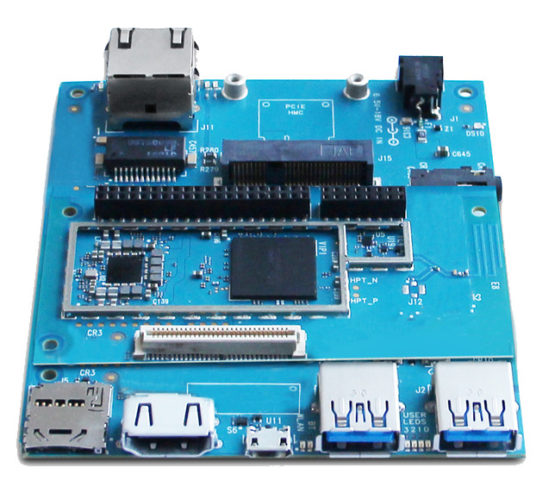
Qualcomm Snapdragon 820E processor was recently launched a version of Snapdragon 820 without LTE modem, easier to source, and targeting the embedded market. The long expected DragonBoard 820c is the first board to feature the new processor, but Geniatech has also been working on their own Developer Board 8 that follows 96Boards CE Extended form factor, and is very similar to DragonBoard 820c. Developer Board 8 (DB8) specifications: SoC – Qualcomm Snapdragon 820E quad core Kryo processor up to 2.35 GHz with Adreno 530 GPU System Memory – 3 GB LPDDR4-1866 (PoP) Storage – 32 GB UFS Flash + micro SD 3.0 (UHS-I) slot Video Output – HDMI 2.0 up to 4K @ 60 Hz Audio – Via HDMI, 3.5mm audio jack Connectivity – Gigabit Ethernet, 802.11 b/g/n/ac WiFi, Bluetooth 4.2, GPS (TBC) USB – 2x USB 3.0 ports, 1x micro USB 2.0 device port Camera – Support for up […]
Qualcomm Snapdragon 820E Launched for the Embedded Market, DragonBoard 820c Board Selling for $199
Qualcomm Snapdragon processors are mainly used in smartphones manufactured in high volume, and in the past if you contacted the company to use their processor for your custom project with a target yearly production of a few thousands pieces, they’d just ignore you. This started to change in late 2016 with the launch of Snapdragon 410E and 600E processors based on mobile version of Snapdragon 410 and 600 processors minus the modem, but instead targeting the embedded space and the Internet of Things, which anybody could purchase easily through Arrow Electronics, and offering a 10-year life cycle. Those are good if you are satisfied with entry-level or mid-range processor, but the company has now announced the launch of Snapdragon 820E for customers requiring better performance for their application. Snapdragon 820E specifications appears to be moslty the same as Snapdragon 820 except for the lack of X12 cellular modem: CPU – 4x Qualcomm […]
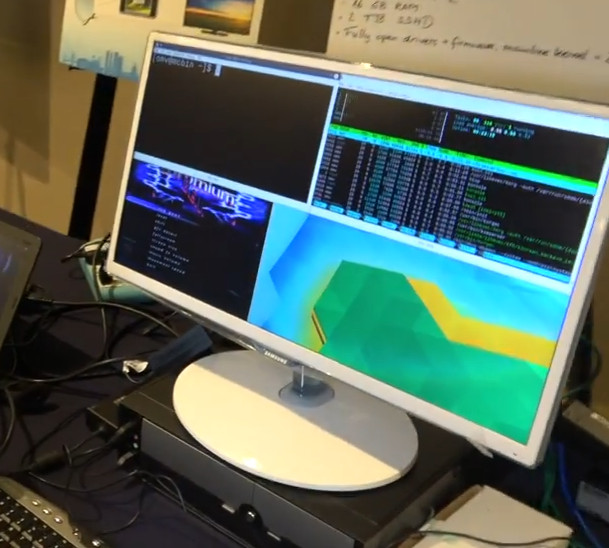
Lab in a Box Concept Embeds x86 Server and 6 ARM Boards into a PC Case for Automated Software Testing
The Linux kernel now has about 20 millions line of code, Arm has hundreds of licensees making thousands of processors and micro-controllers, which end up in maybe hundreds of thousands of different designs, many of which are not using Linux, but for those that do, Linux must be tested to make sure it works. The same stands true for any large software used on multiple hardware platforms. Manual testing is one way to do it, but it’s time consuming and expensive, so there are software and hardware continuous integration solutions to automate testing such as Linaro LAVA (Linaro Automated Validation Architecture), KernelCI automated Linux kernel testing, and Automotive Grade Linux CIAT that automatically test incoming patch series. Both CIAT and KernelCI focus on Linux, and rely on LAVA, with KernelCI leveraging hardware contributed by the community, and proven to be effective as since it’s been implemented, failed build configs dropped […]
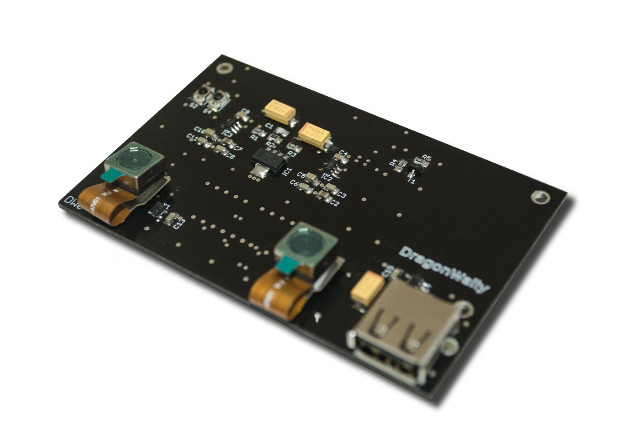
Dragonwally is a Stereoscopic Computer Vision Mezzanine for 96Boards CE Boards
Hardware based on 96Boards specifications may not have the number of sales as Raspberry Pi or Orange Pi boards, but there’s heavily used by Linaro member and other developer working on bleeding edge software. More and more companies are designing boards compliant with the standard, and several new mezzanine expansion boards such as Secure96, were showcased at Linaro Connect SFO 2017, and are yet to be show up on 96Boards Mezzanine page. Another 96Boards mezzanine expansion board in development is Dragonwally, designed for stereoscopic computer vision, currently used with DragonBoard 410c board, and targetting applications such as object recognition, people counting, access control, or driver identification and safety. DragonWally DW0 board specifications: MIPI DSI interface with high speed connector 2x 5MP cameras 1x USB port 96Boards CE compliant The two Brazilian developers working on the project interfaced it with DragonBoard 410c running Linaro Debian, and using OpenCV and Python for […]
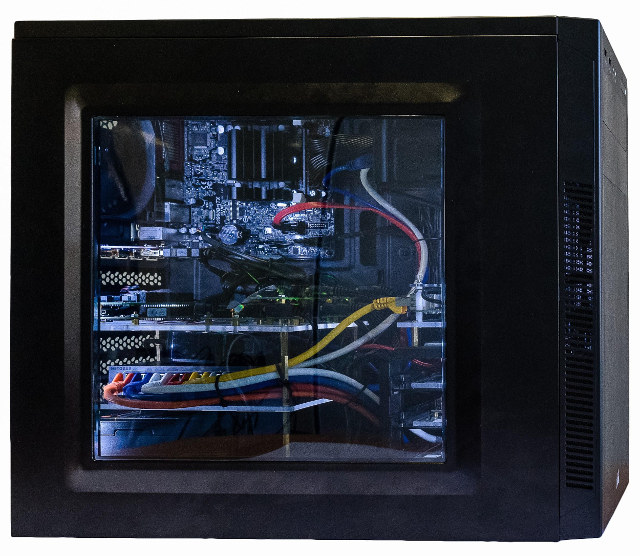
MACCHIATOBin based DIY ARM Desktop, DragonBoard 820c based DIY ARM Laptop (Video)
2017 may be the year of the (ARM based) Linux desktop, sort of. We’ve already seen GIGABYTE ARM development PC powered by a Socionext SC2A11 Synquacer 24-core ARM Cortex A53 processor that will be available in December, and apparently working fairly well already. But there are even more options, as Bernhard Rosenkränzer (Bero) from the Linaro Mobile Group, and unofficial Linaro superstar, has decided to create his own ARM based desktop and laptop, based on respectively MACCHIATOBin board with a Marvell ARMADA 8040 quad core Cortex A72 processor, and DragonBoard 820c board with a Qualcomm Snapdragon 820 quad core Krait processor. Since MACCHIATOBin board complies with mini-ITX form factor, he could simply use off the shelf parts with a standard desktop case with power supply, NVIDIA or AMD Radeon graphics card, 16GB memory modules, and a 2 TB SSD drive. The AMD Radeon card fried due to overheating, so the […]
Amazon AWS Greengrass Brings Local Compute, Messaging, Data Caching & Sync to ARM & x86 Devices
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides cloud computing services to manage & store data from IoT Nodes over the Internet, but in some cases latency may be an issue, and Internet connectivity may not be reliable in all locations. AWS Greengrass provides a solution to those issues by running some of the IoT tasks within the local network in ARM or x86 edge gateways running Linux. You can still manage your devices from AWS cloud, but a Linux gateway running Greengrass Core runtime will be able to run AWS Lambda functions to perform tasks locally, keep device data in sync, and communicate with devices running AWS IoT Device SDK. Greengrass benefits include: Response to Local Events in Near Real-time Offline operation – Connected devices can operate with intermittent connectivity to the cloud, and synchronizes with AWS IoT once it is restored Secure Communication – AWS Greengrass authenticates and encrypts device data […]
Linux 4.9 Release – Main Changes, ARM and MIPS Architectures
Linus Torvalds released Linux 4.9 on Sunday: So Linux 4.9 is out, and the merge window for 4.10 is thus open. With the extra week for 4.9, the timing for the merge window is obviously a bit awkward, and it technically closes in two weeks on Christmas Day. But that is a pure technicality, because I will certainly stop pulling on the 23rd at the latest, and if I get roped into Xmas food prep, even that date might be questionable. I could extend the merge window rather than cut it short, but I’m not going to. I suspect we all want a nice calm winter break, so if your stuff isn’t ready to be merged early, the solution is to just not merge it yet at all, and wait for 4.11. Just so you all know (I already bcc’d the main merge window suspects in a separate mailing last […]
Linux 4.8 Release – Main Changes, ARM & MIPS Architectures
Linus Torvalds has officially released Linux 4.8 last Sunday: So the last week was really quiet, which maybe means that I could probably just have skipped rc8 after all. Oh well, no real harm done. This obviously means that the merge window for 4.9 is open, and I appreciate the people who already sent in some pull requests early due to upcoming travel or other reasons. I’ll start pulling things tomorrow, and have even the most eager developers and testers hopefully test the final 4.8 release before the next development kernels start coming 😉 Anyway, there’s a few stragging fixes since rc8 listed below: it’s a mixture of arch fixes (arm, mips, sparc, x86), drivers (networking, nvdimm, gpu) and generic code (some core networking, with a few filesystem, cgroup and and vm things). All of it pretty small, and there really aren’t that many of them. Go forth and test, […]