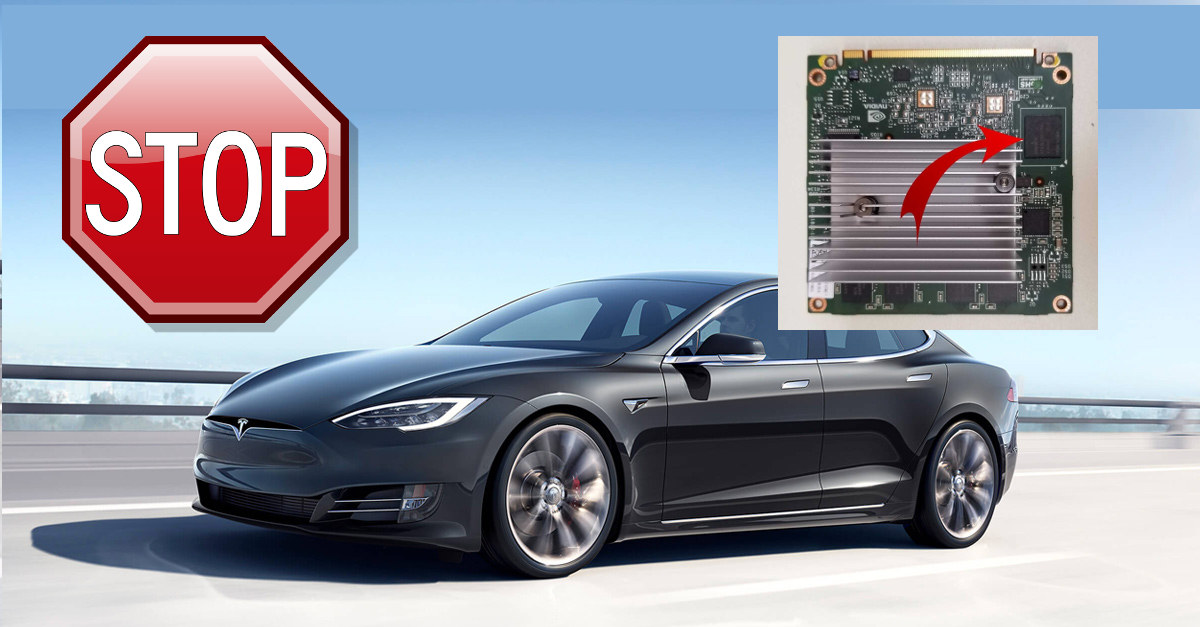
Despite wear-leveling techniques, eMMC flash memories tend to wear out over time as they have limited write cycles. So we’ve seen in the past the importance of wear estimation in eMMC flash chips, and methods to limit write operation such as disabling logging when possible or write the log to RAM with log2ram in order to extend the life of flash-based storage devices. My Xiaomi A1 smartphone basically became unusable after a little over a year due to eMMC flash issues, but that was not that big of an issue since I could just get another phone and the most important data is saved in the cloud nowadays. That’s one thing when it happens to a phone, and another when it happens to your car, as some Tesla S & X owners realized when they lost access to the control screen in the car because the eMMC flash was worn […]
Wear Estimation for Devices with eMMC Flash Memory
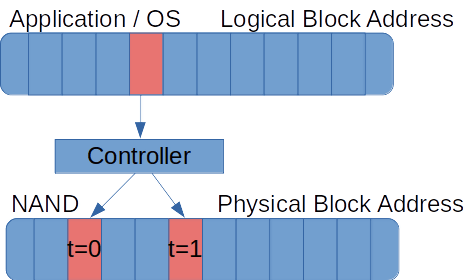
CNXSoft: This is a guest post by Marcel Ziswiler, Platform Manager – Embedded Linux, Toradex and Leonardo Graboski Veiga, Technical Marketing Engineer, Toradex related to Marcel’s upcoming talk “Wear Estimation for Devices with eMMC Flash Memory” at the Embedded Linux Conference 2019 later this month. Flash memory has been an important topic in embedded systems for decades. It allows for drastic improvements to the size and robustness of electronic devices compared to other storage technologies. Other benefits of flash storage include a lack of moving parts and reduced power consumption. However, the challenges that come with flash memory are not as widely publicized in consumer electronics. Among them are limited durability and greater software complexity. As shown in Figure 1, flash memory is everywhere in our daily lives, ranging from devices used specifically to store data, such as thumb drives, SD cards and SSDs, to other consumer electronics that use […]
Xiaomi Mi A1’s eMMC Flash Storage Failing after One Year?
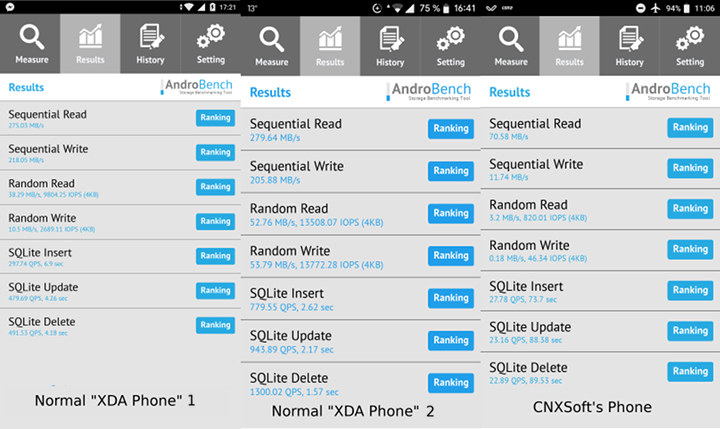
Xiaomi Mi A1 Android One smartphone has been my main and only phone since last October, and I’ve been pretty satisfied with it with monthly firmware updates, and the smartphone performing as I would expect, except I found the camera to be lacking in some conditions, but nothing critical. However on the 7th of this month, the phone felt really sluggish, especially when loading app, as one an app was loaded it would run fairly smoothly most of the time. I’m talking about messaging apps taking 20 to 30 seconds to load, YouTube maybe one minute, and CSR2 Racing game about 5 minutes to load… My first guess was some background app taking lots of resources, or accessing storage very frequently hence slowing down other apps, but Android Battery settings did not report any such apps, and battery life was normal. I still tried to remove some apps, but no […]
Embedded Linux Conference & Open Source Summit Europe 2017 Schedule
The Embedded Linux Conference & IoT summit 2017 took place in the US earlier this year in February, but there will soon be a similar event with the Embedded Linux Conference *& Open Source Summit Europe 2017 to take up in Europe on October 23 – 25 in Prague, Czech Republic, and the Linux Foundation has just published the schedule. It’s always useful to find out what is being discussed during such events, even if you are not going to attend, so I went through the different sessions, and compose my own virtual schedule with some of the ones I find the most interesting. Monday, October 23 11:15 – 11:55 – An Introduction to SPI-NOR Subsystem – Vignesh Raghavendra, Texas Instruments India Modern day embedded systems have dedicated SPI controllers to support NOR flashes. They have many hardware level features to increase the ease and efficiency of accessing SPI NOR […]
Samsung eMMC and UFS 2.0 embedded Flash Chips and Performance in 2016
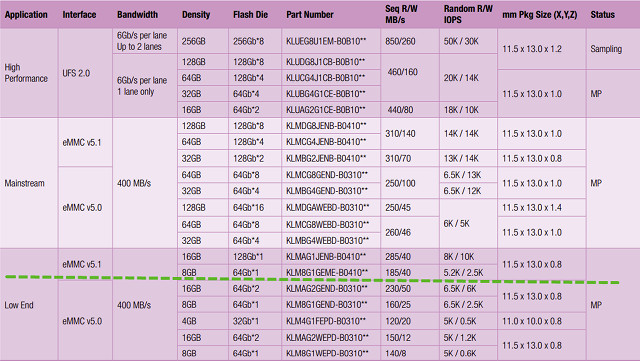
Samsung does not always keep up its website up-to-date when it comes to its embedded flash chips, and performance metrics such as sequential read/write and random read/write values are not shown for all devices. The former is mostly important for data storage, while the latter may make a big difference for the operating systems responsiveness, and applications that rely on many short write and/or read operations. A table with the latest Samsung eMMC 5.0/5.1 and UFS 2.0 chips, and performance metrics somehow dropped in my computer. The company offers low end eMMC 5.0/5.1 flash with capacities between 4 and 16 GB with performance up to 285/40 R/W MB/s and 8K/10K R/W IOPS, mainstream chips between 32 and 128 GB delivery up to 310/140 MB/s and 14K IOPS, and all UFS 2.0 device are faster than any of the eMMC flash (limited in theory to 400 MB/s) with capacity between 16GB […]
Linux on eMMC: Optimizing for Performance – ELC 2012
Ken Tough, principal engineer at Intrinsyc Software, discusses Linux on eMMC at Embedded Linux Conference 2012. Abstract: Embedded devices are increasingly choosing eMMC instead of raw NAND flash as their main storage, for increased independence from component vendors and changing storage densities. This presentation examines Linux configuration for eMMC, how to effectively measure your eMMC performance, and tips to improve it. Topics covered include: filesystem bearing on MMC/SD performance, IO scheduler configuration, and optimal partition layout. Target audience is embedded systems developers or users interested in getting the most out of their eMMC/SD card. You can also download the presentation slides on elinux.org. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com