CNXSoft: This is a guest post by Cesanta If you walked into any Hardware hackathon over the last year, you would see they are about innovation and bringing new ideas to this world and most of them are centered around the connected devices nowadays. However, just walk the floor, talk to the teams and you can quickly see an elephant in the room. The Hackathons are about connected devices, but with the ‘recommended’ and frequently sponsored hardware distributed to the teams such as Intel Galileo, Raspberry Pi, etc…. developers may struggle for a long time to even connect it to the cloud! Not to mention the innovation is usually hindered by a tedious environment setup which takes hours, things to learn about the specific hardware and how it can be programmed using low level languages. So many teams spent most of the time fighting with those issues and oftentimes still […]
Canonical Refocuses Ubuntu Development Efforts on Cloud and IoT, Drops Convergence and Mobile
Mark Shuttleworth has published a new blog post in Ubuntu Insights, and this is not all good news, as the title “Growing Ubuntu for Cloud and IoT, rather than Phone and convergence” implies. Canonical has decided to drop Unity8, and replace it with Gnome in Ubuntu 18.04, and by extension stop any investment in Ubuntu phone and convergence. The main reasons given for the drop were that few commercial partners were interested in the project, preferring to stick with the most popular mobile operating systems like Android, and the community did not see the work as innovation, but instead fragmentation, probably referring to the Mir vs Wayland saga. On the better news, Canonical is still committed to work on Ubuntu desktop, and will focus on the Cloud and IoT applications such as automotive, robotics, networking, and machine learning, for which the company has gone well so far with multiple commercial […]
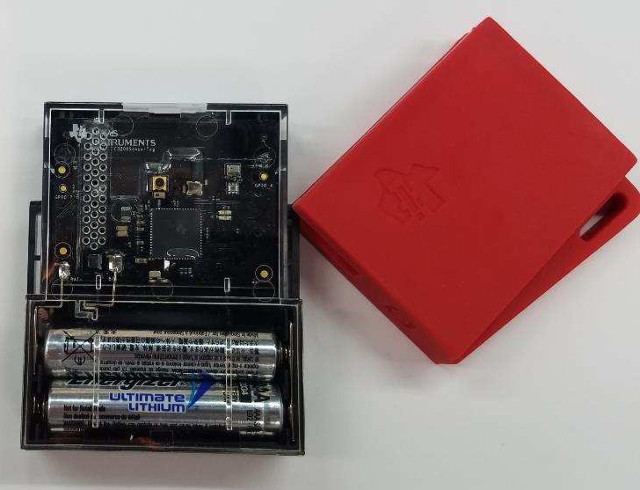
Texas Instruments CC3200 WiFi SensorTag is Now Available for $40
Texas Instruments launched SensorTag in 2013, and at the time there was just a Bluetooth 4.0 LE version with 6 different sensors. I bought one for $25 at the time, and tried it with a Raspberry Pi board and a BLE USB dongle. Since then, the company has launched a new multi standard model (CC2650STK) supporting Buetooth low energy, 6LoWPAN, and ZigBee, and has just started to take orders for CC3200 WiFi SensorTag for $39.99, which seems expensive in a world of $2 ESP8266 modules. But let’s see what the kit has to offer: Wireless MCU – Texas Instruments CC3200 SimpleLink ARM Cortex-M4 MCU @ up to 80 MHz, with up to 256KB RAM, Hardware Crypto Engine, DMA engine Storage – 1 MB serial flash memory Connectivity – 802.11 b/g/n WiFi with on-board inverted-F antenna with RF connector for conducted testing Sensors – Gyroscope, accelerometer, compass, light sensor (OPT3001), humidity […]
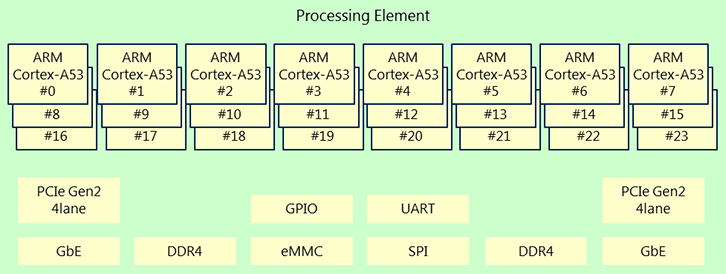
Socionext SC2A11 Low Power Server Processor Comes with 24 Cortex-A53 Cores, Scales up to 1536 Cores via PCIe
Socionext SC2A11 is an 24-core (tetracosa) ARM Cortex-A53 processor designed for low-power server system suitable for edge computing, web server & indexing, cloud computing, and any applications that do not require high single thread peak performance. The company also designed SC2A20 switch SoC that allows up to 64 SC2A11 processors (1536 cores) to communicate over PCI Express using Socionext DDT (Direct Data Transaction). SC2A11 SoC specifications: Processor – 24x ARM Cortex-A53 MPCore cores @ up to 1GHz, with 32KB/32KB I/D L1 cache, 256 KB L2 cache, and 4MB L3 cache Memory I/F – DDR4-2133Mbps 64-bit + ECC Flash I/F – HSSPI, eMMC PCIe – PCI Express Gen2, Root/Endpoint select, 4 lanes (2 systems/ for SoC IF) LAN – 2x 1Gbps with IPSec Network Offload Engine (wire-speed) Serial I/F – UART, I2C, GPIO The company did not provide any info about software, but it’s safe to assume it’s running Linux. There’s […]
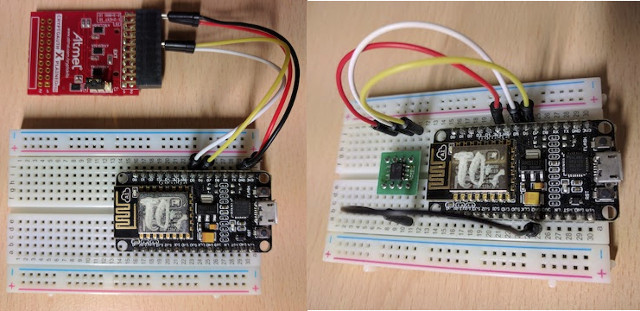
Secure IoT Connectivity with NodeMCU ESP8266 Board, ATECC508A Crypto Chip, Mongoose OS, and AWS IoT
There are many examples of Internet of Things projects, but more often than not the implementation is not secure, either because the device is exposed to the Internet with minimum or no security (worst case), or a gateway (hopefully) provides secure connection to the Internet, but the communication between sensor nodes and the gateway in the local network is not secure, due to memory limitation of the nodes, for example it might be challenging to implement security on ESP8266. Mongoose OS is an open source operating system for the Internet of Things developed by Cesanta working on ESP32, ESP8266, STM32, and TI CC3200, and the developers have demonstrated a secure solution with Mongoose OS running on ESP8266 connecting over a TLS connection to AWS IoT (Amazon Web Service IoT) and using TLS credentials stored in Microchip ATECC508A CryptoAuthentication Device. The addition of ATECC508 chip either using “XplainedPro extension board for […]
Netgem SoundBox is a Speaker with Built-in Set-Top Box Features
Netgem, a company specializing in Connected TV & Home, has sent a press release about profit growth, and two new “innovations int its smart home roadmap” with voice control with Amazon, and SoundBox, a connected speaker which embeds set-top box technology. Netgem does not sell directly to consumers, but instead sell its products and solutions to service providers, and they have not provided a great deal of technical details. But we still know the company has improved Netgem Home Platform, a cloud service allowing the deployment and management of multi-screen features, content discoverability, with support for multi-room, multi-source music service through technology from Voxtok. SoundBox will then offer both video and audio service, and be controlled by voice using Amazon Alexa. The SoundBox will be customized for each Telco to adapt to the needs of local markets. A few more details may eventually surfaced on Netgem’s SoundBox product’s page. They’ll […]
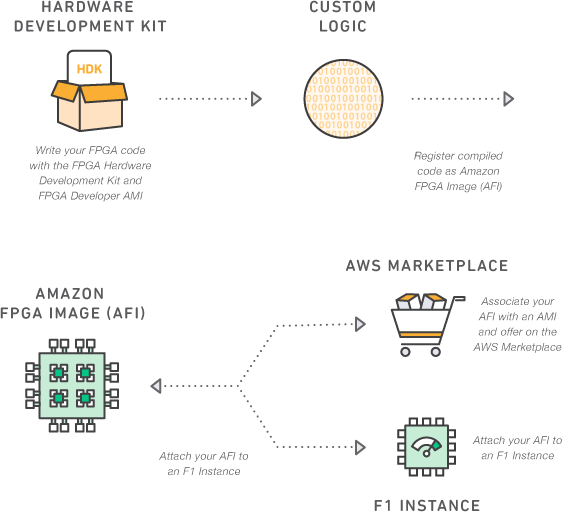
Amazon EC2 F1 Instances Put Xilinx Virtex Ultrascale+ FPGA Boards into the Cloud
We’ve covered several board and modules based on Xilinx Zynq Ultrascale+ MPSoC such as the AXIOM Board and Trenz TE0808 SoM, both featuring ZU9EG MPSoC, with systems selling for several thousands dollars. But I’ve been informed you may not need to purchase a board to use Virtex UltraScale+ FPGAs, which are different from Zynq UltraScale+ since they lack the ARM CPU & GPU and normally feature a more capable FPGA, as last November, Amazon launched a developer preview of F1 instances giving access to this type of hardware from their cloud. That’s the FPGA hardware you’ll be able to access from one F1 instance: Xilinx UltraScale+ VU9P manufactured using a 16 nm process. 64 GB of ECC-protected memory on a 288-bit wide bus (four DDR4 channels). Dedicated PCIe x16 interface to the CPU. Approximately 2.5 million logic elements. Approximately 6,800 Digital Signal Processing (DSP) engines. Virtual JTAG interface for debugging. […]
SigFox Launches Spot’it Low Cost GPS-Free IoT Geolocation Service
Asset tracking was traditionally done using a combination of cellular and GPS technology, and LPWAN standards like LoRa & Sigfox promised to lower the cost of communication and hardware while still relying on GPS technology, but Sigfox has just announced Spot’it geolocation service, which will get rid of GPS all together, and instead use radio signal strength analysis and deep learning techniques in order to provide location information both outdoors and indoors. Key benefits listed by the company include: Lowest-cost IoT location service – Spot’it does not require any additional hardware or software upgrades, and the device does not have to transmit more messages, meaning there is no impact on the solution operating cost for customers. Low energy – Spot’it does not rely on energy intensive GPS technology, nor require additional processing or any more energy than what Sigfox-enabled devices already consume. Enabled through a planetary network – Spot’it is embedded […]