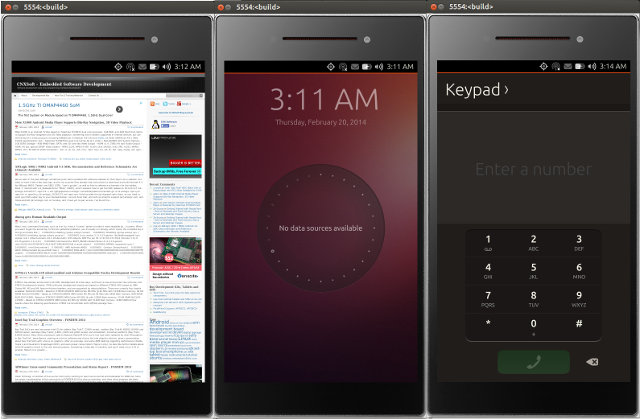
Canonical has just announced Meizu (China) and Bq (Europe) will be the first manufacturers to launch Ubuntu Touch phones at the end of 2014. But if you want to try Ubuntu Touch, and don’t own a Google Nexus 4 or 7, or simply don’t want to flash Ubuntu Touch to your devices, you can do so using Ubuntu Touch x86 Emulator in your computer running Ubuntu , or in an Ubuntu Virtual machine in Virtualbox or VMWare. The emulator has been available since last November, but Ricardo Salveti announced an updated version, the first public preview, with the following changes: Better TLS handling (not using the Android slots, but using pthread_set/getspecifics instead) Qt packages compatible with OpenGL ES 2.0 available at https://launchpad.net/~rsalveti/+archive/qt-gles-test It has been tried on Ubuntu Trusty (14.04), but I could run it just fine on Ubuntu Saucy (13.10), by following the instructions below in a terminal: Download […]
DragonBox Pyra Open Source Handheld Game Console To Feature TI OMAP5432 SoC.. or AllWinner A80, or Intel Bay Trail, or Qualcomm Snapdragon…
Pandora is an open source handheld console which development started as far back as 2007. The project has had ups and downs, and some people have yet to receive the device they pre-ordered. As many components are now more difficult to source, Pandora has reach end-of-life, as Pandora 2 is now being developed with a subset of the original team, but has been renamed to DragonBox Pyra to start afresh. The new version aims to take to the good aspects of the original Pandora, and improve on the bad ones, so that DragonBox will have a faster hardware with a better looking case and better control. Here are the specifications listed on the project website: SoC – Texas Instruments OMAP 5432 SoC with 2x ARM Cortex-A15 @ 1.7Ghz with NEON SIMD, 2x ARM Cortex-M4, Imagination Technologies PowerVR SGX544-MP2 GPU for 3D graphic, and Vivante GC320 GPU for 2D graphics System […]
Developers Are Working on Chromecast Functionality From Any Android Apps via Any Android Devices
If you don’t just come back from (too long) holidays, you should know Google has released the Chromecast, a $35 HDMI TV Stick that uses a protocol called DIAL to let users stream online videos on the TV via your mobile device or mirror your Chrome browser on the TV. However, there are currently quite a few limitations. It can only be used with apps specifically designed for Chromecast (e.g. YouTube, Netflix,…), and Chromecast is the only available receiver, and can only be purchased in the US. Luckily these may not be an issue soon… Koushik Dutta (Kouch) has taken care of the first issue by modifying Cyanogenmod to allow any video or audio app to stream the media files via the TV, using Android notifications. Perfect. Moving to the second issue. If you don’t live in the US, you’re still stuck, and if you do live in the US, […]
BeagleBone GamingCape Transforms your BeagleBone Black into an Hand-held Gaming Console
The BeagleBone GamingCape is an open source project featuring the BeagleBone Black together with extra hardware such as a Cape, LCD display, and enclosure that turns your Beablebone board into a battery powered hand-held gaming console. The gaming console, which has been designed within 6 weeks by Max Thrun, has the following key hardware features: 320×240 16Bit Color TFT LCD Analog joystick + 2 Thumb Buttons 3D Gyro, 3D Accelerometer, 3D Magnetometer Headphone Out + Mic In and it can emulate NES, GameBoy, GameBoy Color, GameBoy Advance, Sega Master System, Sega Game Gear, and also run Doom. It will not be mass produced, but the whole design is open source, and the necessary files are available for: The Cape: Schematics, layout, and CadSoft EAGLE file can be found Bill of Materials The Case composed of 11 laser cut pieces of Delrin – 3D files Emulators: Osmose – Sega Master System / […]
Tizen 1.0 SDK and Source Code Release
The Tizen Technical Steering Group has announced, today, the release of Tizen 1.0 “Larkspur”. Tizen 1.0 release provides several new SDK features and improvements including: Simulator: A new browser-based tool that supports the Tizen APIs and allows you to run and debug your web applications, and simulate running applications with various device profiles. IDE: Enhancements include more flexibility around templates and debugging tools. Emulator: Significantly improved emulator performance through Intel’s Hardware Acceleration Manager for Windows and OpenGL acceleration for Linux. Updates to the platform source code include: Web: Support for additional features of W3C/HTML5 specification Location: Support for POI (Point of Interest) and route search Connectivity: Wi-Fi Direct key features added You can see the full list of changes by reading the release notes for the SDK and the source code. Tizen has also added a bug tracker and a wiki for the community and a few back-end changes have been […]
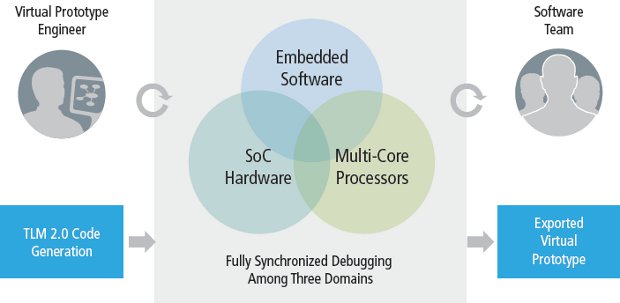
Virtual Hardware Platforms: Test & Debug Software Before the Silicon is Ready
Historically software could only be tested and debugged when the first silicon sample was ready, and the software team could not participate in the design process. But thanks to Virtual Hardware Platforms, software can be executed at speeds close to real time on an abstract model of the hardware, available long before a design has been completed. The virtual platform is designed to simplify the creation and support of virtual prototypes and allow design teams to begin developing software weeks to months before a hardware prototype is available, and software teams can use it as their application development platform. For example, Freescale is using a Virtual Hardware Platform for their new Vybrid Controllers to emulate both Cortex A5 and Cortex M4 cores, as well as peripherals and run OS such as Linux or MQX before the Controllers are ready (Q2 2012). One Virtual Hardware Platform has just won the ACE […]
Android SDK Tools and ADT Revision 17 with VM Acceleration for x86 Emulator
Google has released revision 17 of the SDK Tools and the Eclipse plugin. This release brings new features and bug fixes in for Lint static checker, the build system, and the emulator among other things. Here’s what’s new for Lint in r17: Lint API Check – Added check for Android API calls that require a version of Android higher than the minimum supported version. You can use the @TargetApi annotation to specify local overrides for conditionally loaded code. New Lint Rules – Added over 40 new Lint rules for a total of over 80, including checks for performance, XML layouts, manifest and file handling. Ignoring Lint Warnings – Added ability to suppress Lint warnings in Java code with the new @SuppressLint annotation, and in XML files with the new tools: namespace prefix and ignore attribute. New Eclipse Lint UI – Improved HTML and XML reporting and Eclipse integration. Improvements to […]
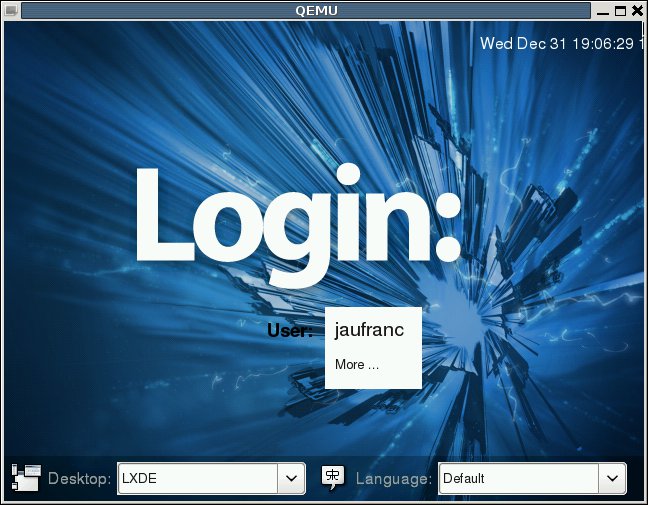
Instructions to Run Raspberry Pi Fedora 14 Remix in QEMU
As mentioned in my previous post, the Raspberry Pi Foundation has just released the Fedora 14 Remix SD card image that can be installed either via installer (easiest method) or using dd / windd as with the previous image. In this blog post, I’ll give the instructions how to run Raspberry Pi Fedora 14 Remix in QEMU using a similar method than the one I used for Debian Squeeze. I tested since in machines with Ubuntu 10.04 LTS and Debian 6.0.4. Download the image using BitTorrent raspberrypi-fedora-remix-14-r1.img.gz.torrent or via the HTTP link available on Raspberry Pi Download page. Decompress the image:
|
1 |
gzip -d raspberrypi-fedora-remix-14-r1.img.gz |
Download kernel 3.0.4 image for qemu, if you don’t have it yet.
|
1 |
wget http://dl.dropbox.com/u/45842273/zImage |
Since the rootfs is full (in the real board it will be resized to the size of the SD Card), we need to increase the size of the rootfs partition. First create and empty 3G […]