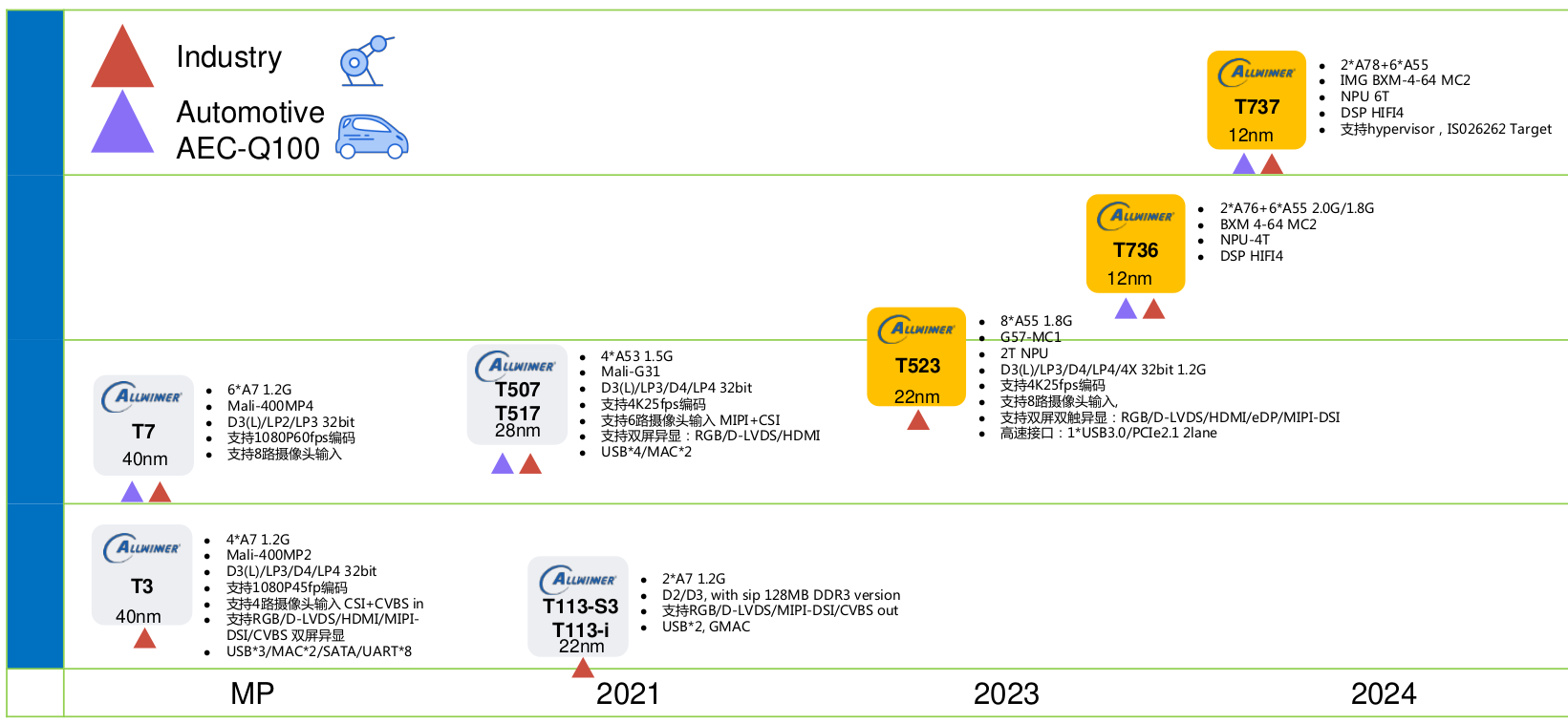
Allwinner should launch new Cortex-A76/A55 and Cortex-A78/A55 processors in 2024 according to the company’s roadmap including the Allwinner A736/A737 for tablets and the T736/T737 designed for automotive and industrial applications. In recent years, we’ve seen Rockchip and Amlogic introduce more powerful processors with the Rockchip RK3588 octa-core Cortex-A76/A55 processor and Amlogic A311D2 octa-core Cortex-A73/A53 or the more recent Amlogic S928X Cortex-A76/A55 for 8K TV boxes. But we’re still seeing some recent boards based on Allwinner Cortex-A7 32-bit processors, although recently we covered the Allwinner A523 octa-core Cortex-A55 processor for tablets. So today, I decided to go on a quest to find out whether Allwinner plans to use 64-bit Arm “big” cores in their future design. I first ended up on the linux-sunxi website where they list the Allwinner T736 octa-core “sun60i” processor with two Cortex-A76 cores and six Cortex-A55 cores, but no other details. This leads me to some “notes” […]
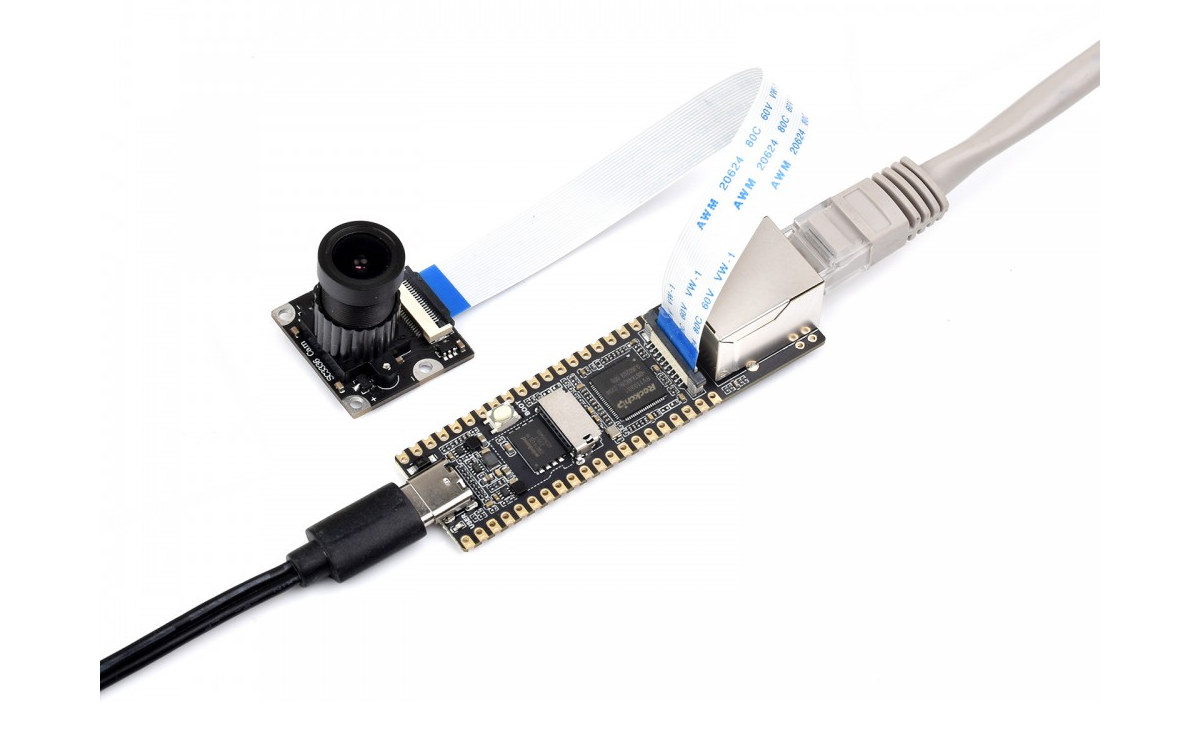
LuckFox Pico Rockchip RV1103 Cortex-A7/RISC-V camera board comes with an optional Ethernet port
LuckFox Pico is a small Linux camera board based on the Rockchip RV1103 Cortex-A7 and RISC-V AI camera SoC and offered with an Ethernet port in a longer version of the PCB called LuckFox Pico Plus. Both models come with 64MB RAM (apparently embedded in RV1103), a microSD card slot for storage, a MIPI CSI camera connector, a USB Type-C port for power, and a few through holes for expansion through GPIO, I2C, UART, and so on. LuckFox Pico and Pico Plus specifications: SoC – Rockchip RV1103 with Arm Cortex-A7 processor @ 1.2GHz, RISC-V core, 64MB DDR2, 0.8 TOPS NPU, 4M @ 30 fps ISP Storage MicroSD card slot LuckFox Plus only – 1Gbit (128MB) SPI flash (W25N01GV) Camera – 2-lane MIPI CSI connector Networking (LuckFox Pico Plus only) – 10/100M Ethernet RJ45 port USB – USB 2.0 Host/Device Type-C port Expansion – 2x 20-pin headers with up to 24x […]
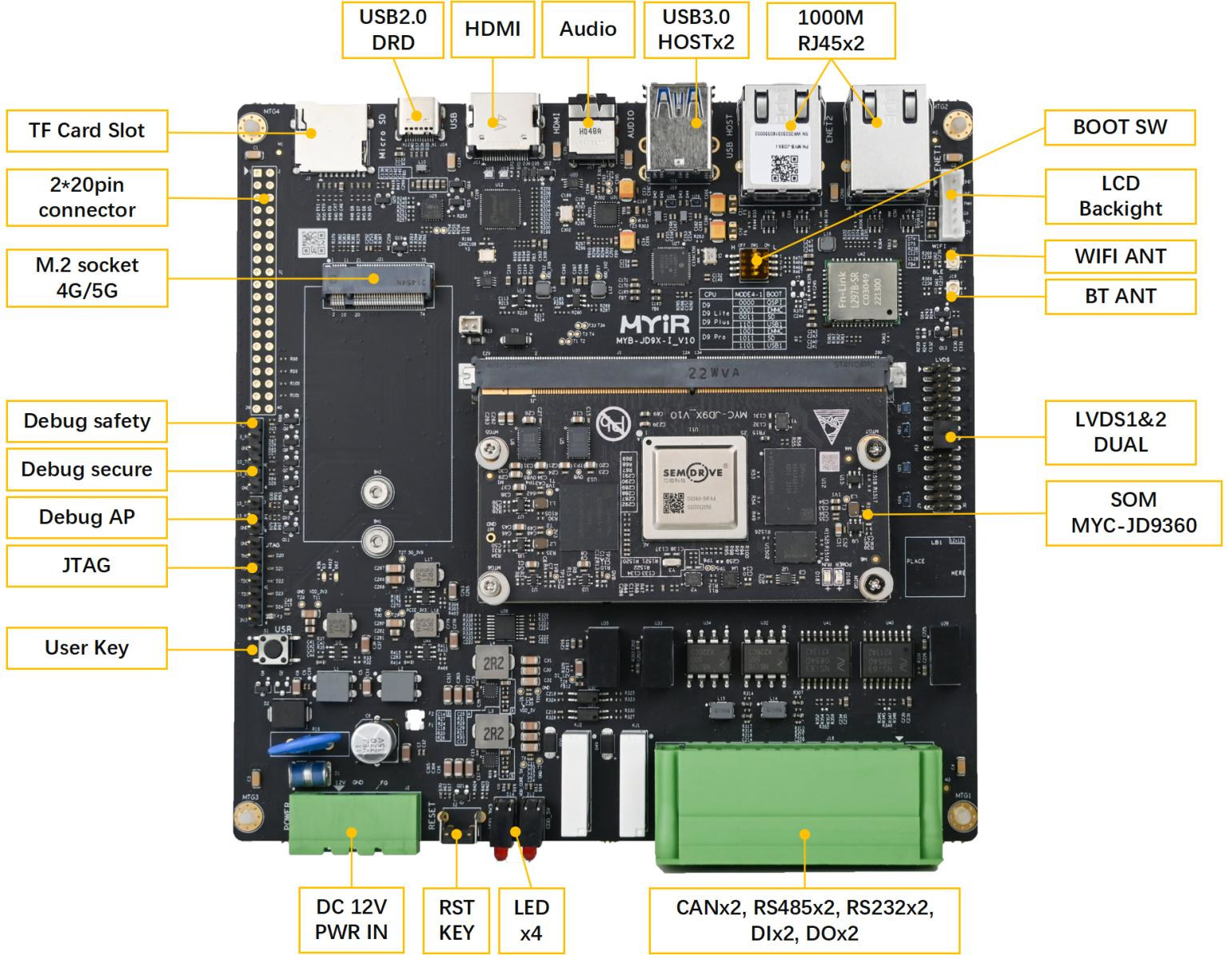
SemiDrive D9-Pro (D9360) Arm Cortex-A55/R5 processor powers industrial CPU module for motor control
MYiR MYC-JD9360 is a CPU Module powered by SemiDrive D9-Pro (D9360) processor with six Arm Cortex-A55 application cores, a dual-core lock-step Cortex-R5 real-time core along with a PowerVR GPU, 4Kp30 H.265/H.264 VPU and a 0.8 TOPS NPU, and designed for motion control and industrial applications. The MYC-JD9360 CPU module also comes with 2GB LPDDR4, 16GB eMMC flash, 16MB QSPI Flash, 256Kbit EEPROM, and exposes I/Os such as PCIe 3.0, USB 3.0, CAN FD, and TSN-enabled Gigabit Ethernet through a 314-pin MXM connector. The company also provides the MYD-JD9360 development board to quickly get started with the module and evaluate the solution. MYiR MYC-JD9360 CPU module with SemiDrive D9-Pro SoC Specifications: SoC – SemiDrive D9-Pro (D9360) CPU Application – Hexa-core Arm Cortex-A55 processor @ 1.6 GHz Real-time – Dual-core lock-step Cortex-R5 cores @ 800MHz GPU – Imagination PowerVR 9XM GPU @ 100 GFLOPS VPU – 4Kp30 H.265/VP8/VP9 video decoder, 4Kp30 H.264 […]
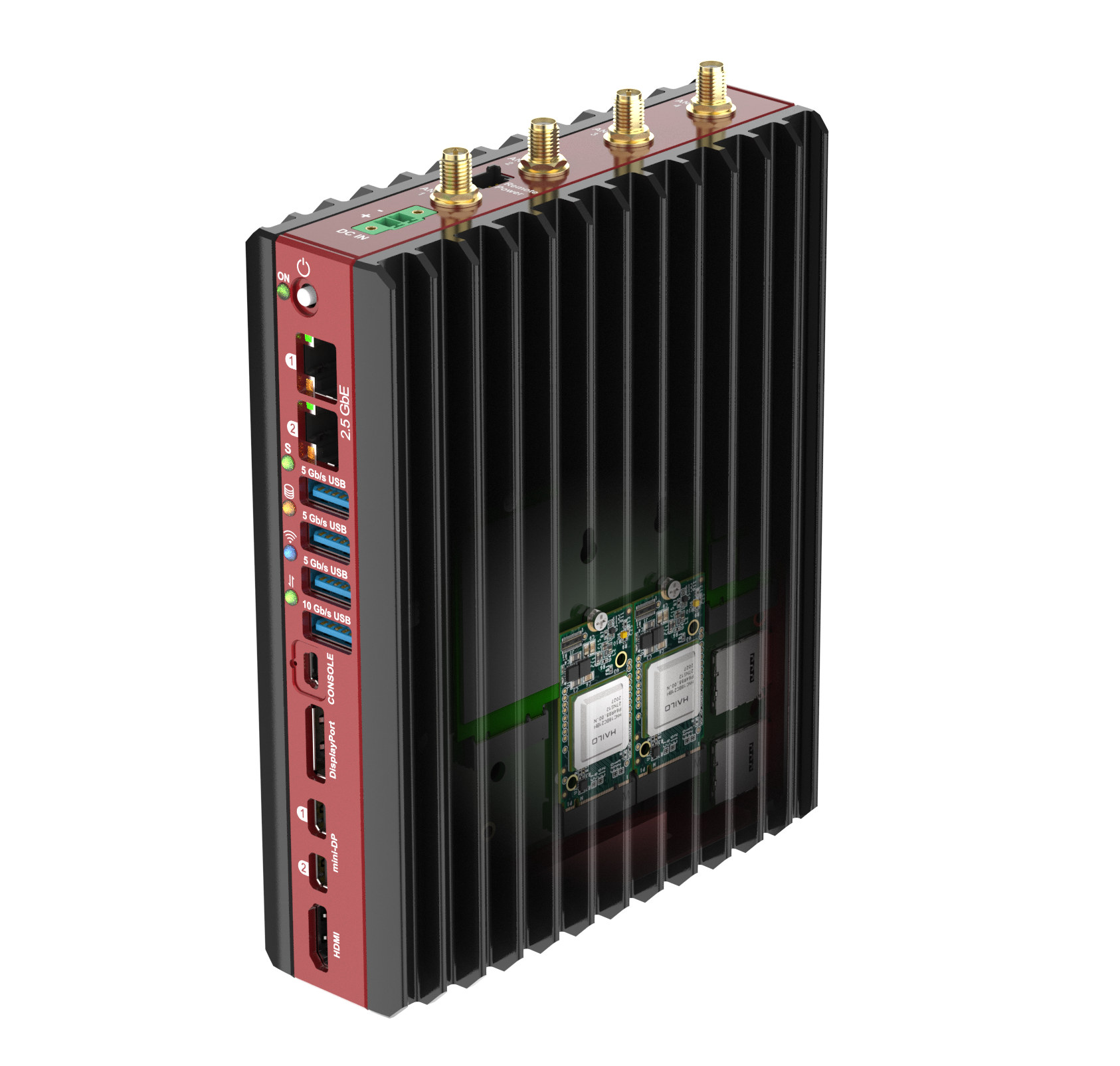
Bedrock R7000 Edge AI fanless computer combines AMD Ryzen 7 7840HS CPU with Hailo-8 AI accelerators
SolidRun Bedrock R7000 Edge AI fanless computer combines an 8-core AMD Ryzen 7840HS/U Zen4 processor and up to three Hailo-8 AI accelerators for artificial intelligence applications in harsh environments with an industrial temperature range of -40ºC to 85ºC. The industrial embedded system comes with up to 64GB DDR5 memory, supports up to three M.2 NVMe SSD, and offers various interfaces such as dual 2.5GbE and four 4K-capable display interfaces using HDMI and DisplayPort. Just like the previous generation mode, the AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000-powered Bedrock V3000 fanless industrial computer, the BedRock R7000 is offered in three different form factors including the 30W and 60W dissipation model with integrated heatsink fins, and a tile variant designed to be fastened to a cold plate on a chassis. Bedrock R7000 Edge AI specifications: SoC – AMD Ryzen 7 7840HS or 7840U octa-core Zen4 processor clocked at 3.8 GHz / 5.1GHz (Turbo) with Radeon […]
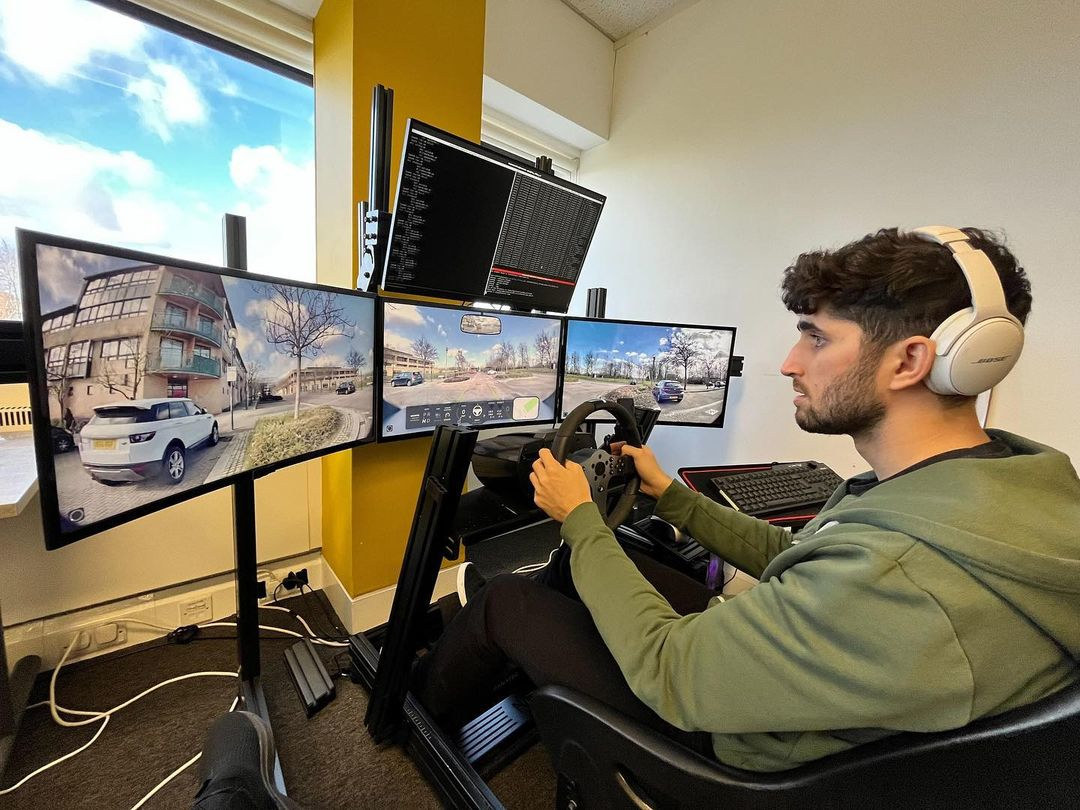
“Drive from Work” remote driving services are now a thing
I’ve been following autonomous cars’ progress for many years, but it’s taking longer to bring the technology to market than expected. So some companies are now offering “Drive from Work” services where they hire drivers that sit in an office to remotely drive passengers around. That seems insane, but that’s what Fetch does in the UK with their drivers remotely controlling cars from the head office using cellular network connectivity, 360-degree cameras, and a “workstation” with a steering wheel and pedals as well as four displays. It looks like a game, but this is real life… The service is now only offered in Milton Keynes, UK, and has been trialed for 18 months so far. This could pave the for cheaper drivers based overseas, but I suppose the lag is an issue as is the potential loss of connection, so the Hackaday article that informed us of this option also […]
Linux 6.4 release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V and MIPS architectures
Linux 6.4 has just been released by Linus Torvalds on the Linux Kernel Mailing List (LKML): Hmm. Final week of 6.4 is done, and we’ve mainly got some netfilter fixes, some mm reverts, and a few tracing updates. There’s random small changes elsewhere: the usual architecture noise, a number of selftest updates, some filesystem fixes (btrfs, ksmb), etc. Most of the stuff in my mailbox the last week has been about upcoming things for 6.5, and I already have 15 pull requests pending. I appreciate all you proactive people. But that’s for tomorrow. Today we’re all busy build-testing the newest kernel release, and checking that it’s all good. Right? Released around two months ago, Linux 6.3 brought us AMD’s “automatic IBRS” Spectre defense mechanism, additional progress on the Rust front with User-mode Linux support (on x86-64 systems only), the NFS filesystem (both the client and server sides) gained support for […]
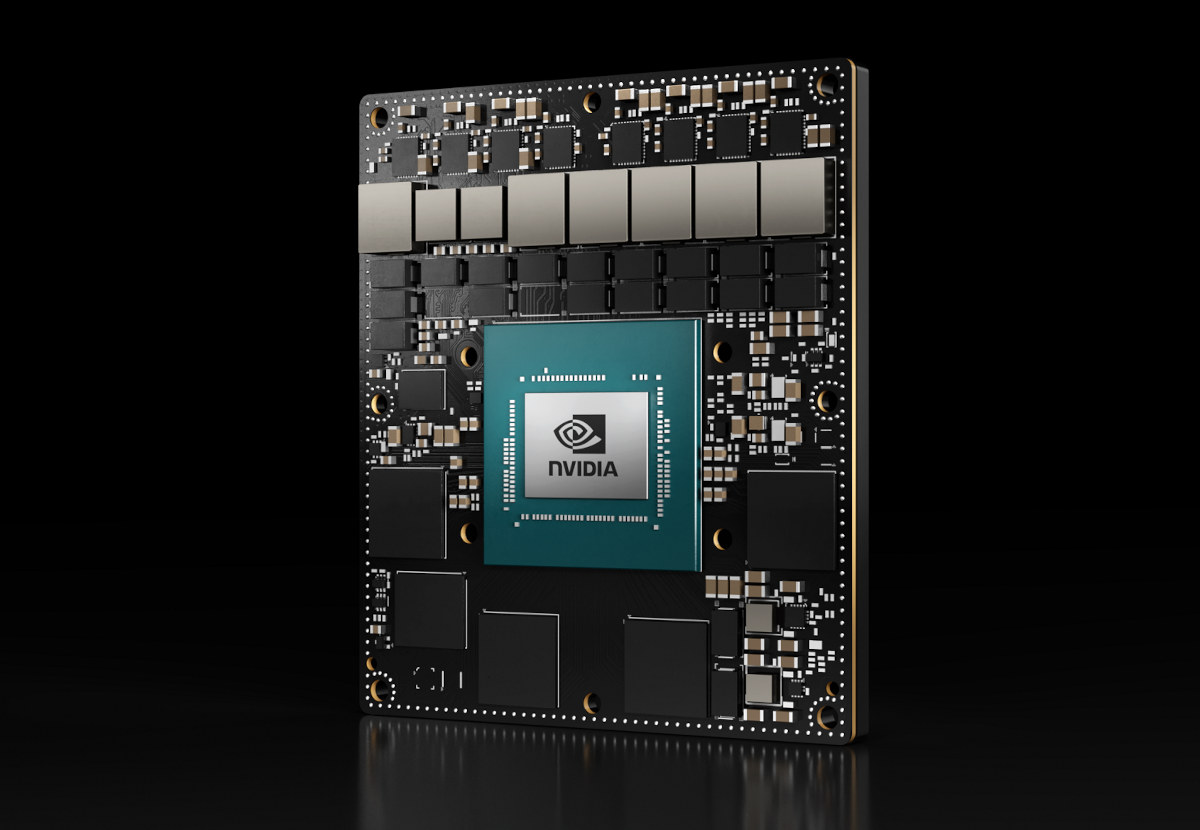
NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin Industrial offers ECC memory, extended temperature range, improved robustness
NVIDIA has recently introduced the Jetson AGX Orin Industrial module that comes with an extended temperature range, operating lifetime, shock and vibration specifications, as well as support for error correction code (ECC) memory, and delivers up to 248 TOPS of AI performance with power configurable between 15-75 W. The industrial-grade system-on-module is based on the Jetson AGX Orin 64GB module but with lower operating frequencies to enable a longer operating lifetime and improved endurance. It’s form-factor and pin-compatible with Jetson AGX Orin, and NVIDIA says it delivers more than eight times the AI performance of the 30 TOPS Jetson AGX Xavier Industrial introduced in 2021, but does not integrate Cortex-R5F cores. NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin Industrial specifications: CPU – 12-core Arm Cortex-A78AE v8.2 64-bit processor @ 2.0 GHz with 2MB L2 + 4MB L3 cache GPU / AI accelerators NVIDIA Ampere architecture with 2,048 NVIDIA CUDA cores and 64 Tensor […]
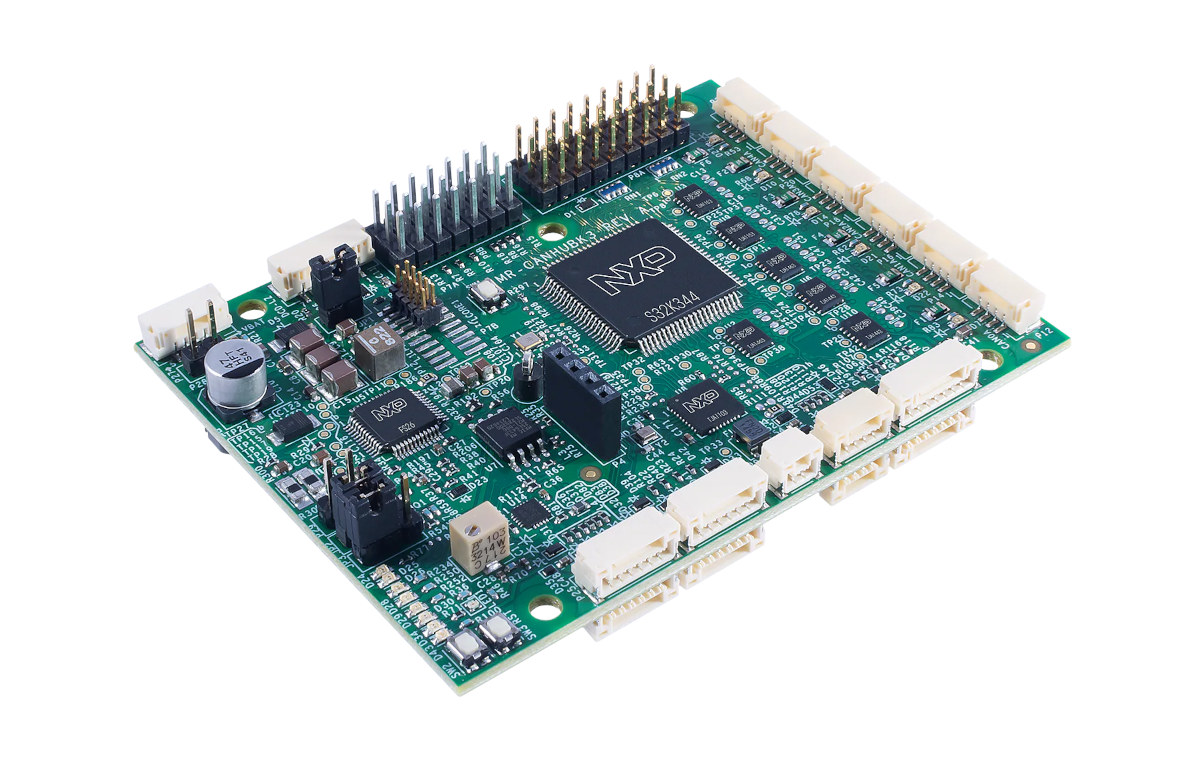
NXP S32K344 evaluation board for mobile robots offers one 100BaseT1, six CAN-FD interfaces
MR-CANHUBK344 is an evaluation board based on NXP S32K344 Arm Cortex-M7 automotive general-purpose microcontroller designed for mobile robotics applications such as autonomous mobile robots (AMR) and automated guided vehicles (AGV) with a 100baseT1 Ethernet interface and six CAN-FD ports. The six CAN bus connectors come in three pairs of CAN-FD, CAN-SIC (signal improvement), and CAN-SCP (secure) interfaces using NXP chips. The board can notably be used for tunneling CAN over Ethernet using IEEE1722, plus the board is equipped with an SE050 Secure element with NFC for authentication, and various general-purpose peripheral interfaces via DroneCode standard JST-GH connectors. MR-CANHUBK344 evaluation board specifications: MCU – NXP S32K344 lockstep Cortex-M7 microcontroller @ up to 160 MHz with 4MB flash, 512KB SRAM, 6x CAN bus interfaces, up to 218 I/Os, AEC-Q100 compliant Ethernet – ASIL-B compliant 100BASE-T1 Ethernet PHY (TJA1103) 6x CAN-FD interfaces with 2x CAN Bus with flexible data rate through TJA144x automotive […]