Do you remember the ARM Android Based Rubiks Cube Solver ? Last year it could solve the puzzle in an average of 15 seconds. David Gilday has upgraded its robot with the help of Mike Dobson and named the device CubeStormer II. They released a video showing the CubeStormer II solve the Rubik’s Cube in 5.352 seconds, faster than the human world record (5.66 seconds). The mechanics are constructed entirely from LEGO, including four MINDSTORMS NXT kits, with the addition of a Samsung Galaxy S II smartphone running a custom Android app as the robot’s brain. The app uses the phone’s camera to capture images of each face of the Rubik’s Cube which it processes to determine the scrambled colours. The solution is found using an advanced two-phase algorithm, originally developed for Speedcuber (originally developed by Mike Dobson), enhanced to be multi-threaded to make effective use of the smartphone’s dual-core […]
Get CFLAGS for a Package with pkg-config
As I tried to cross-compile an application that required glibconfig.h, I found a way to retrieve the CFLAGS for a given package. Here’s the output for glib-2.0 and gtk-2.0 in qemu for overo: pkg-config –cflags glib-2.0 -I/usr/include/glib-2.0 -I/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabi/glib-2.0/include pkg-config –cflags gdk-2.0 -pthread -I/usr/include/gio-unix-2.0/ -I/usr/include/pango-1.0 -I/usr/include/glib-2.0 -I/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabi/glib-2.0/include -I/usr/include/freetype2 -I/usr/include/libpng12 -I/usr/include/gtk-2.0 -I/usr/lib/gtk-2.0/include -I/usr/include/cairo -I/usr/include/gdk-pixbuf-2.0 -I/usr/include/pixman-1 Finally, I found out that glibconfig,h was in /usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabi/glib-2.0/include as this file is generated by configure and is platform dependent. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
Generate a Custom ARM Rootfs Easily with Rootstock
You may need to generate your own rootfs for your ARM target board, but do not want to cross-compile all libraries manually. You can achieve this with rootstock, a utility that generates Ubuntu armel rootfs tarballs and/or qemu image, to be uncompressed onto a root device. First install roostock: sudo apt-get install rootstock Then generate a rootfs with the required libraries: sudo rootstock –fqdn beagleboard –login cnxsoft –password temppasswd \ –imagesize 3G –seed xfce4,gdm,pkg-config,python,perl,g++,bison,flex,\ gperf,libnss3-dev,libgtk2.0-dev,libnspr4-0d,libasound2-dev,libnspr4-dev,\ libgconf2-dev,libcairo2-dev,libdbus-1-dev,libstdc++6-4.5-dev,libexpat1-dev,\ libxslt1-dev,libxml2-dev,libbz2-dev –dist natty Here are the details of the command line parameters: –fqdn: Hostname to be used for the target system –login: Login ID of the admin user created during setup –password: Password of the admin user created during setup –imagesize: Size of the target filesystem to be created (default 1GB) –seed: List of packages to install –dist: Specify Release to build (jaunty, karmic, lucid, maverick or natty) Alternatively you could also use an […]
Dropbear: Lightweight SSH Server / Client
You may need to remotely access your embedded device, or your embedded systems is simply headless. You could use telnet, but this is insecure. A secure way to access a device remotly is to use SSH protocol. OpenSSH is one implementation but this is relatively too large and may use uncesary space on a device with limited storage. That’s where Dropbear comes into play. Dropbear is a lightweight implementation of an SSH client and server and is ideal for embedded systems. Dropbear ARM executable is only 200 KB. Here’s how it’s described on its website: Dropbear is a relatively small SSH 2 server and client. It runs on a variety of POSIX-based platforms. Dropbear is open source software, distributed under a MIT-style license. Dropbear is particularly useful for “embedded”-type Linux (or other Unix) systems, such as wireless routers. The main features of dropbear: A small memory footprint suitable for memory-constrained […]
Cross-comping zlib for ARM target
Zlib is defind as “A Massively Spiffy Yet Delicately Unobtrusive Compression Library” and used in many projects requiring compression. Here are the instructions cross-compile zlib for ARM: Download zlib1.25 wget http://cdnetworks-kr-2.dl.sourceforge.net/project/libpng/zlib/1.2.5/zlib-1.2.5.tar.gz Extract it tar xzvf zlib-1.2.5.tar.gz cd zlib-1.2.5 Configure, build and install zlib. CC=armv5tel-redhat-linux-gnueabi-gcc ./configure –prefix=/home/jaufranc/edev/rootfs make make install This will install libz.a (static library) and libz.so (dynamic library) in /home/jaufranc/edev/rootfs/lib and copy the header files to /home/jaufranc/edev/rootfs/include. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
Installing an ARM Toolchain in Fedora
You can easily install an arm cross-compiler on Fedora as follows: cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ sudo wget http://ftp.linux.org.uk/pub/linux/arm/fedora/cross/cross.repo sudo yum install armv5tel-redhat-linux-gnueabi-gcc You can check the installation worked by checking the cross-compiler version [jaufranc@localhost ~]$ armv5tel-redhat-linux-gnueabi-gcc -v Using built-in specs. Target: armv5tel-redhat-linux-gnueabi Configured with: ../configure –prefix=/usr –mandir=/usr/share/man –infodir=/usr/share/info –enable-shared –enable-threads=posix –enable-checking=release –with-system-zlib –enable-__cxa_atexit –disable-libunwind-exceptions –enable-languages=c,c++ –disable-libgcj –with-sysroot=yes –enable-version-specific-runtime-libs –target=armv5tel-redhat-linux-gnueabi Thread model: posix gcc version 4.1.2 20070925 (Red Hat 4.1.2-33.fa1) This will only install the C compiler (gcc), to install the C++ compiler, run the following command: sudo yum install armv5tel-redhat-linux-gnueabi-gcc-c++ Tested in Fedora 12. Jean-Luc Aufranc (CNXSoft)Jean-Luc started CNX Software in 2010 as a part-time endeavor, before quitting his job as a software engineering manager, and starting to write daily news, and reviews full time later in 2011. www.cnx-software.com
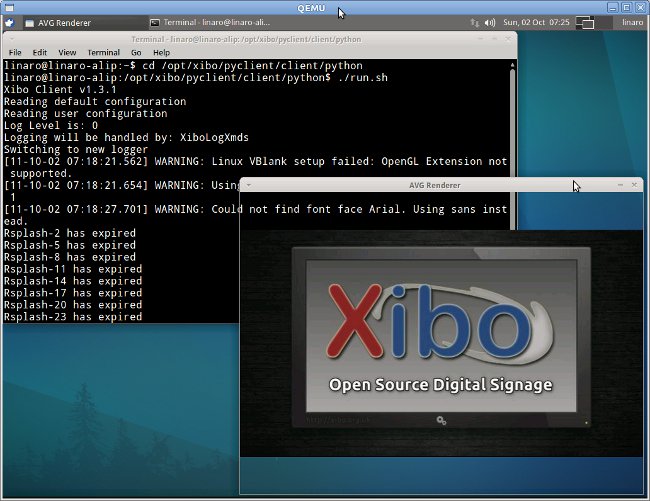
Xibo Digital Signage on ARM (Beagleboard / Overo)
Xibo (pronounced eX-E-bO) is an open source, multi-display, multi-zone, fully scheduled digital signage solution written in Python (there is also a dotnet version). This is a client /server solution that can run on Windows or Linux. If you are not familiar with Xibo you can visit http://xibo.org.uk/ or/and read my introduction XIBO: An Open Source Digital Signage Server/Client. Since I had not seen digital signage solution running on low cost ARM development platform such as Beagleboard, Pandaboard or Origen, I decided to give the Xibo python client a try using qemu to emulate Gumstix Overo COM (OMAP 3530). Porting Xibo to ARM could provide several benefits compared to x86 platform: Lower hardware cost Lower power consumption (and electricity bill) Smaller form factor allowing easier integration in displays and in transportation (e.g. buses, subway trains). Easier to implement new digital signage features such as touch screen support, 3G connectivity, location based […]
Cross Compiling libavg for ARM
libavg is a high-level development platform for media-centric applications using Python as scripting language and written in C++. Bear in mind that are many dependencies with libavg 1.6. I have not built all the libraries required, but instead simply taken the pre-built binaries and header files in the qemu overo image and copied the files as follows: mkdir mnt sudo mount -o loop,offset=$[106496*512] overo_sd_alip.img mnt mkdir ~/edev/beagleboard/libs/lib -p mkdir ~/edev/beagleboard/libs/include cp mnt/usr/lib/* ~/edev/beagleboard/libs/lib/ -rf -d cp mnt/lib/* ~/edev/beagleboard/libs/lib/ -rf -d cp /mnt/usr/include/* ~/edev/beagleboard/libs/include -rf -d sudo umount mnt The -d flag skips the symlink, so we need to recreate then for all library so that the compiler can find libname.so instead of libname.so.12. Save the following scripts to symlinks.sh:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
#!/bin/sh liblist=`ls *.so.??` for f in $liblist do echo $f fileres=`echo $f | sed 's/\..\{2\}$//'` ln -s $f $fileres done liblist=`ls *.so.?` for f in $liblist do echo $f fileres=`echo $f | sed 's/\..\{1\}$//'` ln -s $f $fileres done |
and run it where the arm libraries are located (in my case in /home/jaufranc/edev/beagleboard/libs/lib, /home/jaufranc/edev/beagleboard/libs/lib/arm-linux-gnueabi and /home/jaufranc/edev/beagleboard/libs/lib/mesa). This will create symlinks for most libraries, but not all. Some will still […]