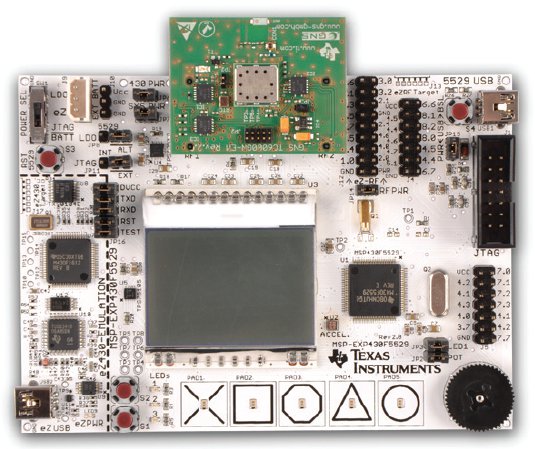
Yesterday, Texas Instruments unveiled the SimpleLink GPS CC4000, a GPS self-contained module that can be interfaced with any MCU or MPU having a UART interface. Due to limited resources of microcontrollers, several GPS features have been implemented in hardware such as the push-to-fix function which can simply be controlled by the MCU via a GPIO to receive National Marena Electronics Association (NMEA) strings containing location, time and velocity information. TI Simplelink GPS CC4000 enables GPS-based applications such as asset tracking, industrial M2M, sports and fitness, and precision timing. It can deliver better than 2.5 meter accuracy and provides pulse-per-second output functions to provide precise location and timing data. It can also automatically reuse previously decoded satellite information thanks to its “watchful-eye” feature in order to deliver fast time to first fix (TTFF) and optimize power consumption. Here are SimpleLink GPS CC4000 key features: Driverless, fully integrated GPS solution which requires […]
FSLBOT: Freescale (Dancing) Robot Kit
Freescale unveiled the FSLBOT prototype last year (and I missed it!), and today, the company has announced further improvements to the Freescale Tower System mechatronics robot and board, a bipedal robot and development board that allows designers to write software for a variety of sensor applications while making a robot walk and respond to touch, motion, vibration, tilt and other external stimuli. The new version of the robot uses a new programming language based on StickOS, has wireless capabilities and adds an Xtrinsic MAG3110 magnetometer. This robot has been designed with the collaboration of StickOS and CPUStick.com with the goal “to create a tool that would enable casual users and consumers of technology to become creators and innovators”. The Freescale FSLBOT Robot Kit comes with the following: Freescale Tower System mechatronics board powered by a 32-bit ColdFire MCU with 64K of RAM and 512K of flash. Leg mechanics and associated […]
iWave Systems Rainbow-G15M-Q7: Qseven SOMs Based on Freescale i.MX 6 Series
iWave Systems, an embedded systems company based in Bangalore, India, has launched Qseven Modules powered by Freescale i.MX 6Quad (quad-core Cortex A9 processor), i.MX 6Duo (dual -core) and i.MX6 Solo. The Rainbow-G15M-Q7 modules are compliant with Qseven specification R1.20 and target the Industrial, Automotive and Medical markets. Here are the modules specifications: CPU: Freescale i.MX6 Cortex A9 Q/D/S core @ 1 GHz Memory: 1GB DDR3 SDRAM– Expandable to 4GB Optional 8GB eMMC Flash On-Board Micro SD slot Qseven Edge Connector : PCIe v2.0 HDMI 1.4 SATA 3.0 Gigabit Ethernet Dual LVDS LCD Support 4 x USB 2.0 Host | 1x USB 2.0 device AC97 Audio 8-Bit SD/MMC CAN1, SPI & I2C ports Debug Port Expansion Connector: 2x Camera CSI MIPI CSI & DSI 24 Bit RGB LCD IF Triple UART 4×4 Key Matrix ESAI (Embedded Software Application Interface) , SPDIF MLB (Media Local Bus), CAN2 I2C, PWM, GPIO, Memory bus Form […]
Microchip Unveils Wi-Fi Comm Demo Board with 32-bit PIC32 MCU
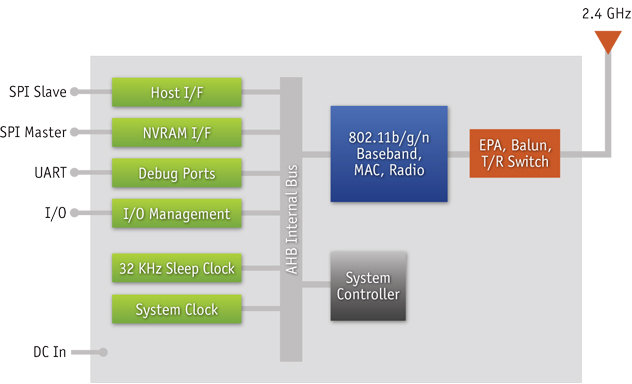
After TI and Qualcomm, here’s another WiFi solution for MCU aimed at the internet of things (IoT). Yesterday, Microchip Technology announced the Wi-Fi Comm Demo Board, which combines a Microchip 32-bit PIC32 microcontroller (PIC32MX695F512H) with a low-power MRF24WB0MA embedded Wi-Fi radio transceiver module. This small (and cheap) demo board can be used to integrate with existing embedded designs and/or to evaluate Wi-Fi connectivity with a 32-bit MCU. Contrary to TI and Qualcomm, the IP network stack is not implemented in hardware, but Microchip provides a TCP/IP stack that can be freely downloaded at http://www.microchip.com/get/A3VP. This TCP/IP stack includes HTML, DHCP, DNS, IPv4/v6, SSL, etc… (See diagram below) The memory footprint is 28-34 KB depending on the modules used. I could not find details about power consumption, but the company claims their solution can also run with just 2 AAA batteries. Microchip explains that this solution can enable the rapid growth […]
Qualcomm Atheros AR4100P Provides WiFi Connectivity to the Internet of Things
In January, Texas Instruments was the first company (to my knowledge) to release a WiFi chip for the internet of things, the SimpleLink Wi-Fi CC3000, where WiFi is mostly implemented in hardware to lower power consumption. Now, the company has some competition with the announcement of Qualcomm Atheros AR4100P, an improved version of its AP4100 WiFi chipset, including IPv4/IPv6 support. The AR4100 targets the home, enterprise, smart grid and home automation and control applications that have lower data rates and transmit or receive data on an infrequent basis. The AR4100 system-in-package (SIP) features the following: Low energy Power saving modes as low as 5 µA Wake-up times as low as 2.2 ms Support for Quad SPI flash for faster wake times Low system resource requirements Low footprint host driver (25K Flash and 8K RAM) Simple, low-cost wireless system integration LGA package simplifies 2- or 4-layer PCB design Near zero RBOM […]
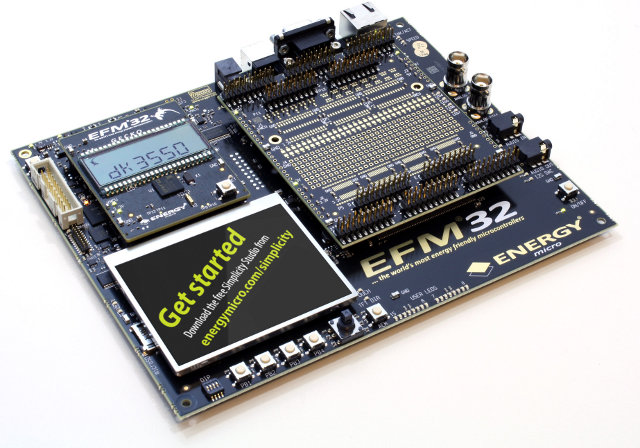
Energy Micro Announces EFM32G-DK3550 Gecko (Cortex-M3) Development Kit
Energy Micro has just announced the availability of the EFM32G-DK3550 development kit based on ARM Cortex-M3 EFM32G890F128 MCU. The kit (pictured below) is based on the main board from the bigger Leopard and Giant Gecko kits and supports SEGGER J-Trace and J-Link in order to reduce the need for additional debugging tools. Here are the development kit specifications: EFM32G890F128 Gecko Cortex-M3 MCU 4MB PSRAM 16MB NOR-Flash 320 x 240 RGB resistive touch TFT display Ethernet MAC/PHY microSD slot audio I/O and I2S DAC USB debug interface, SEGGER J-Link debugger Advanced Energy Monitoring (AEM) system to monitor the prototype’s energy consumption. 2x RS232, IrDA Switches, Joystick, LEDs, potentiometer… EXP32 Prototyping area (right side of the picture) For software development, Energy Micro provides Simplicity Studio suite, which includes energyAware Profiler that can interface with the AEM system via USB, gather all relevant system data, and display real-time graphs of current consumption on a […]
uClinux Running on Freescale Kinetis K70 MCU (Cortex-M4) Module
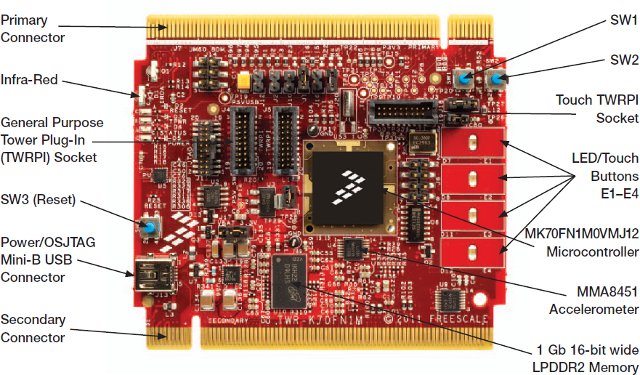
Last year, I posted about Linux for Cortex M3 & M4 Micro-controllers and noted it was difficult to find cost effective Cortex-M based boards able to run uClinux or Linux (RAM being the main issue). Freescale TWR-K70F120M is a module based on Kinetis K70 MCU (Cortex M-4) with plenty of RAM (128MB) to run Linux or uClinux. It is available for 109 USD or 179 USD with Freescale Tower system (TWR-K70F120M-KIT). Here are the key features of the module: Freescale MK70FN1M0VMJ12 Cortex-M4 MCU @ 120 MHz (Product Brief) Touch Tower Plug-in Socket General purpose Tower Plug-in (TWRPI) socket On-board JTAG debug circuit (OSJTAG) with virtual serial port 128 MB DDR2 SDRAM memory 256 MB SLC NAND flash memory Three axis accelerometer (MMA8451Q) Potentiometer Micro-SD Card slot I could not find an open source uClinux implementation for Kinetis K70, but emCraft has a Linux Board Support Package (BSP) for the Freescale TWR-K70F120M-KIT […]
Samsung Exynos 5250 Dual-core Cortex A15 and GAIA SMDK Development Board
Samsung showcased its new Exynos 5250 Dual-core Cortex A15 processor at Mobile World Congress as well as the corresponding Samsung Exynos 5 GAIA SMDK Development board. Announced in November 2011, the new Samsung Exynos 5250 processor features 2 Cortex A15 clocked at 1.7 GHz or 2 GHz, with a Mali-T604 GPU and support for dual-channel 800 MHz LPDDR3 RAM that allows for a data bandwidth of up to 12.8 GB/s. The processor is manufactured using 32-nm HKMG (High-K Metal Gate) technology that reduces leakage by 30% proving lower power consumption. Samsung claims the new Exynos 5 processors are twice as fast and consume twice as less power than its previous Exynos 4 application processor based on Cortex A9. This seems to confirm TI OMAP 5 vs. Nvidia Tegra 3 benchmark results. The Exynos 5250 supports embedded DisplayPort (eDP) interface up to WQXGA resolution (2560×1600), which is handy for Samsung since […]