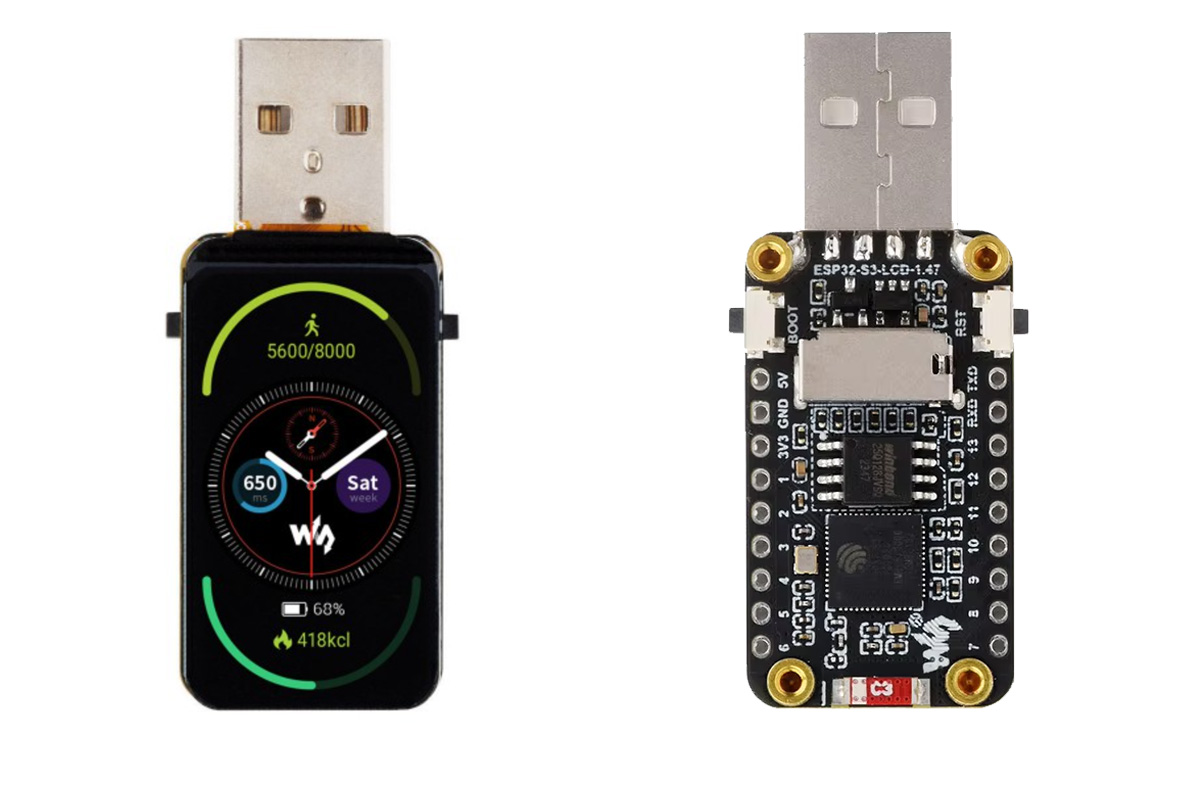
Waveshare ESP32-S3-LCD-1.47 is an ESP32-S3 USB dongle with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, high-capacity Flash and PSRAM, and a 1.47-inch LCD. Additionally, it has an onboard microSD card slot used for storage and some RGB LEDs for visual feedback. All these features make this tiny device suitable for applications like interactive displays, IoT devices, hardware pentesting, and more. Previously we have written about the LILYGO T-HMI a similar ESP32-S3-based development board built for HMI applications, as well as the ESP32-S3-Touch-LCD-4.3B and Waveshare ESP32-S3 LCD Driver Board, but it must be the first time we’ve come across a USB dongle-like ESP32-S3 board with an integrated display. ESP32-S3-LCD-1.47 specifications: Wireless MCU – Espressif Systems ESP32-S3R8 CPU – Dual-core Tensilica LX7 @ up to 240 MHz with vector instructions for AI acceleration. Memory – 512KB RAM, 8MB PSRAM Storage – 384KB ROM Connectivity – 2.4 GHz WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE with support for long-range, up […]
LILYGO T-Deck Plus – A Blackberry-like ESP32-S3 devkit with QWERTY keyboard, trackball, LoRa, GPS, battery, and more
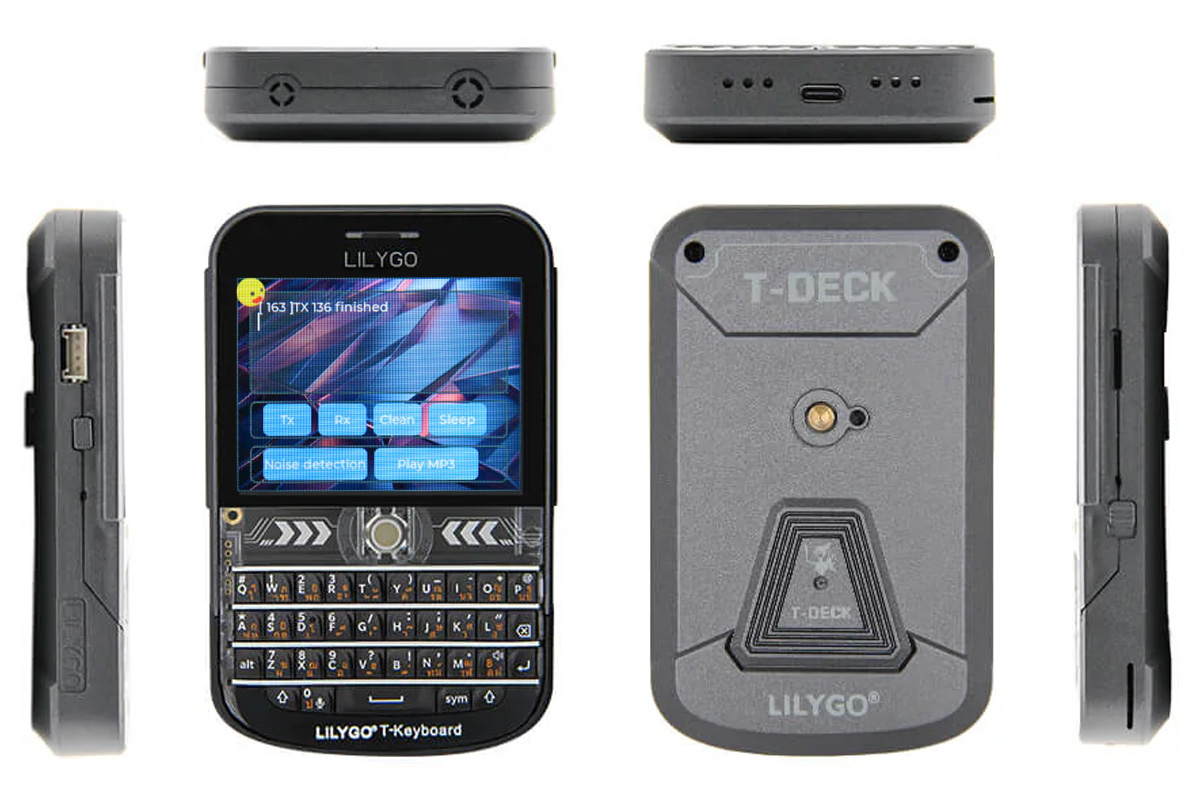
The LILYGO T-Deck Plus is an ESP32-S3 based handheld development kit that resembles a Blackberry phone with a QWERTY keyboard and trackball. The device features a 2.8-inch IPS LCD, a GPS module, a LoRa transceiver, and a 2,000mAh battery which means you can take it outside and do some pen-testing and research. Additionally, the board features a microphone, a speaker, and a microSD card slot for storage. Just last year, LILYGO introduced the LILYGO T-Deck ESP32-S3 development board with LoRa and a 2.8-inch display, and the T-Deck Plus builds on the earlier design but also adds a GPS module and a higher capacity battery. LILYGO T-Deck Plus specifications ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 wireless module SoC – ESP32-S3FN16R8 dual-core Tensilica LX7 microcontroller @ up to 240 MHz with 2.4 GHz 802.11n WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE connectivity Memory – 8MB PSRAM Storage – 16MB SPI flash PCB antenna Storage – MicroSD card slot Display – […]
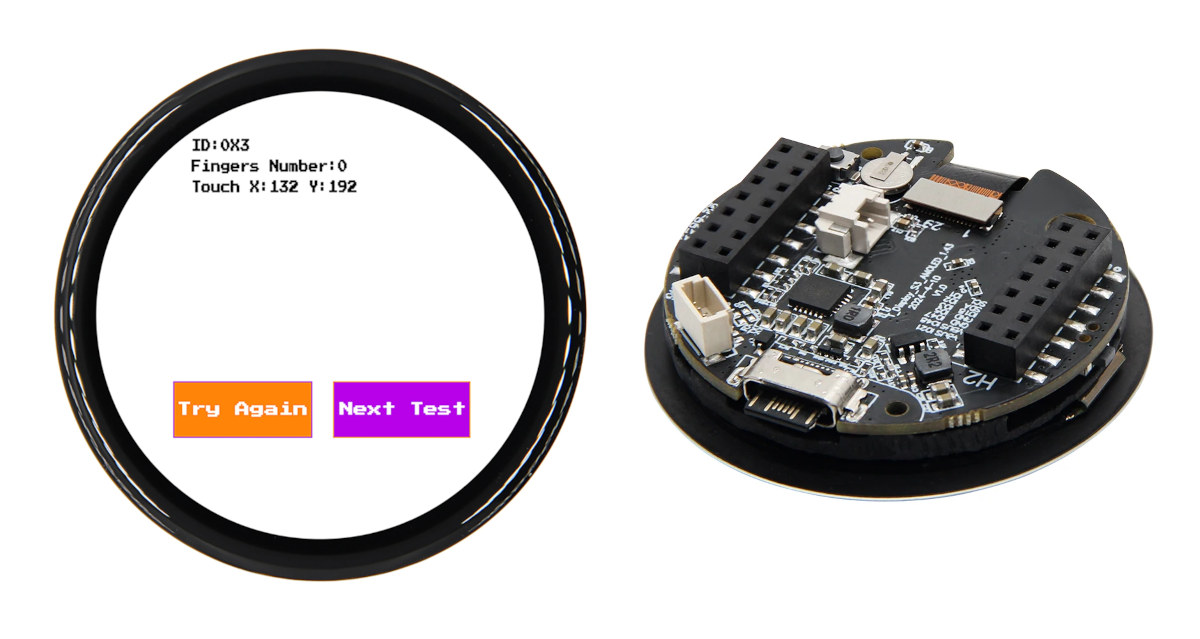
T-Display-S3-AMOLED-1.43 – A 1.43-inch round AMOLED touchscreen display with an ESP32-S3 wireless MCU
We’ve already seen a few ESP32-S3 boards with an AMOLED display and plenty with round displays such as SB Components’ Dual Roundy, LILYGO T-RGB ESP32-S3, MaTouch ESP32-S3 Rotary IPS display among others, but I had yet to see an ESP32-S3 board with a round AMOLED display. That’s just what the LILYGO T-Display-S3-AMOLED-1.43 has to offer. The ESP32-S3 board features a 1.43-inch round AMOLED with 466×466 resolution and a capacitive touchscreen, a microSD card slot for storage, an RTC with backup battery, two 14-pin headers and a Qwiic UART connector for expansion, a USB-C port for power/charging and programming, and a 2-pin connector for a LiPo battery. T-Display-S3 AMOLED-1.43 specifications: SoC – Espressif ESP32-S3R8 CPU – Dual-core Tensilica LX7 microcontroller up to 240 MHz with vector instructions for AI acceleration Memory – 8MB PSRAM Wireless – WiFi 4 and Bluetooth 5.0 LE + Mesh connectivity Storage – 16MB SPI flash, MicroSD […]
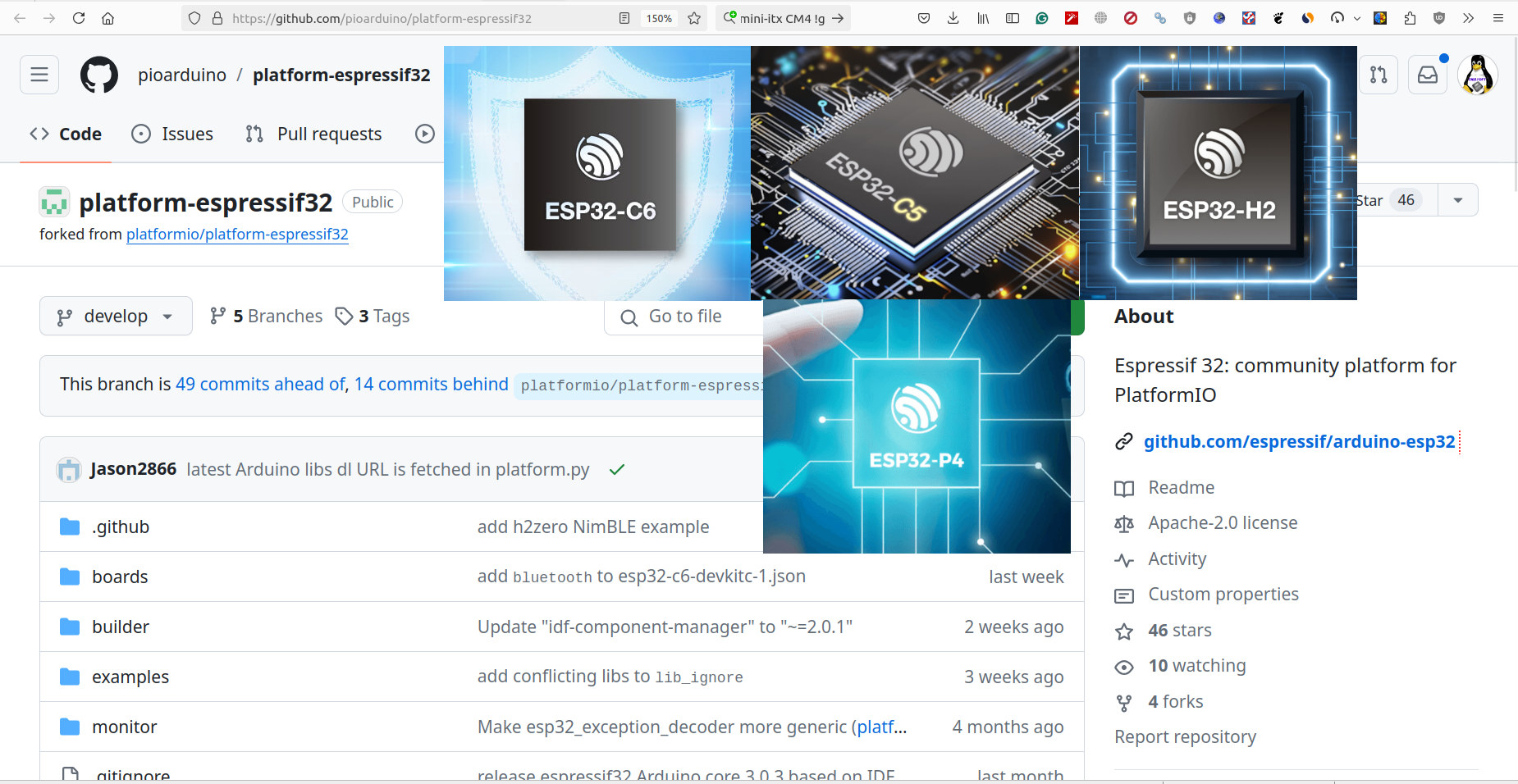
platform-espressif32 fork to enable PlatformIO support for ESP32-C6, ESP32-C5, ESP32-H2, and ESP32-P4 SoCs
When Espressif Systems released Arduino ESP32 Core 3.0.0 we noted that PlatformIO support was in doubt due to business issues between Espressif and Platform IO developers. There has been no progress since then, and PlatformIO is not even reviewing or merging community contributions to their platform-espressif32 library. So if you want software that’s officially supported by Espressif, you should stick to the Arduino ESP32 Core. But if you are a fan of PlatformIO for ESP32, there’s hope even for the newer chips like ESP32-C6, ESP32-H2, and ESP32-P4 among others, as pioarduino community members have now forked the platform-espressif32 library to keep the project alive. Users can still rely on the official PlatformIO repository for existing ESP32 boards and microcontrollers, but new ESP32-C6, ESP32-H2, ESP32-C5, ESP32-H4, and ESP32-P4 SoC will only be supported by the fork. pioarduino which stands for “people initiated optimized arduino” will maintain the fork, and currently, Arduino […]
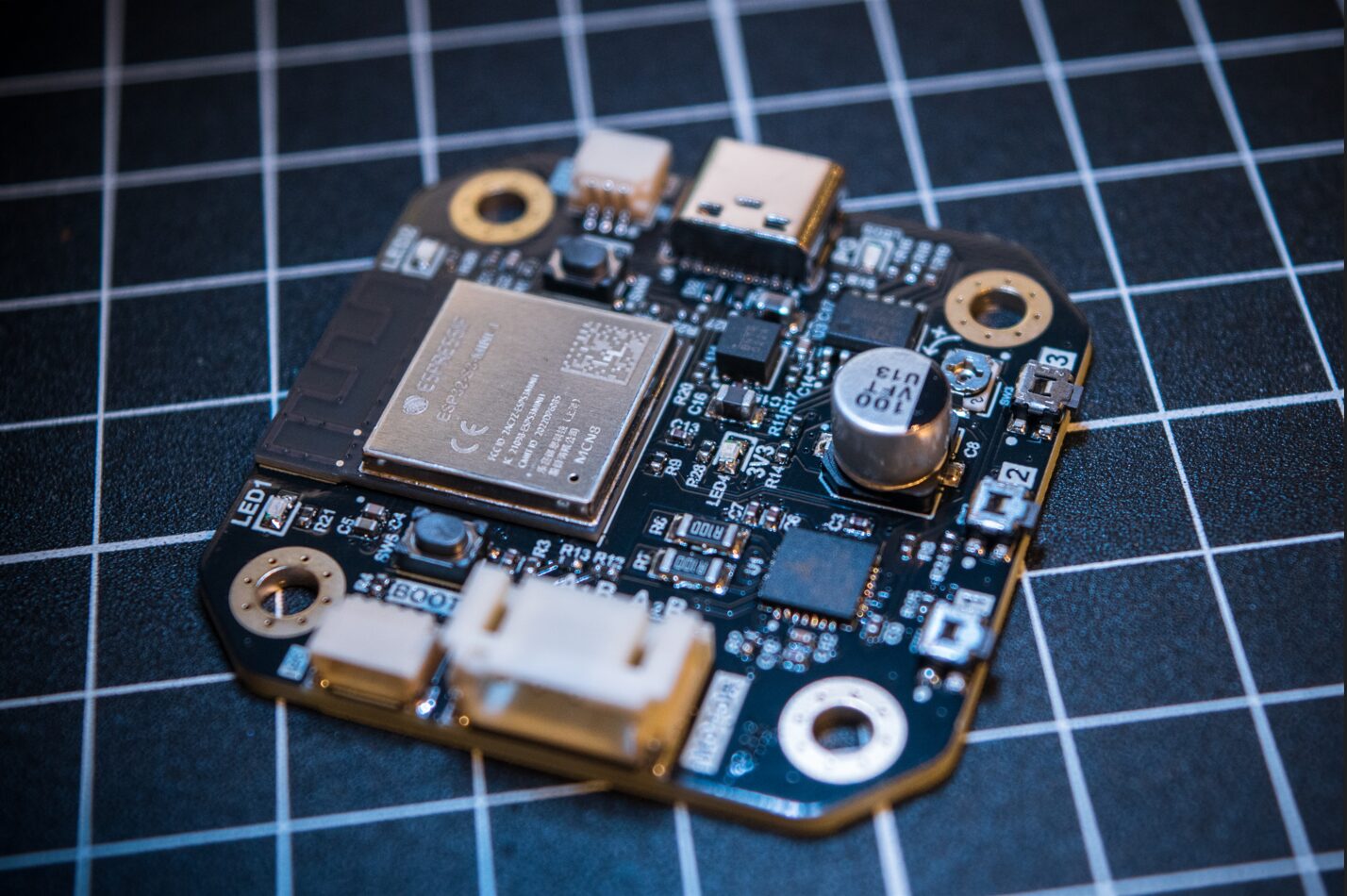
Integrated motor driver and controller bundles ESP32-S3 and TMC2209 for IoT applications
The PD Stepper is a NEMA 17 integrated stepper motor driver and controller board powered by USB power delivery that combines an ESP32-S3 wireless microcontroller, the Trinamic TMC2209 ultra-silent motor driver, and other components onto a single board for Smart Home and automation applications. The maker, Josh R., states that the PD Stepper isn’t another “just because we can” project. It addresses the need for an integrated motor driver and controller module that can used in compact or space-constrained designs. The ESP32-S3 SoC controls the other components on the board and provides wireless connectivity as well as access to development tools and libraries such as ESPHome and ESP-Now. The motor driver IC, Analog Devices’s Trinamic TMC2209, offers efficient, noiseless control of two-phase stepper motors. Other onboard components and connectors include an AS5600 magnetic rotary position sensor, a 3.3V buck converter, a Qwiic/Stemma QT connector, a motor connector, and an AUX […]
Arduino Core for ESP32 gets a Zigbee wrapper library
Some of the newer Espressif Systems wireless SoCs such as the ESP32-H2 and ESP32-C6 support Zigbee through their built-in 802.15.4 radio. It’s been working since the release of the ESP-IDF 5.1 framework along with the ESP-Zigbee-SDK for a while, but Arduino support was less straightforward. But this is about to change as an Espressif engineer nicknamed P-R-O-C-H-Y has recently added a Zigbee wrapper library for the ESP-Zigbee-SDK to Arduino Core for ESP32 that works with ESP32-C6 and ESP32-H2 as standalone nodes and other SoC can be used as radio co-processor attached to an RPC (802.15.4 radio layer). The wrapper library currently supports the following: Zigbee classes and all Zigbee roles Zigbee network scanning Allow multiple endpoints on the same Zigbee device (not tested yet) Supported Home Assistant devices On/off light + switch Color Dimmable light + switch Setting Manufacturer and model name Other tasks currently planned include supporting “Temperature sensor […]
WiCAN Pro – An ESP32-S3-powered OBD scanner for vehicle diagnostics with Smart Home integration (Crowdfunding)
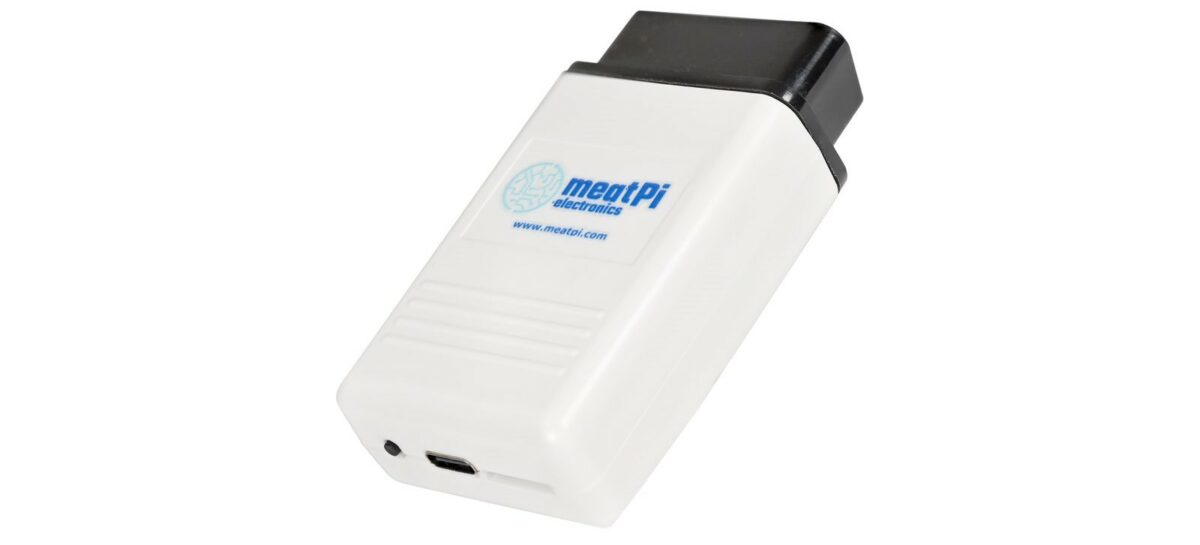
MeatPi Electronics introduced the WiCAN Pro, an ESP32-S3-based OBD scanner, and the successor to WiCAN-OBD. Equipped with an OBD-II interface IC, it provides full support for all legislated OBD-II protocols. It offers compatibility with multiple CAN Bus protocols, including three standard CAN Bus and single-wire CAN Bus. The previous generation WiCAN module came in an OBD or USB-based version. The WiCAN Pro only has an OBD interface, but another significant difference from the previous product is that it features a USB host port. This port can power USB devices up to 1.5 amps at 5 volts and enables capabilities like adding GPS or cellular-based radios, like with meatPi’s ESPNetLink add-on. WiCAN Pro specifications: Wireless Module – ESP32-S3-WROOM-1-N16R8 SoC – Espressif Systems ESP32-S3R8 dual-core Tensilica LX7 @ up to 240 MHz with vector instructions for AI acceleration, 512KB RAM, 8MB PSRAM Storage – 16 MB flash Wireless – 2.4 GHz WiFi […]
$119 MoreSense MS-06 air quality monitor features a Sensirion SCD40 sensor and an ESP32-S3 MCU
The MoreSense MS-06 is an ESP32-S3-based air quality monitor that takes CO², temperature, and humidity readings through a Sensirion SCD40 sensor which offers reliable performance and a lifespan of more than ten years. The MS-06 monitor’s results are identical to the Aranet4’s (considered best-in-class), putting it in a pretty good spot accuracy-wise. It is the latest entry in the MoreSense line of air quality monitors and comes with a more compact design and a touchscreen display. The built-in web server runs an interface that displays measurements, historical data visualizations, setup options, and firmware updates. Operation is completely local; sensor data can be stored on the device or a microSD card. The MoreSense MS-06 air quality sensor can be used to control a ventilation system, contributing to significant energy savings. This can be achieved through your home automation system or by using a smart plug. MoreSense MS-06 specifications: Microcontroller – ESP32-S3 […]