Hardkernel released their first Samsung Exynos 5422 octa-core board in July 2014 with ODROID-XU3, which at the time was really a powerful board, but also pricey at $179. Later that year, the company released a cheaper version ($99) called ODROID-XU3 Lite, which I had the chance to review with Ubuntu 14.04 and Android 4.4. The company’s adventure with Exynos 5422 processor did not stop there, as in 2015 they released the smaller and even cheaper ($74) ODROID-XU4 board, and last year launched a fanless version of the board with ODROID-XU4Q featuring a large heatsink. More recently, the company also introduced ODROID-HC1 and ODROID-MC1 solutions for respectively network storage and clusters applications. That’s the short history of Hardkernel Exynos 5422 boards as I remember it, and that means that since 2014, or nearly 4 years so far, the company has kept updating Ubuntu and Android firmware for their board, including the […]
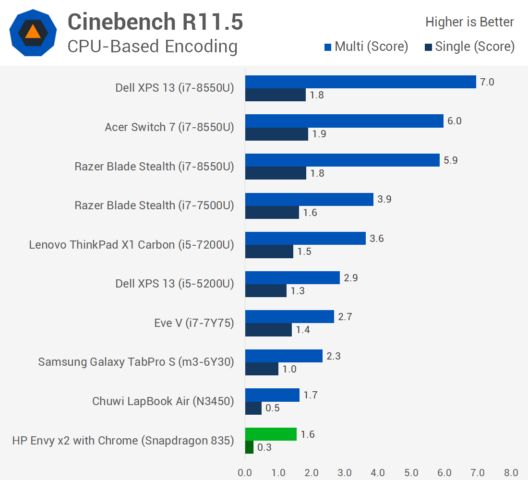
Snapdragon 835 based Always-Connected PC Benchmarks Show Performance Similar to Intel Apollo Lake Laptop (in Most Cases)
The first Windows 10 Arm Mobile PCs were announced a few months ago, all based on Qualcomm Snapdragon 835 processor, with products such as HP Envy x2 (2017) and ASUS NovaGo TP370. The new products promised LTE connectivity, very long battery price, a user experience similar to the one on Intel/AMD based laptops, and at price points ($600 and up) that should command good performance. But TechSpot ran some benchmarks on HP Envy x2 (a $1,000 device), and in most cases, the new always-connected PCs come with performance similar or even lower than a Chuwi laptop based on an Intel Celeron N3450 Apollo Lake processor that sells for a little over $400. That appears to be valid for both x86 emulation and native apps. In some case, the Snapdragon laptop does pretty well with performance close to Core m3 / Core i5-5200U processors such as in the Microsoft Excel workload […]
Intel NUC7CJYSAL “June Canyon” Gemini Lake NUC Mini PC Review with Windows 10 and Ubuntu
The hardware specification for mini PCs has recently evolved past the traditional fixed amount of memory and storage. Now mini PCs are shipping with SODIMM slots allowing RAM expansion and a variety of M.2 or SSD combos providing flexible storage options. Recent mini PCs are also coming to market with desktop processors rather than mobile processors because there has been a gradual acceptance of the necessary inclusion of a small internal fan. In doing so not only is this addressing the key limiting factors for mini PCs but it is also redefines the very definition of a mini PC. Until recently Intel NUCs (Next Unit of Computing) were seen as small-form-factor personal computers primarily because they consisted of the traditional motherboard with a processor, included removable RAM and storage and were enclosed in a case with an external power supply. They were also sold as kits meaning they were essentially […]
Vorke V1 Plus Celeron J3455 Mini PC Review with Windows and Ubuntu
Most Intel based mini PCs use processors classified as ‘Mobile’ as these have lower thermal design power (TDP) ratings which is the maximum amount of heat generated by the processor: However, the new Vorke V1 Plus has incorporated a ‘Desktop’ processor namely the Intel Celeron J3455. On paper this processor looks like it should perform similar to the Intel Pentium N4200 processor but with a tradeoff between being a cheaper processor to purchase but more expensive to run due to the increased power requirements. Geekbuying provided a Vorke V1 Plus for review so let’s start by taking a look at the physical characteristics. The device comes in a plain box and was supplied with the ‘right AC Adapter’ for my country. The first observation is that it is quite a large device. At just over 6” square (153mm) and nearly 1.5” tall (38mm) it is the biggest mini PC I’ve […]
Intel Compute Cards Review – Windows 10 and Ubuntu 17.04 on CD1C64GK, CD1P64GK and CD1M3128MK
The Intel Compute Stick revolutionized the mini PC market through the introduction of x86 based processors making Windows available as an OS option. However, for Intel the biggest target market turned out to be business rather than consumer with digital signage being a key user. As a result Intel have responded with the introduction of the Intel Compute Card. So far they have released four versions of card: and they they differ from compute sticks by no longer being standalone mini PCs but dependent on a dock or host device. The card itself is relatively small with a footprint slightly larger than a standard credit card: and is distinguished by the back being printed with details about the card including the model: The lack of emphasis on the consumer market is also evident in the rather unobtrusive plain packaging: On the end that inserts into the dock or host device […]
Review of GOLE 10 Mini PC with 10.1″ Touchscreen Display – Part 2: Windows 10 Pro
Depending on your point of view, GOLE 10 is a mini PC with a touchscreen display, or a really thick tablet with an inclined display. I’ve already received a sample, and had a look at the hardware in the first part of the review, so in the second I tested the performance and stability, and thought about and test some use cases for this type of products. GOLE 10 (aka F6) Setup and System Info There are various way to use the mini PC, either as a standalone screen without any peripheral connected using the touchscreen, or as a mini PC with USB keyboard and mouse and potential other accessories, or in a dual display setup with the device connected to an HDMI TV or monitor. I decided to connect it to my “test” TV, add a USB 3.0 drive, USB keyboard and mouse, Ethernet cable, and of course the […]
MINIX NEO N42C-4 Pro Review – Part 3: Ubuntu / Linux
In the second part of MINIX NEO N42C-4 review (and on linuxium website), we looked at the device and the performance using Windows. In this third part, we will look at how to install and the performance of using Linux (Ubuntu). The BIOS does not include an option to select Linux as a boot OS and a standard Ubuntu ISO written to a USB will not boot. So to install Ubuntu to the eMMC as dual-boot first it was necessary to respin a standard Ubuntu ISO using my ‘isorespin.sh’ script with the ‘–apollo’ option, and which after creating a LiveUSB using the ‘dd’ command was used to boot and install Ubuntu. First let’s remind ourselves of the hardware configuration by running some standard Linux commands:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 |
linuxium@N42C-4:~$ lsb_release -a Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 17.04 Release: 17.04 Codename: zesty linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ uname -a Linux N42C-4 4.10.0-19-generic #21-Ubuntu SMP Thu Apr 6 17:04:57 UTC 2017 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ inxi -Fc0 System: Host: N42C-4 Kernel: 4.10.0-19-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: N/A Distro: Ubuntu 17.04 Machine: Device: desktop Mobo: MINIX model: N42C-4 v: Default string serial: Default string UEFI: American Megatrends v: 5.12 date: 11/14/2017 CPU: Quad core Intel Pentium N4200 (-MCP-) cache: 1024 KB clock speeds: max: 2500 MHz 1: 897 MHz 2: 2394 MHz 3: 1333 MHz 4: 2319 MHz Graphics: Card: Intel Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Integrated Graphics Controller Display Server: X.org 1.19.3 drivers: modesetting (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) tty size: 204x62 Advanced Data: N/A for root Audio: Card Intel Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Audio Cluster driver: snd_hda_intel Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture v: k4.10.0-19-generic Network: Card-1: Realtek RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller driver: r8169 IF: enp1s0 state: up speed: 1000 Mbps duplex: full mac: a0:1e:0b:09:64:59 Card-2: Intel Device 24fb driver: iwlwifi IF: wlp2s0 state: down mac: 5e:8e:91:6c:84:80 Drives: HDD Total Size: NA (-) ID-1: /dev/mmcblk0 model: N/A size: 31.3GB Partition: ID-1: / size: 9.8G used: 5.8G (62%) fs: ext4 dev: /dev/mmcblk0p5 RAID: No RAID devices: /proc/mdstat, md_mod kernel module present Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 47.0C mobo: N/A Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A Info: Processes: 212 Uptime: 7 min Memory: 633.4/3796.5MB Client: Shell (review-tests.sh) inxi: 2.3.8 linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev tmpfs 380M 6.3M 374M 2% /run /dev/mmcblk0p5 9.8G 5.8G 3.6G 62% / tmpfs 1.9G 12K 1.9G 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mmcblk0p2 96M 74M 23M 77% /boot/efi tmpfs 380M 172K 380M 1% /run/user/1000 /dev/mmcblk0p4 19G 17G 2.1G 90% /media/linuxium/309476E59476ACCA tmpfs 380M 0 380M 0% /run/user/0 linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ lsblk -a NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT loop0 7:0 0 0 loop loop1 7:1 0 0 loop loop2 7:2 0 0 loop loop3 7:3 0 0 loop loop4 7:4 0 0 loop loop5 7:5 0 0 loop loop6 7:6 0 0 loop loop7 7:7 0 0 loop mmcblk0 179:0 0 29.1G 0 disk ├─mmcblk0p1 179:1 0 499M 0 part ├─mmcblk0p2 179:2 0 100M 0 part /boot/efi ├─mmcblk0p3 179:3 0 16M 0 part ├─mmcblk0p4 179:4 0 18.5G 0 part /media/linuxium/309476E59476ACCA └─mmcblk0p5 179:5 0 10G 0 part / mmcblk0boot0 179:8 0 4M 1 disk mmcblk0boot1 179:16 0 4M 1 disk mmcblk0rpmb 179:24 0 4M 0 disk linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ sudo lshw -C cpu *-cpu description: CPU product: Intel(R) Pentium(R) CPU N4200 @ 1.10GHz vendor: Intel Corp. physical id: 34 bus info: cpu@0 version: Intel(R) Pentium(R) CPU N4200 @ 1.10GHz slot: SOCKET 0 size: 2399MHz capacity: 2500MHz width: 64 bits clock: 100MHz capabilities: x86-64 fpu fpu_exception wp vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp constant_tsc art arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperf tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx est tm2 ssse3 sdbg cx16 xtpr pdcm sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave rdrand lahf_lm 3dnowprefetch cat_l2 intel_pt tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid fsgsbase tsc_adjust smep erms mpx rdt_a rdseed smap clflushopt sha_ni xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1 xsaves dtherm ida arat pln pts cpufreq configuration: cores=4 enabledcores=4 threads=4 linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ sudo lshw -C memory *-firmware description: BIOS vendor: American Megatrends Inc. physical id: 0 version: 5.12 date: 11/14/2017 size: 64KiB capacity: 5056KiB capabilities: pci upgrade shadowing cdboot bootselect socketedrom edd int13floppy1200 int13floppy720 int13floppy2880 int5printscreen int9keyboard int14serial int17printer acpi usb biosbootspecification uefi *-memory description: System Memory physical id: 2e slot: System board or motherboard size: 4GiB *-bank:0 description: SODIMM DDR3 Synchronous 1600 MHz (0.6 ns) product: M471B5173EB0-YK0 vendor: Samsung physical id: 0 serial: 96537C8F slot: ChannelA-DIMM0 size: 4GiB width: 64 bits clock: 1600MHz (0.6ns) *-bank:1 description: DIMMProject-Id-Version: lshwReport-Msgid-Bugs-To: FULL NAME <EMAIL@ADDRESS>POT-Creation-Date: 2009-10-08 14:02+0200PO-Revision-Date: 2012-02-02 13:04+0000Last-Translator: Joel Addison <jaddi27@gmail.com>Language-Team: English (Australia) <en_AU@li.org>MIME-Version: 1.0Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bitX-Launchpad-Export-Date: 2017-04-04 11:54+0000X-Generator: Launchpad (build 18335) [empty] physical id: 1 slot: ChannelB-DIMM0 *-cache:0 description: L1 cache physical id: 32 slot: CPU Internal L1 size: 224KiB capacity: 224KiB capabilities: synchronous internal write-back configuration: level=1 *-cache:1 description: L2 cache physical id: 33 slot: CPU Internal L2 size: 2MiB capacity: 2MiB capabilities: synchronous internal write-back unified configuration: level=2 linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ free -mh total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 3.7G 573M 2.4G 158M 744M 2.8G Swap: 472M 0B 472M linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ sudo lshw -C network *-network description: Ethernet interface product: RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller vendor: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. physical id: 0 bus info: pci@0000:01:00.0 logical name: enp1s0 version: 07 serial: a0:1e:0b:09:64:59 size: 1Gbit/s capacity: 1Gbit/s width: 64 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: pm msi pciexpress msix vpd bus_master cap_list ethernet physical tp mii 10bt 10bt-fd 100bt 100bt-fd 1000bt 1000bt-fd autonegotiation configuration: autonegotiation=on broadcast=yes driver=r8169 driverversion=2.3LK-NAPI duplex=full firmware=rtl8168e-3_0.0.4 03/27/12 ip=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes port=MII speed=1Gbit/s resources: irq:369 ioport:e000(size=256) memory:a1200000-a1200fff memory:c0000000-c0003fff *-network description: Wireless interface product: Intel Corporation vendor: Intel Corporation physical id: 0 bus info: pci@0000:02:00.0 logical name: wlp2s0 version: 10 serial: 5e:8e:91:6c:84:80 width: 64 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: pm msi pciexpress bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless configuration: broadcast=yes driver=iwlwifi driverversion=4.10.0-19-generic firmware=22.361476.0 latency=0 link=no multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11 resources: irq:373 memory:a1100000-a1101fff linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ dmesg | grep "MMC card" [ 2.456272] mmc0: new HS400 MMC card at address 0001 linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ lsusb Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0003 Linux Foundation 3.0 root hub Bus 001 Device 003: ID 8087:0aa7 Intel Corp. Bus 001 Device 005: ID 046d:c52b Logitech, Inc. Unifying Receiver Bus 001 Device 004: ID 10d5:55a4 Uni Class Technology Co., Ltd Bus 001 Device 002: ID 1a40:0101 Terminus Technology Inc. Hub Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub linuxium@N42C-4:~$ linuxium@N42C-4:~$ lspci 00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Host Bridge (rev 0b) 00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Integrated Graphics Controller (rev 0b) 00:0e.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Audio Cluster (rev 0b) 00:0f.0 Communication controller: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Trusted Execution Engine (rev 0b) 00:12.0 SATA controller: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series SATA AHCI Controller (rev 0b) 00:13.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series PCI Express Port A #2 (rev fb) 00:13.2 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series PCI Express Port A #3 (rev fb) 00:15.0 USB controller: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series USB xHCI (rev 0b) 00:1c.0 SD Host controller: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series eMMC Controller (rev 0b) 00:1f.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series Low Pin Count Interface (rev 0b) 00:1f.1 SMBus: Intel Corporation Celeron N3350/Pentium N4200/Atom E3900 Series SMBus Controller (rev 0b) 01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller (rev 07) 02:00.0 Network controller: Intel Corporation Device 24fb (rev 10) linuxium@N42C-4:~$ |
This shows the memory will be dual-channel once the second slot (bank:1) is populated and also confirms that the eMMC 5.1 (mmc0) is running […]
MINIX NEO N42C-4 Mini PC Review – Part 2: Windows 10 Pro
MINIX NEO N42C-4 is the first Apollo Lake mini PC from the company, which also happens to be their first one with a fan, using internal antennas for WiFi and Bluetooth, and offering user-upgradeable storage and memory thanks to M.2 and SO-DIMM slots. The device also features three video output via HDMI 2.0, mini DiplayPort, and USB Type C ports supporting up to three independent display. I’ve received a sample and already checked the hardware, and showed how to install an M.2 SSD and SO-DIMM RAM to the device in the first part of the review entitled MINIX NEO N42C-4 Triple Display Capable Mini PC Review – Part 1: Unboxing and Teardown, so I’ll report my experience with Windows 10 Pro in the second part of the review, and there should also be a third part specifically dealing with Linux support. MINIX NEO N42C-4 Setup, System Info, BIOS The device […]