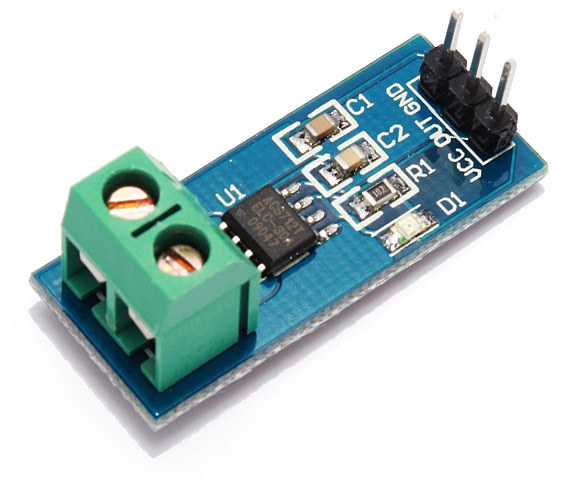
Usually, if I buy a high power electric appliance, I like to double check it power consumption either with a Kill-a-watt when possible, and when not, e.g. cable directly hooked to the device or current intensity is too high, I use a digital electric clamp meter. Both methods are quite convenient as you don’t need to cut any wire to measure the current and determine the power consumption, but they don’t allow for data gathering since they don’t connect to the network. Earlier this week, I’ve come across a projects using ESP8266 for a mains energy monitor for a solar panel setup, and measuring mains current, electric meter, and gas meter. They use a photosensor to measure power consumption on their electric meter, which works, but may be problematic if the meter is on the street, and iSnail current sensor, using hall effect just like clamp meter, but instead of […]
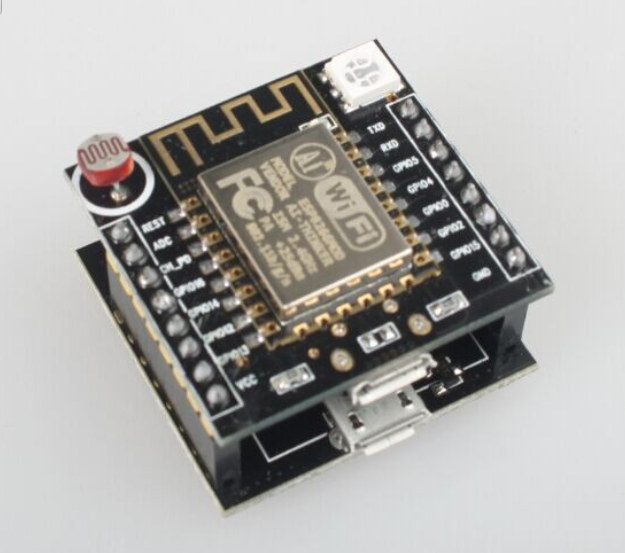
$3 Compact ESP8266 Board Includes RGD LED, Photo Resistor, Buttons and a USB to TTL Interface
In case you need a cheap and compact ESP8266 board with integrated USB to TTL debug interface, a photo resistor, and/or some buttons, a white brand board based on ESP-12F could be interesting. “Witty cloud” development board specifications: ESP-12F module with Espressif ESP8266EX SoC Connectivity – WiFi 802.11 b/g/n 2x 8-pin headers with GPIOs, VCC, GND, Reset, ADC, and UART USB – 2x micro USB port (one for power, one for debugging ?) Misc – Photo resistor, RGB LED, three buttons for power, reset and firmware upgrade (I think) Dimensions – Small Witty cloud might not be the same of the board itself, but could be a cloud service launched in China, as some of the screenshot on Aliexpress could imply. All I could find are some websites vaguely mentioning GoKit 3.0 and Witty Cloud 3.0, but it does not make much sense. If Chinese readers could provide some insights […]
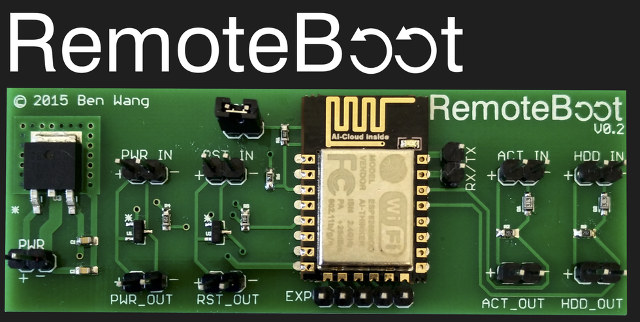
RemoteBoot is an ESP8266 based Board to Power on or Reboot Your Computer over WiFi (Crowdfunding)
Wake-on-LAN is a features that allows you to remotely start your computer by sending magic network packets to the LAN interface, but it requires support from your motherboard. So Ben Wang, an Australian high-school student, decided to make his own little board called RemoteBoot to power off and reboot computers that do not support the feature, or even access the serial console on embedded boards. The board is pretty basic and includes an ESP8266 module: ESP12-E WiFi module 2x digital switching outputs for power and reset buttons 2x digital protected inputs for power and activity LEDs 3x extra general purpose inputs/outputs broken out Tx/Rx for serial console There’s also a feature disabled by default, where a watchdog monitor the activity LED, and automatically reboots the computer after a user-defined timeout. Everything will be control via a simple web interface, and if you have multiple RemoteBoot devices, access to Remoteboot Cloud […]
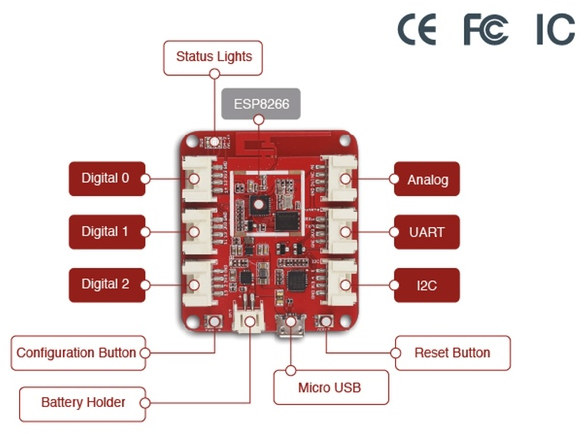
Wio Link is an ESP8266 Board Designed to Make IoT Projects Easier (Crowdfunding)
There are already plenty of board or modules based on Espressif ESP8266 WiFi SoC, but if you don’t like soldering, or would rather avoid breadboards and some cables for your or your kids’ projects, Wio Link may be interesting, as all you need to is to connect Grove modules required for your applications to get started, and Seeed Studio also took care of the low level software part and a drag-and-drop mobile app is provided, so software programming has been made easy too. Wio Link hardware specifications: SoC – Espressif ESP8266EX Tensila SoC Storage – 4MB flash Connectivity – 802.11b/g/n WiFi, with WEP/TKIP/AES encryption support Expansion – 6x Grove connectors: 3x digital, 1x analog, 1x UART and 1x I2C (3.3V I/Os) Power Supply 5V via micro USB port 3.4 ~ 4.2V via external battery Output DC Current – 1000mA MAX Charge Current: 500mA MAX Dimensions – 55mm*48mm Weight – 26g […]
Sonoff & Slampher are $5 RF and WiFi Smart Switches and Lightbulb Adapters (Crowdfunding)
ITEAD Studio has launched two new low cost home automation products with Sonoff smart switch, and Slampher smart E27 light bulb adapter both supporting control via WiFi and your Android smartphone, or 433MHz with a simple remote control, while still retaining the capability to control your electrical appliances and lights with a manual switch. Installation is pretty easy, and safer than some other products like Semlamp. Sonoff – You simply need to cut the cable to your appliance, and insert two wires into the IN part, and the other two wires into the OUT part. Turn if on, and add it to the app if you are going to use a smartphone Slampher – Remove your light bulb from its current socket, screws the bulb to Slampher, and put it back into your socket. Register the light in to the app and your done. Both devices will send data to […]
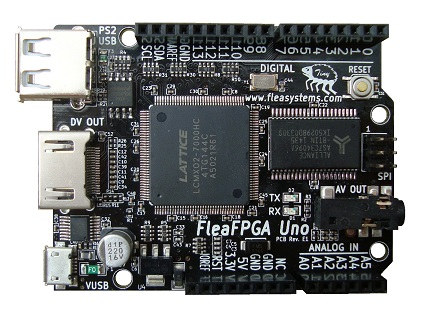
FleaFPGA Uno Board Combines a Lattice FPGA, Arduino UNO Form Factor, HDMI Output, and an ESP8266 WiFi Module
FPGA board with Arduino headers are not exactly a rarity, for example Digilent ARTY in a larger form factor, and some developers have designed FPGA boards using Arduino Mega form factor, such as Papilio DUO and Arduissimo. But FleaFPGA Uno is the first Arduino Uno like FPGA board I’ve seen and it includes HDMI output, one USB host port, as well as an optional WiFi module based on ESP8266. FleaFPGA Uno specifications: FPGA – Lattice Semi MachXO2-7000HC with 6864 LUTs, 256 Kbits flash, and 240+54 Kbits SRAM System memory – 512KB 10nsec User SRAM. Storage – 16MB User Flash ROM. Video Output 24-bit Digital Video out via HDMI port up to 800×600 Composite NTSC video via 3.5 mm jack Audio – Stereo audio out via 3.5mm jack. USB 1x micro USB port for power and slave serial port 1x USB 1.1 host port (PS/2 port) On-board USB JTAG for easy […]
Konke Mini K and Mini Pro Wifi Smart Sockets are Based on ESP8266 SoC
ESP8266 WiFi modules are very popular in the maker community, but so far I have not seen it in any devices myself, until I saw a tweet from @EspressifSystem about a Mini K smart socket. A search on Aliexpress lead me to two devices made by Konke, who also made Kankun KK-SP3 WiFi socket, with Mini K and Mini Pro smart sockets. Both models has basically the same features, except Mini-Pro adds infrared support: Connectivity – 802.11 b/g/n Rated Voltage – AC 100-240V 50/60Hz Rated Power – 2200 Watts Rated Current – 10A Charging Protection: Yes Misc – Power button, Infrared (Mini Pro model only) Plug – China / AU plugs Dimensions – 5.1 diameter x 2.7 cm (V0 grade PC material) Weight – 70 grams Both devices support on/off timers, cyclical delays and charge protection (turns off when devices are charged) with the Android or iOS app. I understand […]
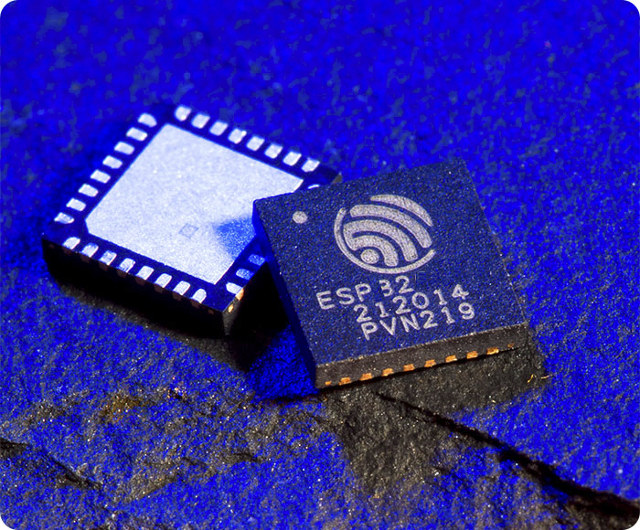
Espressif ESP32 Dual Core SoC Features Faster WiFi, Bluetooth 4.0 LE, and More Peripherals
Espressif teased us about a successor to ESP8266 a few months ago that would support both WiFi and Bluetooth Low Energy, and John Lee, working for Espressif Systems, has now sent a letter to ESP8266 developers announcing the new wireless SoC with two Tensilica L108 cores and called ESP32. Espressif ESP32 key improvements over ESP8266: Faster WiFi – Wifi has been upgraded to support HT40 speed (144.4 Mbps) and has a new RF architecture to simplify the application schematics Bluetooth Low Energy and Classic Dual core processor – 2x Tensilica L108 processors clocked at up to 160 MHz Low Power Mode Improvements – ADC conversions, level thresholds, etc.. can now be performed in deep sleep Peripherals – Capacitive touch, ADCs, DACs, I2C. UART, SPI, SDIO, I2S, RMII, PMW, etc… but no USB. More RAM – ~400 KB on-chip RAM Security – Hardware accelerated AES and SSL, and more undisclosed improvements. […]