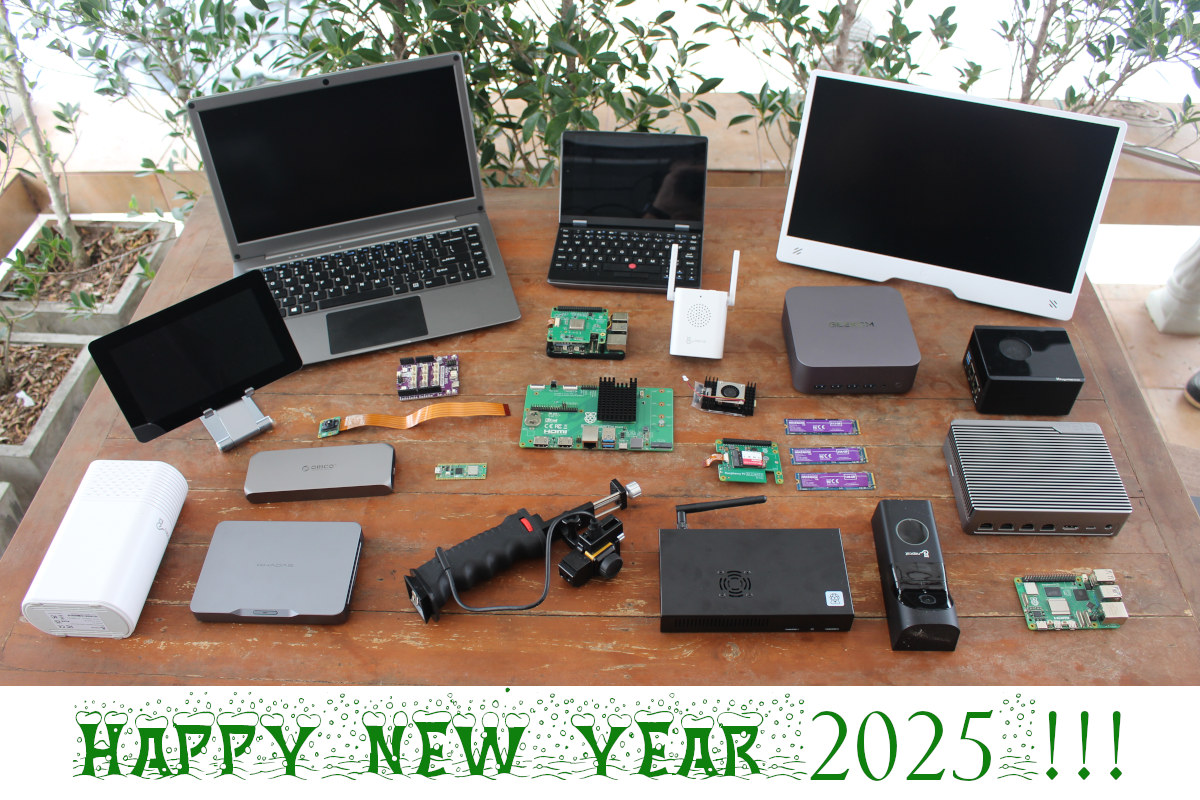
That’s it! 2024 is almost over, and it’s time to reflect on what happened during the year. So I’ll look at the highlights of 2024, share some CNX Software website traffic statistics, and speculate on what may be ahead of us in 2025. Looking back at 2024 Raspberry Pi was super active this year with 22 product launches that included boards and modules like the Raspberry Pi 5 with 2GB RAM, Raspberry Pi Pico 2 and Pico 2 W, Raspberry Pi CM5, expansion modules like the Raspberry Pi AI camera, AI HAT+, and M.2 HAT+, new accessories such as the Raspberry Pi Touch Display 2 and the Raspberry Pi Monitor, and the new Raspberry Pi 500 keyboard PC among others. As usual, there was also plenty of announcement of accessories from third parties, and some boards with the new Raspberry Pi RP2350 Arm/RISC-V microcontroller. There weren’t any ground-breaking Arm processors […]
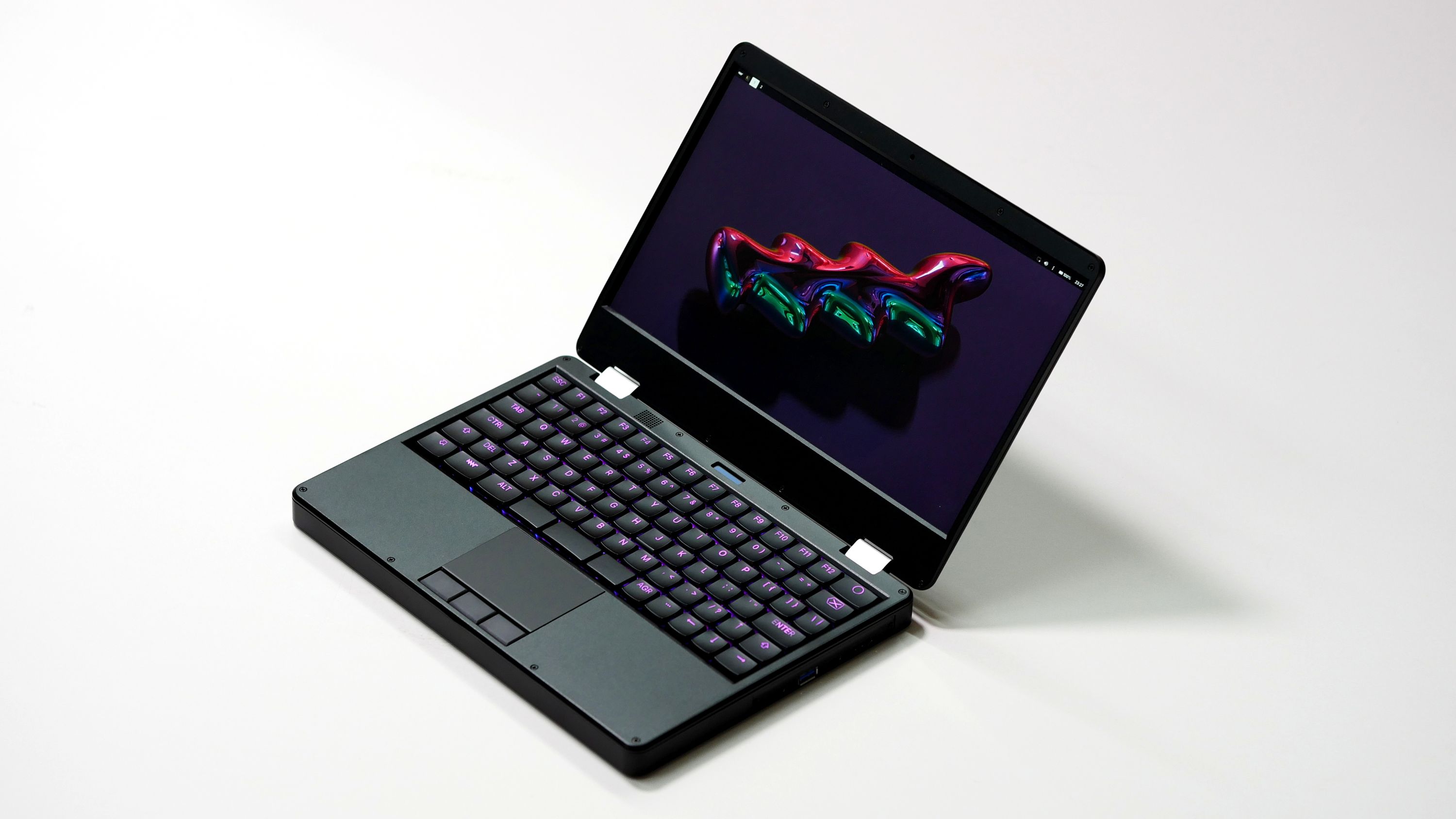
MNT Reform Next is an open-source, RK3588-powered modular 12.5-inch laptop (Crowdfunding)
The MNT Reform Next brings the Rockchip RK3588 processor to the modular laptop series. It retains the open-hardware nature of the older MNT Reform and introduces a lighter and more modular design, complete with a much faster processor. The MNT Reform Next separates the three port boards from the main motherboard, allowing for greater customization and modification than its predecessors. The standard processor module (RCORE) can be swapped with other modules such as the Raspberry Pi CM4, as well as NXP i.MX 8M Plus, NXP LayerScape 1028A, and AMD Kintex-7 FPGA modules. Like the classic MNT Reform and the MNT Pocket Reform, the enclosure for the Reform Next is milled from anodized, bead-blasted aluminum. Apart from being repairable and customizable, the RK3588 modular laptop is powerful enough to be a daily driver for browsing, writing, programming, gaming, graphics design, sound creation, and video editing. MNT Reform Next specifications: SoM SoC […]
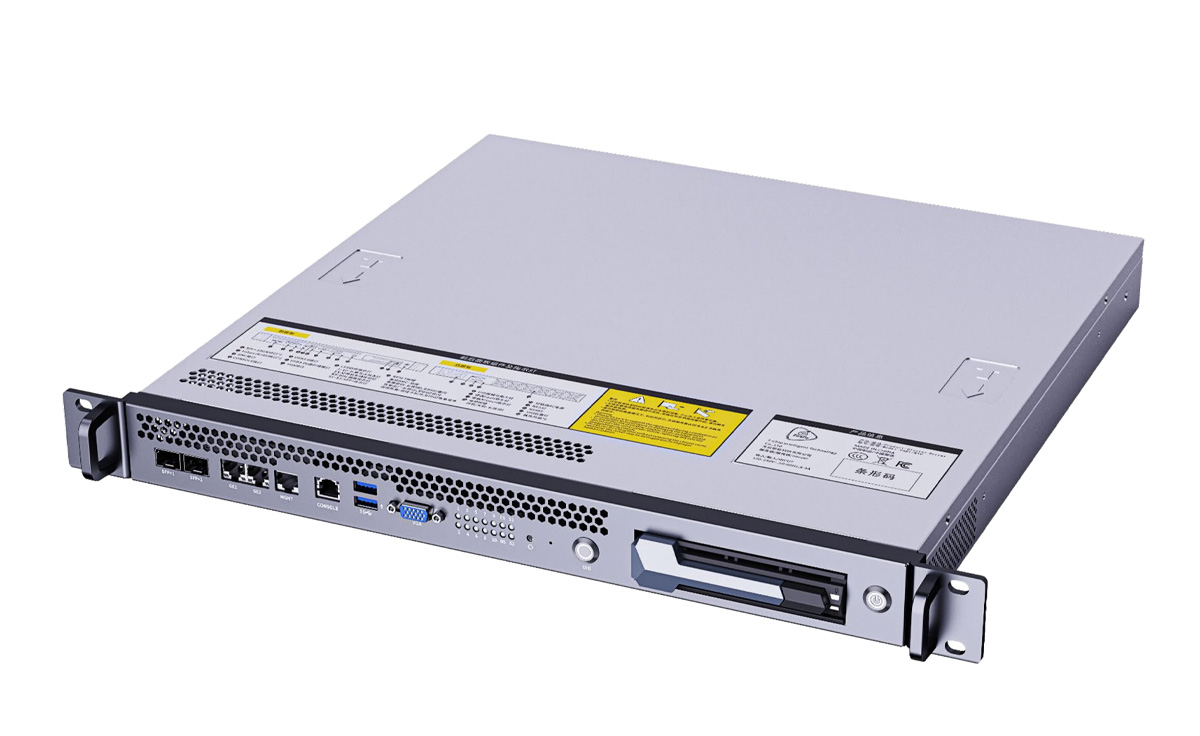
Firefly’s CSB1-N10 series AI cluster servers can deliver up to 1000 TOPS of AI power with Rockchip or NVIDIA Jetson Modules
Firefly has recently introduced the CSB1-N10 series AI cluster servers designed for applications such as natural language processing, robotics, and image generation. These 1U rack-mounted servers are ideal for data centers, private servers, and edge deployments. The servers have multiple computing nodes, featuring either energy-efficient processors (Rockchip RK3588, RK3576, or SOPHON BM1688) or high-performance NVIDIA Jetson modules (Orin Nano, Orin NX). With 60 to 1000 TOPS AI power, the CSB1-N10 servers can handle the demands of large AI models, including language models like Gemma-2B and Llama3, as well as visual models like EfficientVIT and Stable Diffusion. CSB1-N10 series specifications All CSB1-N10 AI servers have the same interfaces, and the only differences are the CPU, memory, storage, multimedia, AI capabilities, and related software support. So it’s likely Firefly has made Rockchip system-on-modules compatible with NVIDIA Jetson SO-DIMM form factor, and indeed we previously noted that Firefly designed Core-1688JD4, Core-3576JD4, or Core-3588JD4 […]
Synaptics SYN20708 low-power IoT SoC features Bluetooth, Zigbee, Thread, Matter, and advanced coexistence
Synaptics has recently introduced the SYN20708 low-power IoT SoC designed to handle simultaneous Bluetooth 5.4 Classic/Low Energy and IEEE 802.15.4 radios with Zigbee, Thread, and Matter protocols. The SoC integrates power and low-noise amplifiers and two separate radios enable simultaneous multiprotocol operations. The SoC is based on a 160 MHz Arm Cortex-M4 processor with user-accessible OTP memory for configuration. Built using a 16-nm FinFET process, it has very low power consumption, and advanced features like high-accuracy distance measurement (HADM), angle-of-arrival (AoA), and angle-of-departure (AoD). These features with versatile antenna support make this SoC suitable for industrial, consumer, and IoT applications. Synaptics SYN20708 specifications CPU – Arm Cortex-M4 processor @ 160 MHz Memory/Storage 544 KB System RAM 1664 KB Code RAM 1640 KB ROM 256 bytes OTP Connectivity Dual-radio Bluetooth 5.4 Bluetooth Classic, Bluetooth Low Energy Supports Bluetooth 6.0 features like HADM (high accuracy distance measurement) Bluetooth Class 1 and Class […]
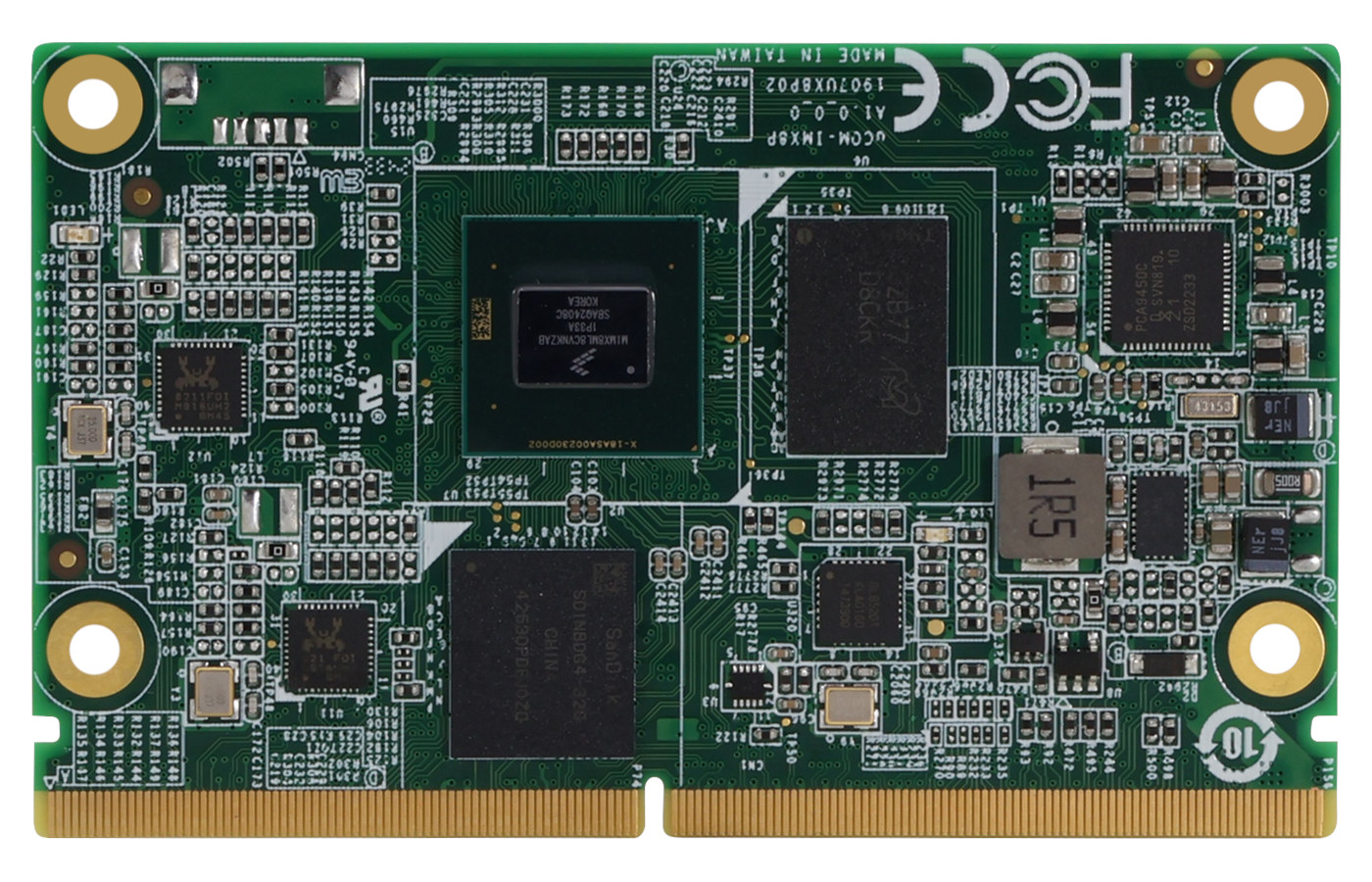
AAEON’s first Arm-based SMARC 2.1 module is NXP i.MX 8M Plus-powered uCOM-IMX8P system-on-module
AAEON has released its first Arm-based SMARC 2.1 compliant CPU module, the uCOM-IMX8P built on the NXP i.MX 8M Plus SoC and offered with up to 4GB RAM, up to 128GB eMMC flash. and support for a range of interfaces such as dual Gigabit Ethernet, USB 3.0, PCIe 3.0, and more. The 82mm x 50mm SMARC system-on-module is designed for industrial use with a -40°C to 85°C operating temperature range, Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) support, CAN Bus, MIPI interfaces, and more. That makes it suitable for applications such as predictive maintenance, process optimization, and automated control systems with cameras and displays. AAEON uCOM-IMX8P specifications: SoC – NXP i.MX 8M Plus CPU – Quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor @ 1.6 GHz GPU – Vivante GC380 2D GPU and GC7000UL 3D GPU VPU – 1080p60 video decoder & encoder AI accelerator – Optional 2.3 TOPS Neural Processing Unit (NPU) System Memory – Up […]
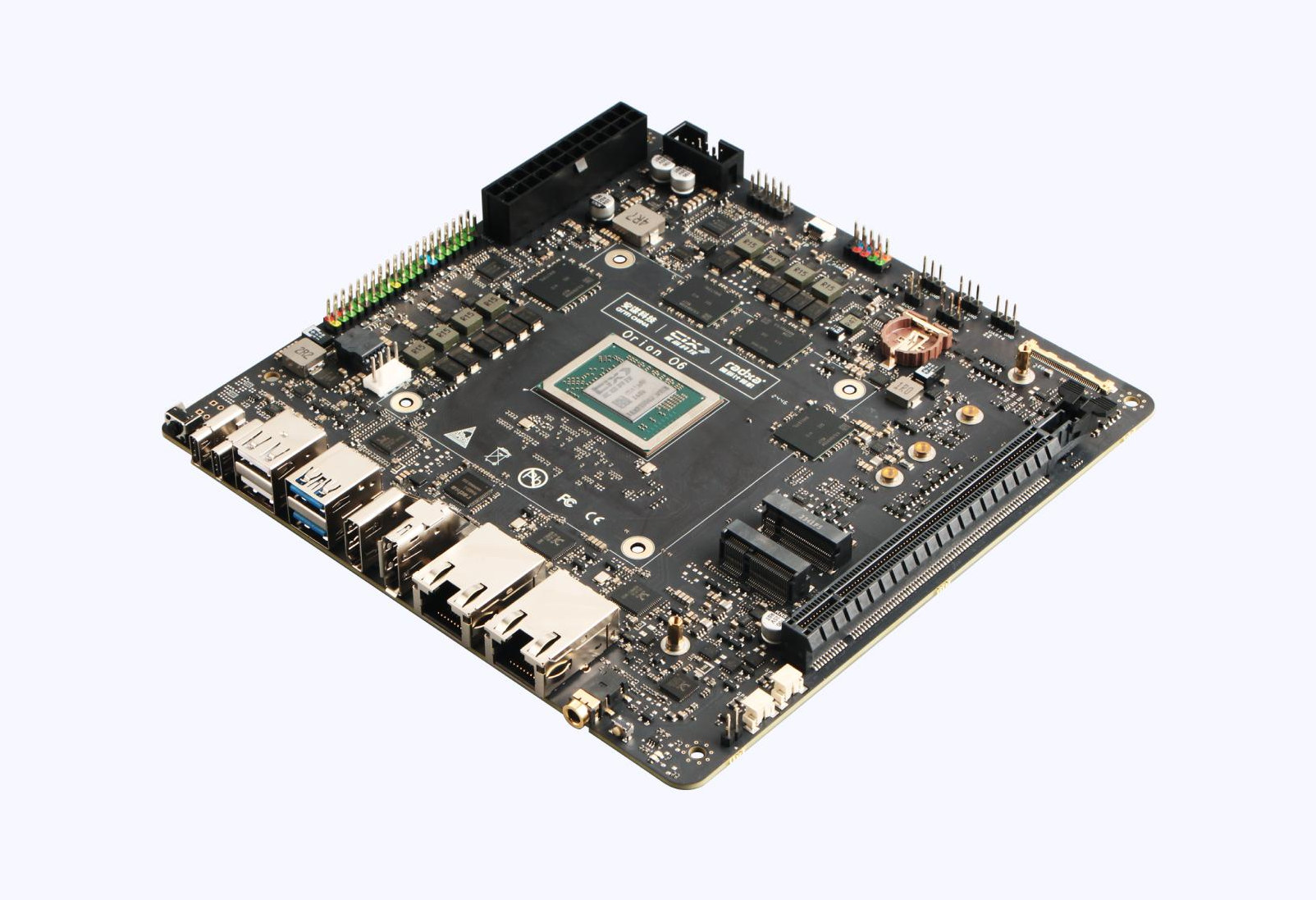
Radxa Orion O6 mini-ITX motherboard is powered by Cix P1 12-core Armv9 SoC with a 30 TOPS AI accelerator
Radxa Orion O6 is an Arm mini-ITX motherboard with performance similar to Apple M1 and Qualcomm 8cs Gen3 platform thanks to the Cix P1 12-core Armv9 processor with four Cortex-A720 cores clocked at 2.8 GHz, four Cortex-A720 cores at 2.4GHz, and four low-power Cortex-A520 cores clocked at 1.8 GHz. The Cix P1 SoC also features an Arm Immortalis-G720 GPU for graphics and AI computing, a 30 TOPS AI accelerator for a combined 45 TOPS of AI inference performance, an 8Kp60 video decoder, and an 8Kp30 video encoder. The Orion O6 SBC ships with up to 64GB LPDDR5, features a 4Kp60 HDMI 2.0 port, a 4Kp120 DP 1.4 connector, two 5Gbps Ethernet ports, M.2 socket for storage and wireless, a PCIe x16 slot, and more. Radxa Orion O6 specifications: SoC – Cix P1 (Codename: CD8180, not the CP8180 variant for AI PCs) 12-core DynamIQ processor 4x Cortex‑A720 big cores @ up […]
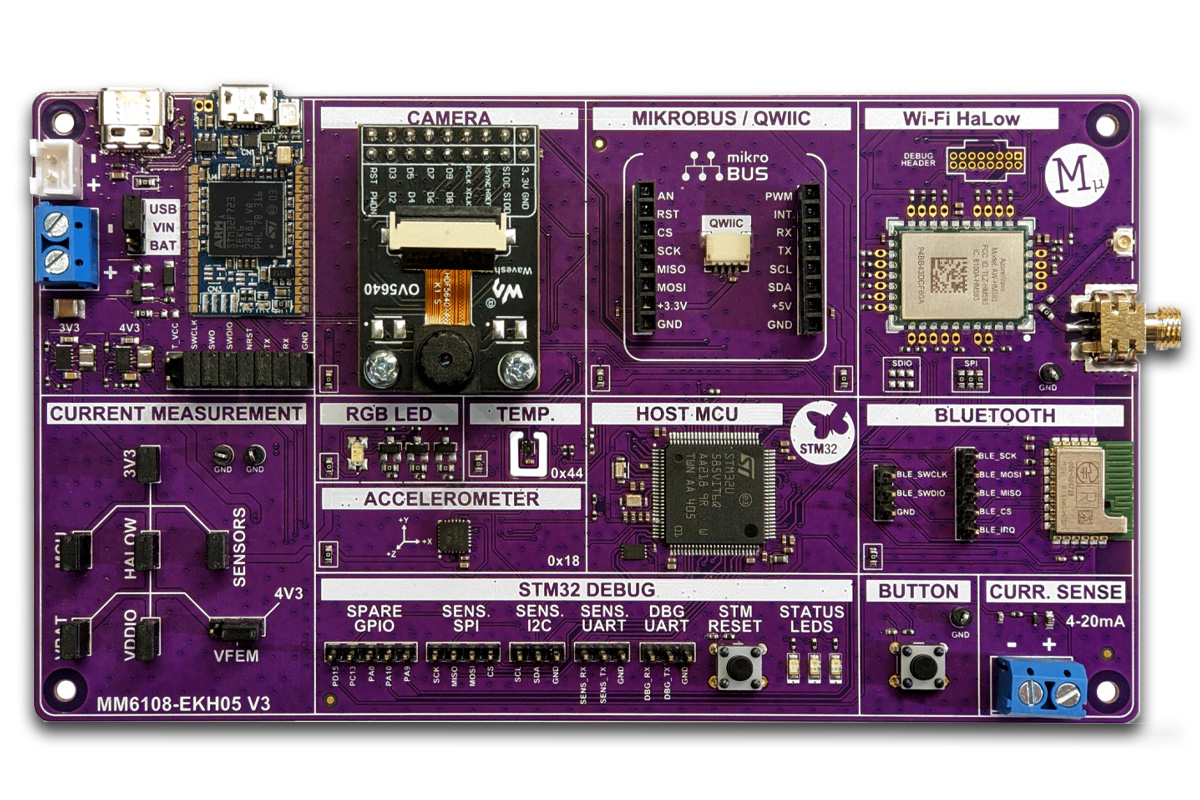
STM32-powered MM6108-EKH05 Wi-Fi HaLow evaluation kit supports Bluetooth, Camera, and Qwicc/MikroBus modules
Morse Micro has recently launched the MM6108-EKH05 Wi-Fi HaLow Evaluation Kit designed to reduce the development and deployment time of IoT products. Built around the Morse Micro MM6108 HaLow SoC, this kit combines long-range, low-power wireless connectivity with a range of integrated sensors, making it ideal for IoT engineers and developers. Key features include Wi-Fi HaLow connectivity, an STM32U585 Cortex-M33 MCU, integrated sensors (temperature, humidity, accelerometer), 16 MB of SPI Flash memory, programmable GPIOs, power measurement tools, and WPA3 security for reliable and secure communication. The kit also includes alternative power options including USB, battery, or external power, and embeds support for a camera, MikroBus and Qwicc expansion modules, Bluetooth, and current measurement circuitry. All these features make this kit useful for applications including smart homes, industrial automation, and agricultural monitoring. MM6108-EKH05 specifications: MCU – STM32U585 Arm Cortex-M33 microcontroller @ 160 MHz with TrustZone, 2 MB Flash Storage – 16Mbit […]
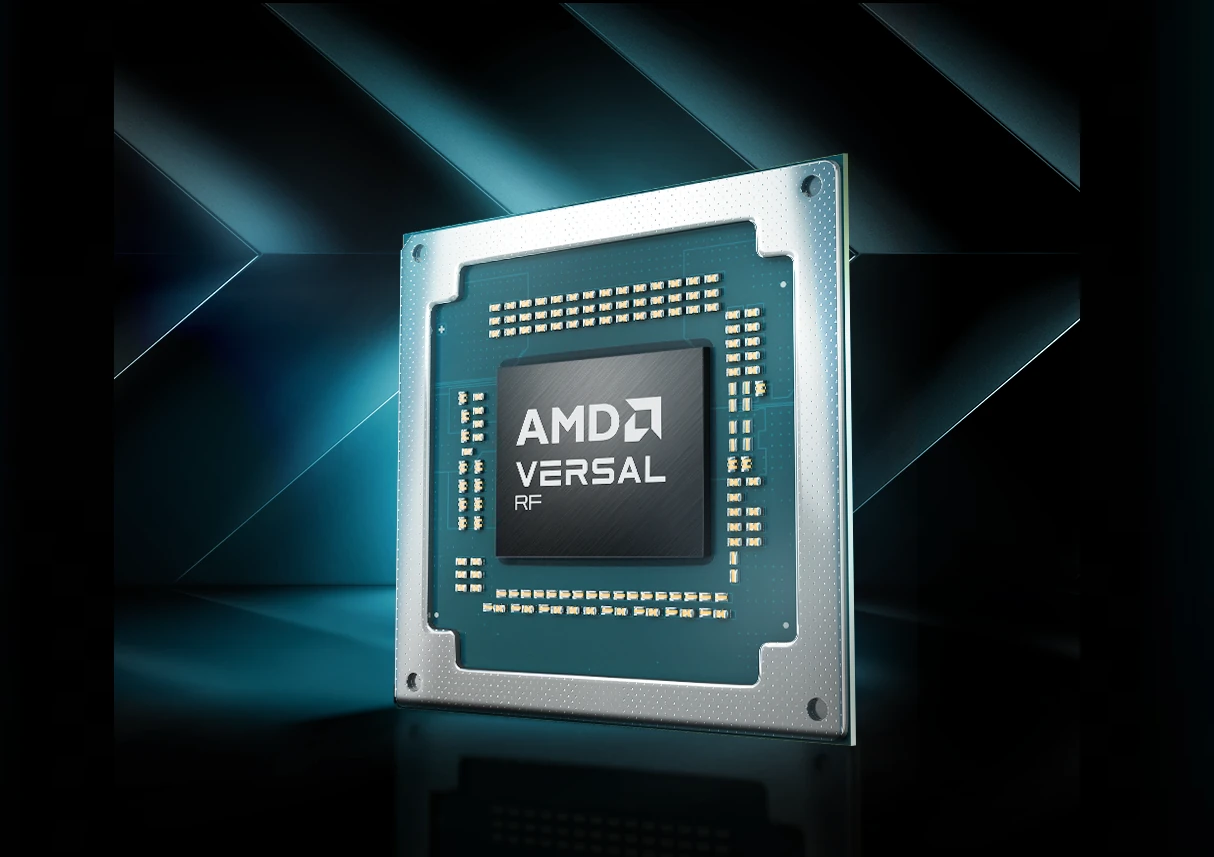
AMD Versal RF Series adaptive SoCs target 6G wireless, aerospace, and electronics test equipment
AMD Versal RF series adaptive system-on-chips (SoCs) combines Arm Cortex-A72 and Cortex-R5F hard cores with FPGA fabric and direct radio frequency (RF)-sampling data converters for pre-6G systems, wireless 6G testers, aerospace and defense applications like radars, and electronics test equipment such as multi-channel testers, oscilloscopes, and wideband spectrum analyzers. Built upon the Xilinx Zynq RFSoC devices, the AMD Versal RF Series supports wideband-spectrum with high-resolution thanks to up to sixteen 18 GHz, 14-bit RF ADCs with up to 32 GSPS and sixteen 14-bit RFV DACs up to 16 GSPS, and delivers 80 TOPS of DSP performance in a size, weight, and power (SWaP)-optimized design. The chips also integrate hard IP such as DDR5 memory controllers, 600 Gbps Ethernet, PCIe Gen5 x4, and various high-speed transceivers. AMD Versal RF Series adaptive SoCs key features and specifications: Processing System Application Processing Unit (APU) – Dual-core Arm Cortex-A72 with 48 KB/32 KB L1 […]