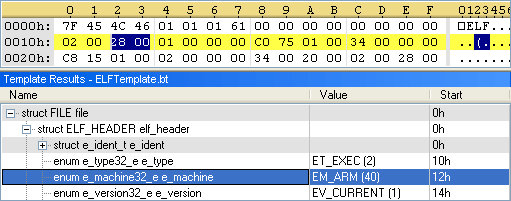
Symantec has recently discovered a new Linux worm, called Linux.Darlloz, that targets Internet-enabled devices running Linux in addition to traditional computers. That means devices such as home routers, set-top boxes and security cameras could be at risk of infection, although no attacks against non-PC devices have been confirmed yet. The worm exploits an “old” PHP vulnerability, which was patched in May 2012 (PHP 5.4.3, and PHP 5.3.13), and currently only affects Intel (x86) based systems. So you’d need an embedded system powered by an Intel processor, running Linux and PHP to be at risk. Having said that, Symantec also explains code for other architectures such as ARM, PPC, and MIPS, is also present in the worm, and these systems could potentially be at risk too with small modifications. Here’s how the worm operates: Upon execution, the worm generates IP addresses randomly, accesses a specific path on the machine with well-known […]
Faraday Technology SoCreative! IV Kit Facilitates Custom SoC Design and Software Implementation
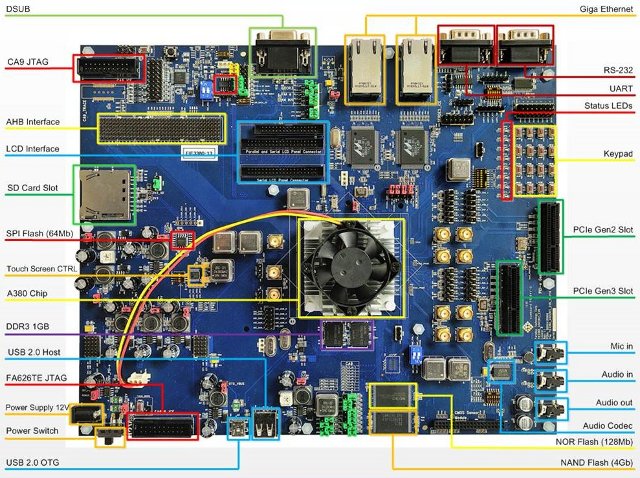
Faraday Technology has unveiled “SoCreative! IV”, a SoC development kit based on Faraday A380 SoC featuring a dual-core ARM Cortex A9 processor, an ARMv5-compliant core developed by the company, and a high speed expansion bus for interfacing with FPGA daughtercards. A380 SoC has been designed for cloud infrastructure market, including networking, computing, and storage applications. The company has not listed the specifications, but here’s what I could derived from the picture above, and the info found on Linux Gizmos article. SoC – Farady A380 dual core Cortex A9 @ 1GHz, with ARMv5-compliant FA626TE RISC processor @ 500MHz, and 512MB L2 cache. BGA package (31x31mm), 40nm process. System Memory – 1GB DDR3-1600 RAM Storage – 4Gb NAND Flash (512MB), 128Mb of NOR flash, 64Mb of SPI flash, I2C EEPROM, and SD Card slot. Video Output – DSUB for 24-bit LCD I/F up to 1280×1280 Audio – Mic In, Audio In/Out, Audio […]
Free Online Courses & Workshops For ARM Cortex-M Microcontrollers
STMicroelectronics and Digikey are co-sponsoring an EE Times University online training course entitled “Fundamentals of Microcontrollers (MCUs): Hands-On Workshop”. The first two 45-minutes sessions will be theoretical and provide and overview of micro-controllers, and explain methods to select an MCU for a given project. The first 1,000 persons based in the US or Canada, who attended the first 2 sessions, will receive a free STM32F4 Discovery Board (ARM Cortex M4). The three next sessions, conveniently taking place about a week later, hopefully after you’ve received your board, will be an actual workshop with STM32F429 Discovery Board. Here’s the detailed schedule for the training: December 2, 2013, 12PM (Eastern Time) – Session 1 – Introduction to Microcontrollers Common microcontroller architectures Pipelining Peripherals: Timers, Communication, Analog December 3, 2013, 12PM (Eastern Time) – Session 2 – Selecting the Right Microcontroller 10 Steps to Selecting a microcontroller What to look for in a […]
Tizen 3.0 Features & Tizen Lite Unveiled
We have just learned about NX300M camera, the first Tizen device, based on Tizen 1.0, but development of the new mobile operating systems is still going on, and the key features of Tizen 3.0, as well as Tizen Lite, Tizen for low-end hardware, have been unveiled at the Tizen Developer Summit on 11th of November 2013. Tizen 3.0 features: Update core OS and toolchain Multiple user support 64-bit Intel and ARM architecture support (New) 3D UI Framework with 3D rendering for 2D and 3D objects in 3D, and a dynamic animation library WayLand based compositor replacing X Crosswalk – HTML5 based application runtime based on Chromium/Blink Tizen 3.0 release is scheduled for Q3 2014, so the first Tizen smartphones and tablets which are expected for Q1 2014 will probably ship with Tizen 2.2.1, or even possibly with an earlier version. Android KitKat 4.4 has been optimized to run smoothly on […]
Weightless Roadmap – Silicon, Modules, SDKs, Base Stations and Networks
The Weightless Standard aims at using the “white space” spectrum, previously used by analog TV broadcasts, for free M2M / IoT communication coupled with low power and cost-efficient hardware offering a range of over 10 km. Longer term the target is to reach $2 hardware cost, and $2 yearly servicing costs. Companies involved with Weightless include Neul, ARM, CSR and Freescale among others. You can read my previous post about Weightless for a longer overview. The Weightless Special Interest Group (SIG) has recently revealed the hardware roadmap for the new standard, which I’ll summarize below. Weightless Chip Neul Iceni, the first weightless silicon, was officially announced in February 2013. The latest version of the chip taped in May 2013 integrates UHF radio operating between 410 and 790 MHz supporting both TV white space and narrowband operation. It is suitable for low volume production applications. A third generation will be taped […]
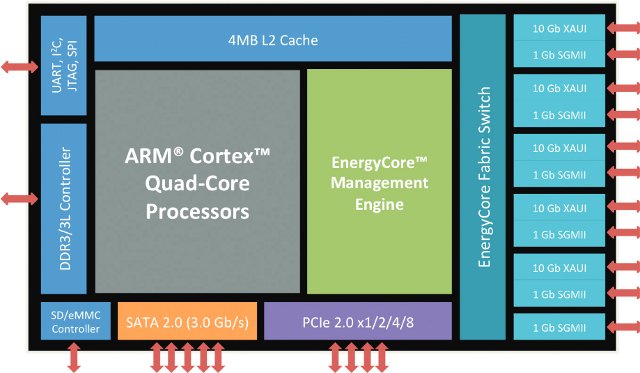
ARM Based Servers and Servers-on-a-Chip (SoCs) at ARM Techcon 2013
ARM Techcon 2013 took place on October 29 – 31, 2013, in Santa Clara, and several companies announced servers, or chips for server based on ARM technology. None of those are for home used, but for now ARM based servers target enterprise and cloud data. Yet end users may them indirectly when they access social networks such as Facebook, or other online services such as Paypal. Calxeda ECX-2000 SoC After their ECX-1000 quad core Cortex A9 Server-on-chip, Calxeda has announced ECX-2000 SoC featuring four Cortex A15 cores. The new SoC provides about twice the performance, 3 times the memory bandwidth, and 4 times the memory capacity (up to 16GB RAM) of the earlier chip. One of the key advantage of Cortex A15 over Cortex A9 is hardware virtualization that allows support for KVM and Xen hypervisors. ECX-2000 is supported in Canonical Ubuntu Linux 13.10 and can run Havana Openstack. Other […]
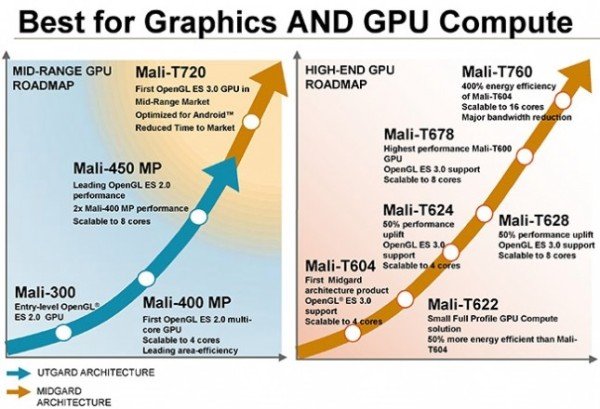
ARM Unveils Mali-T720 and Mali-T760 GPUs
ARM has recently announced two new Mali GPUs: Mali-T760 for high-end smartphones and tablets, and Mali-T720 for entry-level devices, but with better performance and energy performance compared to previous cost-optimized Mali GPUs, as well as OpenGL ES 3.0 support. These new GPUs have already been licensed by companies such as MediaTek, Rockchip, Samsung and LG Electronics. Mali-T760 GPU ARM lists the key benefits and features of the ARM Mali-T760 GPU as follows: An increase in energy efficiency and performance of approximately 400 percent over the ARM Mali-T604 GPU; Scaling to 16 shader cores, which doubles the previous generation, plus an increase in both performance per shader core and overall performance; Reduction of internal and SoC bandwidth utilization, significantly reducing energy consumption, enabled by ARM Frame Buffer Compression (AFBC), and Smart Composition, delivering more than 50 percent reduction in total memory bandwidth utilization; Simplified implementation through reduced wire count and […]
Embedded Linux Conference Europe 2013 Schedule – Build Systems, Security, Device Tree, Debugging & Profiling Techniques, and More
Embedded Linux Conference Europe 2013 will conveniently start right after LinuxCon 2013, last 2 days (October 23-24), and take place at the same location: the Edinburgh International Conference Center, Edinburgh, United Kingdom. The Linux Foundation has published the schedule for the conference, so I’ll make my own virtual schedule with sessions that I find particularly interesting. Thursday – 24th of October 9:30 – 10:10 – Timeline For Embedded Linux by Chris Simmonds, Consultant, 2net Limited Today, Linux is woven into the fabric of our technology. Things such as printers, routers, TVs and phones all have their own “Inner Penguin”. Yet it was never originally intended to be used beyond desktop and server PCs. A lot of things had to happen before Linux could break out of the PC environment and make its way in the world as a jobbing jack-of-all-trades. Since the early beginnings of embedded Linux in the late 1990’s many people have contributed […]