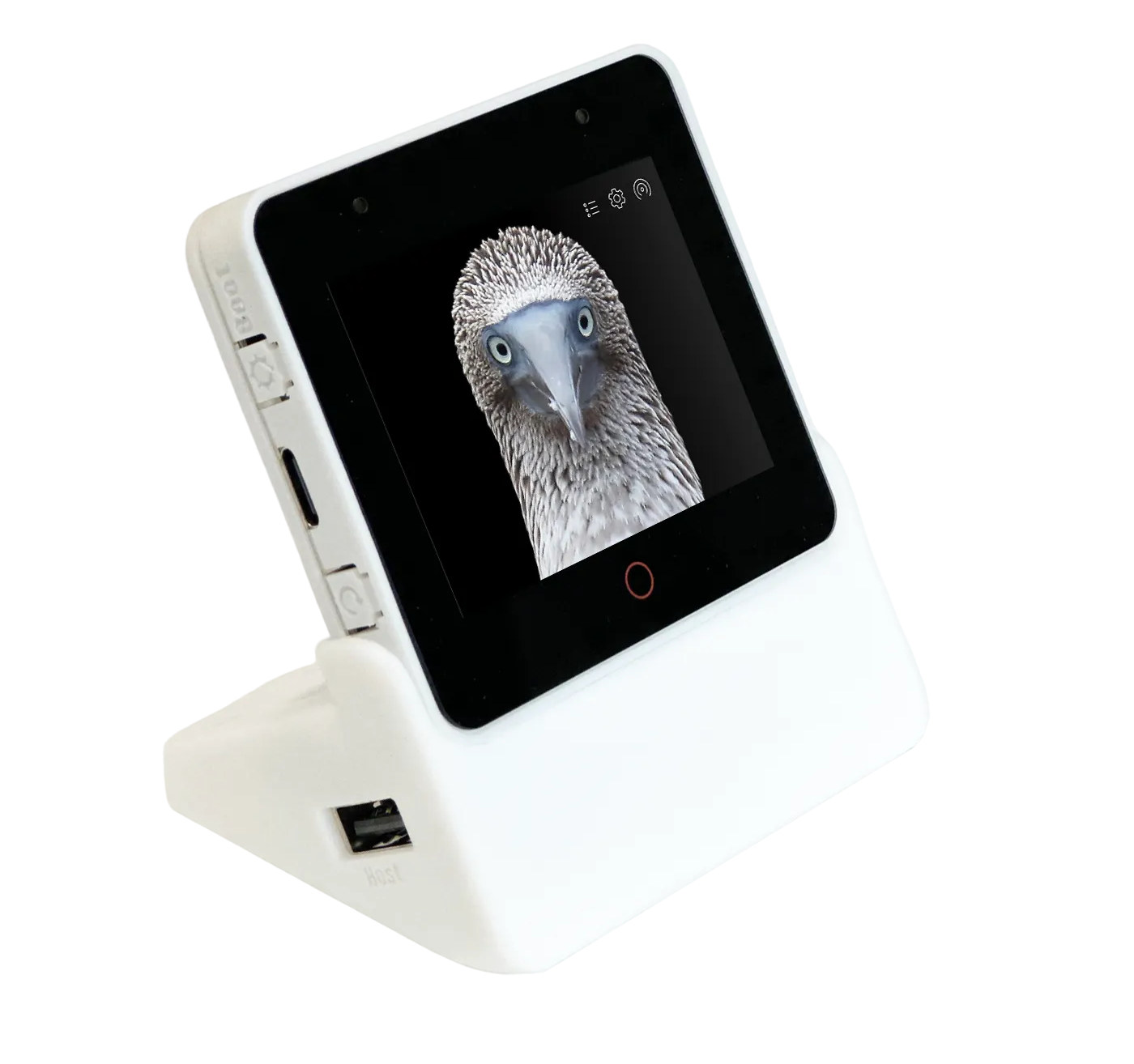
Espressif Systems has launched an update to their ESP32-S3-Box development kit for online and offline voice assistants with the ESP32-S3-BOX-3 devkit that still features a 2.4-inch capacitive touchscreen display with 320×240 resolution, two microphones, a built-in speaker, and a USB-C port, but replaces the PMOD connector by a PCIe connector for various expansion modules. The open-source ESP32-S3 development kit is powered by the ESP32-S3 SoC with AI extensions and can be used to implement all sorts of solutions using the company’s ESP-SR, ESP RainMaker, and Matter solutions such as an offline voice assistant, a chatbot powered by ChatGPT, a handheld gaming console, a tiny robot, a Matter-compatible Smart Home hub, and more. ESP32-S3-BOX-3 specifications: WiSoC – ESP32-S3 dual-core Tensilica LX7 up to 240 MHz with Wi-Fi 4 & Bluetooth 5, AI instructions, 512KB SRAM Memory and Storage – 16MB octal PSRAM and 16MB QSPI flash Display – 2.4-inch capacitive touchscreen […]
SenseCAP Indicator D1Pro Review – An ESP32-S3 & RP2040 IoT devkit with a 4-inch display, LoRa connectivity, sensors
The SenseCAP Indicator D1Pro is an IoT development kit based on ESP32-S3 WiFi & BLE chip, a Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontroller, and offering LoRa connectivity through an SX1262 RF chip. It also features a 4-inch touchscreen display, two Grove interfaces with ADC & I2C, and two USB Type-C ports including one exposing GPIOs, and the D1Pro integrates tVOC and CO2 sensors, plus the kit ships with an external Grove AHT20 TH sensor for temperature and humidity measurements. SenseCAP Indicator D1Pro Features Dual MCUs and GPIO expansion with the Espressif ESP32-S3 and Raspberry Pi RP2040 microcontrollers and support for over 400 Grove-compatible modules. Real-time air quality monitoring thanks to the built-in tVOC and CO2 sensors, and an external Grove AHT20 TH sensor for more precise temperature and humidity readings. Local LoRa Hub for IoT Connectivity thanks to the integrated Semtech SX1262 LoRa chip for connecting LoRa devices to IoT platforms such […]
Using ChatGPT for Robotics – Programming myCobot 280 robotic arm with natural language (Sponsored)
ChatGPT AI chatbot can help engineers write programs, and we recently tested it by letting it write a Python program to read data from an I2C accelerometer. But it can be used for more advanced programs and Microsoft Autonomous Systems and Robotics Group used ChatGPT for robotics and programmed robot arms, drones, and home assistant robots intuitively with (human) language. The long-term goal is to let a typical user control/program a robot without having an engineer write code for the system. Microsoft explains that the current robotics pipelines begin with an engineer or technical user that needs to translate the task’s requirements into code for the system. That’s slow, expensive, and inefficient because a user needs to write code, skilled workers are not cheap, and several interactions are required to get things to work properly. With ChatGPT or other large language models (LLM), a user could “program” the robot with […]
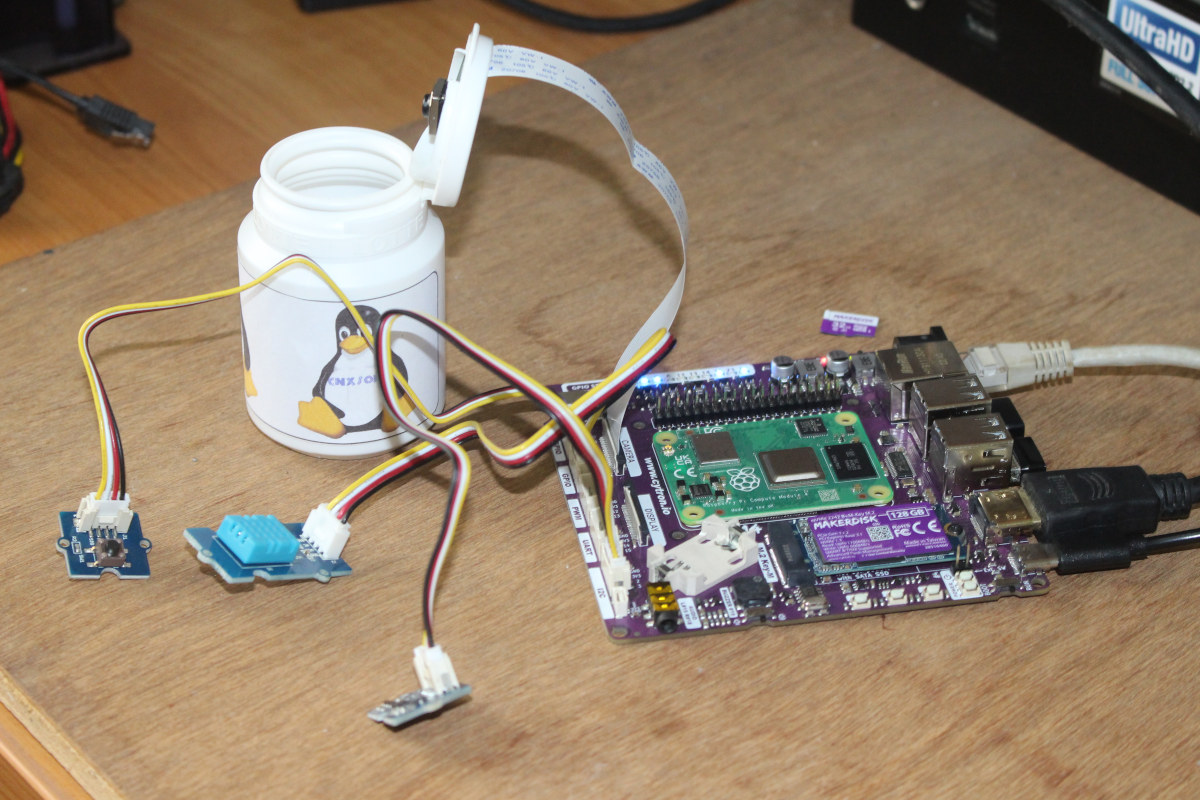
Cytron CM4 Maker Board review – Part 2: NVMe SSD, RTC, Buzzer, Grove modules, ChatGPT…
We’ve already checked out Cytron’s CM4 Maker Board kit with a Raspberry Pi CM4 system-on-module and booted the system with the included 32GB “MAKERDISK” Class 10 microSD card preloaded Raspberry Pi OS in the first part of the review. For the second part of the CM4 Maker review, I’ve mostly used the 128GB NVMe SSD provided by the company and played with other features of the board including the RTC, the buzzer, some Seeed Studio grove modules, and even got help from ChatGPT for one of the Python programs I used. Booting Cytron CM4 Maker Board with the “MAKERDISK” NVMe SSD I connected several Grove modules with GPIO and I2C interfaces, a Raspberry Pi Camera Module 3, an Ethernet cable, two RF dongles for a wireless keyboard and mouse, an HDMI cable to a monitor, and finally inserted the provided 5V/3.5A USB-C power adapter. The MAKERDISK SSD comes with Raspberry […]