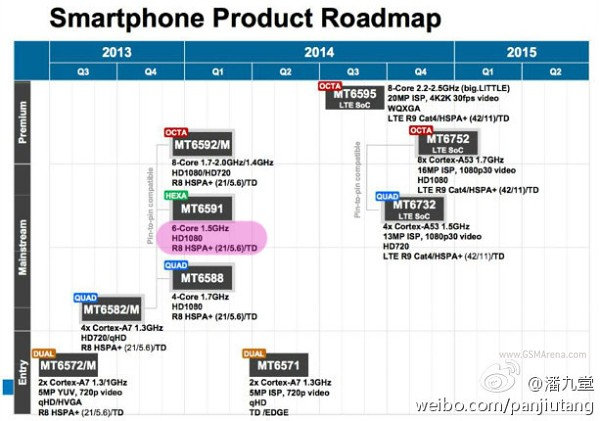
Mediatek already has over a dozen of dual, quad and octa processors for smartphone and tablets based on ARM Cortex A7, A9 and A15 cores, and they’ve already announced a 64-Bit ARM SoC (MT6732) as well as MT6595 with four Cortex A17 cores. A leaked product roadmap show the timeline for Mediatek smartphone SoCs, as well as showing some new application processors such as MT6591 Hexa-core SoC, MT6571 dual core Cortex A7 and MT6752 octa core Cortex A53 with LTE. So let’s recapitulate the new and upcoming SoCs from Mediatek: MT6572/M – Dual core Cortex A7 @ 1.3 GHz / 1.0 GHz with qHD/HVGA screen support. Available since Q3 2013, and found in phones such as Cubot GT72. MT6582/M – Quad core Cortex A7 @ 1.3 GHz with HA720/qHD screen support. Available since Q4 2013, found in phones such as W450. MT6588 – Quad core Cortex A7 @ 1.7 GHz […]
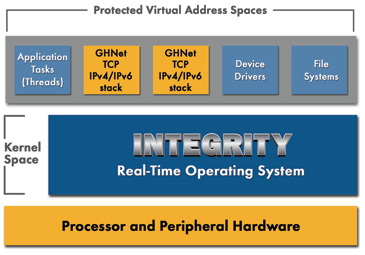
Green Hills Software Announces ARM Cortex A50 Support for INTEGRITY RTOS and Development Tools
The latest SoCs based on 64-bit ARM Cortex A53 and A57 are not only going to be used in servers and high-end mobile devices, and some embedded applications in automotive, industrial, Mil/Aero sector, as well as the Internet of Things (IoT) will also leverage the low power, high performance of ARMv8 processors. Green Hills Software has announced their INTEGRITY real-time operating system (RTOS) and MULTI integrated development environment (IDE) will support SoCs based on ARM Cortex A50 series cores. Green Hills provide the following solutions on ARMv8 Fast Model virtual platform: INTEGRITY RTOS which comes with functional safety certifications in industrial, medical, automotive and railway, and delivers real-time determinism Green Hills C/C++ Optimizing Compilers/assembler and 64-bit toolchain MULTI 64-bit IDE debugger, MISRA C/C++ code quality adherence, profiler and other integrated tools. Only ARMv8-A is supported for now, but not ARMv8-R, destined to be used in safety-related applications in automotive and […]
Marvell ARMADA Mobile PXA1928 SoC Features Four Cortex A53 Cores, Vivante GC5000 GPU, and LTE
So here we are with another 64-bit ARM SoC for mobile device thanks to Marvell ARMADA Mobile PXA1928 with four ARM Cortex A53 cores, Vivante GC5000 GPU, and a 5-mode modem with LTE TDD/FDD, HSPA+, TD-HSPA+, and EDGE. The SoC will be used in conjunction with the company’s Avastar 88W8887 802.11ac Wi-Fi + Bluetooth 4.0 + FM + Near Field Communication (NFC) single chip solution, as well as 88L2000 Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) hybrid location processor, and the new 88NV1088 eMMC 5.0 NAND Flash controller. Key features of Marvell ARMADA Mobile PXA1928 include: 5-Mode Cellular Modem Solution for LTE Cat 4, UMTS Release 7, TD-HSPA+ Release 8, and class 12 GSM/EDGE, and supports multi-radio, CSFB, and VoLTE voice solutions for LTE networks 3G/4G protocol stacks certified on major carrier networks and validated via extensive IOT, GCF and field trial testing Quad-core ARM Cortex A53MP Application Processor Subsystem Support for […]
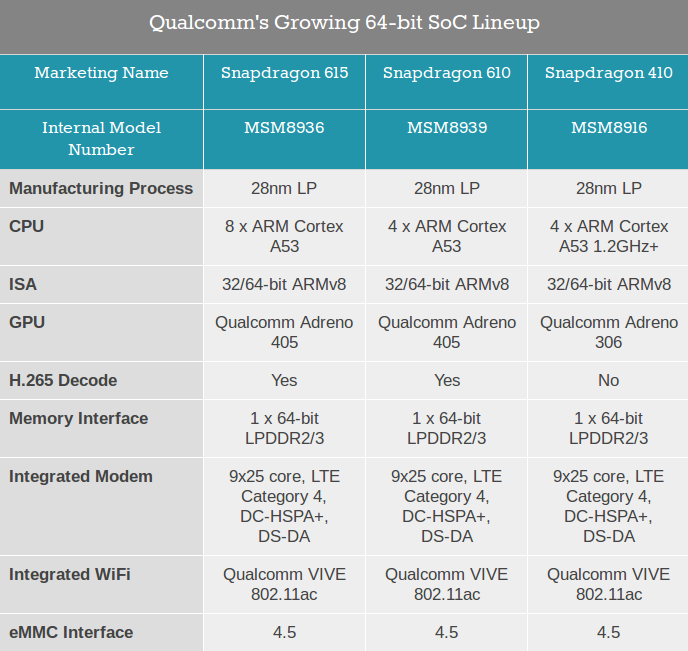
Qualcomm Announces Snapdragon 610 and 615 Quad and Octa Core ARM Cortex A53 SoC
MWC 2014 will apparently be the event where 64-bit ARM mobile SoCs are to be announced. After the official launch of Mediatek MT6732, and the soon-to-be-announced Samsung GH7, Qualcomm has unveiled two new ARMv8 processors, namely Snapdragon 610 (MSM8939) and Snapdragon 615 (MSM8936), respectively featuring 4 and 8 ARM Cortex A53 cores and targeting the mid-range of the market. Both processors will be manufactured using 28nm LP process technology, and features the new Adreno 405 GPU with support for OpenGL ES3.0, OpenCL, and DirectX 11.2 support, and up to 2560 x 1600 resolution, support H.265 video decoding, and integrates an LTE category 4 modem, as well as 802.11ac Wi-Fi via Qualcomm VIVE. Anandtech explains that “Snapdragon 615 is made up of two quad-core clusters, each optimized for a different operating point. One cluster is optimized for low power operation while the other cluster is optimized for high performance. This will likely […]
Mediatek Introduces MT6732 Quad Core ARM Cortex A53 LTE SoC
Meditaked has just announced their first 64-bit ARM SoC with MT6732 featuring four ARM Cortex A53 cores, Mali-T760 GPU, and a Multi-mode 4G LTE Modem at Mobile World Congress 2014. Here are the key features of MT6732: Quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor system @ 1.5GHz ARM Mali-T760 GPU with support for OpenGL ES 3.0 and OpenCL 1.2 APIs Multimedia Features Supports low-power, 1080p, 30fps video playback supporting the emerging video codec standard H.265 and legacy H.264 and 1080p, 30fps H.264 video recording Integrated 13MP camera image signal processor with support for unique features like PIP (Picture-in-Picture), VIV (Video in Video) and Video Face Beautifier MediaTek ClearMotion technology eliminates motion jitter and ensures smooth video playback at 60fps on mobile devices MediaTek MiraVision technology for DTV-grade picture quality Integrated Multi-mode 4G LTE Modem Rel. 9, Category 4 FDD and TDD LTE (150 Mb/s downlink, 50 Mb/s uplink) 3GPP Rel. 8, DC-HSPA+ (42 […]
Samsung GH7 Quad Core 64-bit ARM SoC Code Submitted to Linux
Following my post about Samsung Exynos 5260 hexa core processor, I’ve been informed that some other patches have been submitted about Samsung GH7 ARMv8 SoC, which should be the other processor announced at MWC 2014. A look at the device tree file shows four ARMv8 cores:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
+/ { + model = "SAMSUNG GH7"; + compatible = "samsung,gh7"; + interrupt-parent = <&gic>; + #address-cells = <2>; + #size-cells = <2>; + + cpus { + #address-cells = <2>; + #size-cells = <0>; + + cpu@000 { + device_type = "cpu"; + compatible = "arm,armv8"; + reg = <0x0 0x000>; + enable-method = "spin-table"; + cpu-release-addr = <0x0 0x8000fff8>; + }; + cpu@001 { + device_type = "cpu"; + compatible = "arm,armv8"; + reg = <0x0 0x001>; + enable-method = "spin-table"; + cpu-release-addr = <0x0 0x8000fff8>; + }; + cpu@002 { + device_type = "cpu"; + compatible = "arm,armv8"; + reg = <0x0 0x002>; + enable-method = "spin-table"; + cpu-release-addr = <0x0 0x8000fff8>; + }; + cpu@003 { + device_type = "cpu"; + compatible = "arm,armv8"; + reg = <0x0 0x003>; + enable-method = "spin-table"; + cpu-release-addr = <0x0 0x8000fff8>; + }; + }; |
The patch also include code for Samsung SSDK-GH7 board with 2GB RAM. That’s about all we know for now. Thanks to David for the tip. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
Applied Micro X-Gene X-C1 ARMv8 Server Development Board is Now Available for Pre-order
Applied Micro X-Gene is the very first processor to use ARM 64-bit architecture (ARMv8), not Cortex A53 or Cortex A57, but a custom implementation, and last year we’ve seen the company’s ARMv8 development board running 4 Linux virtual machines via KVM. The platform, called X-Gene X-C1, can now be pre-ordered to develop private cloud, public cloud, and enterprise applications. There’s limited public information for now, but I could derive specifications from a few places on the web and available pictures: SoC – Applied Micro X-Gene eight core ARMv8 processor @ 2+GHz System Memory – 2x DDR3 memory slots Storage – 4x SATA 2/3 ports + SD card slot Connectivity – 3x 10 Gb Ethernet ports USB – 2x SuperSpeed USB 3.0 ports, 1x mini USB port Expansion – PCIe Gen 3 Monitoring DB9 Serial port Power – ATX I don’t know what’s the metallic connector with holes between the two […]
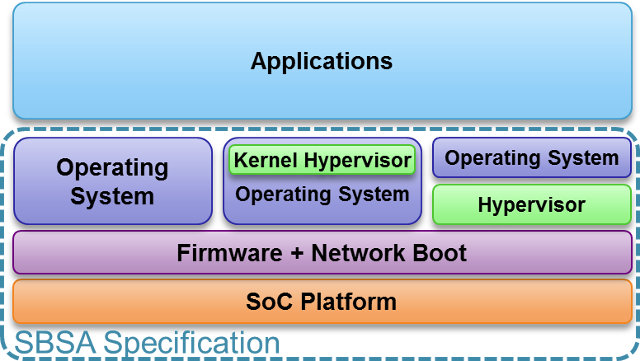
ARM Unveils Server Base System Architecture Specification (SBSA) to Standardize ARM based Servers
64-bit ARM based servers should hit the market later this year or earlier in 2015 with SoCs such as Applied Micro X-Gene or AMD Opteron A1100. ARM still has the lead in terms of efficiency with a lower dollar per watt ratio, but Intel is closing in with their new Avoton server-on-chips. However, there’s one aspect where Intel is clearly in the lead: standardization and compatibility. ARM is very flexible, and allow SoC designers to create more or less what they want, but it comes at the cost that most ARM based systems are not capable of running mainline Linux, and instead use vendor trees. With many applications, that may not be critical, but when it comes to data-centers, companies want to be able to run the latest Linux version with the latest security patches as soon as possible, and want to lower the total cost of ownership (TCO), so […]