+ family with features such as high I/O-to-logic density, UltraRAM, DSP, and more. AMD Artix UltraScale+ AU7P FPGA The new AU7P FPGA is the smallest from the Artix UltraScale+ family with four 12.5Gbps transceivers, up to 82K system logic cells, 216 DSP slices, 4.9 Mbit RAM, and 248 I/Os. It is offered in a 10.5 x 8.5mm InFO package. The company says the chip provides up to 50% lower static power, 20% more I/O-to-logic ratio, and twice as many 3.3V HDIO compared to the AU10P device. The AU7P is designed for space-constrained and/or power-sensitive applications such as medical imaging, machine vision, professional cameras/monitors, and automotive radar/lidar. More details may be […]