NXP has announced a new MCX general-purpose Arm Cortex-M MCU family designed for advanced industrial and IoT edge computing and integrating an NXP neural processing unit (NPU) capable of delivering over 30 times higher performance than running the AI inference tasks on an Arm Cortex-M33 core alone. The new MCX portfolio builds upon the earlier NXP LPC and Kinetis microcontroller families, but does not replace these, and aims to improve machine learning performance and security for a variety of applications including machine learning, wireless, voice, motor control, analog, and more. The new MCX family will be available in four series: MCX N Advanced series Designed for secure, intelligent applications 150 MHz to 250 MHz Neural processing unit (NPU) and DSP for real-time inference EdgeLock Secure Subsystem MCX A Essential series Optimized to provide critical functionality for applications such as motor control 48 MHz to 96 MHz Built-in timers, low pin […]
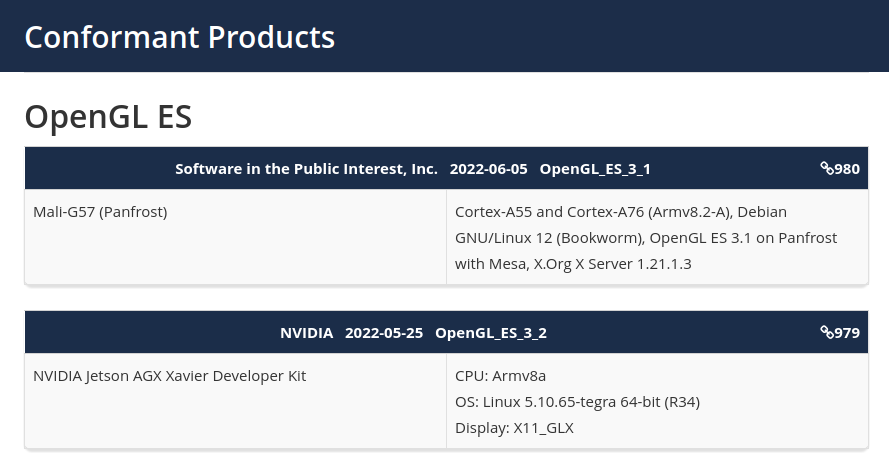
Panfrost now offers a fully-conformant OpenGL ES 3.1 implementation for Mali-G57 (Valhall) GPU
The Mali-G57 GPU part of the Valhall family, and found in several Arm processors such as MediaTek MT8192 and MT8195 SoC powering some Chromebooks, is now supported by the Panfrost open-source driver with a fully-conformant OpenGL ES 3.1 implementation. Last year, Collabora updated Panfrost with support for OpenGL ES 3.1 on Midgard (Mali T760 and newer) and Bifrost (Mali G31, G52, G76) GPUs, and also announced having started working on Valhall GPUs. One part of the work was done in the summer of 2021 with some reverse-engineering work on Mali-G78 GPU’s instruction set, and this has culminated with a fully-conformant OpenGL3.1 for Mali-G57 GPU. Interestingly, it’s not been released by Collabora directly, but through an organization called “Software in the Public Intenerest, Inc.” (or SPI for shorts) which happens to be a non-profit organization incorporated on June 16, 1997, and described as: a non-profit corporation registered in the state of […]
Armbian 22.05 release adds support for Orange Pi R1 Plus LTS, Radxa Zero & Rock 3A, DevTerm A06
The latest release of Armbian, version 22.05, is now out with hundreds of Linux kernel and user space-related bug fixes, a focus on stabilizing existing platforms, while still adding four new boards with Orange Pi R1 Plus LTS (RK3328), Radxa Zero (Amlogic S905Y2), Radxa Rock 3A (RK3568), and DevTerm A06 (RK3399). The community also added two new maintainers for ESPRESSObin and Radxa Rock Pi 4 (Model A) SBCs which should mean the images for those boards will be tested more regularly and potential issues fixed more quickly. You may want to read the more detailed changelog to see if any changes may impact the board(s) you are using. The new Armbian 22.05 release succeeds Armbian 22.02 outed on February 28, 2022. If you’d like to upgrade simply run those two commands on your existing installation:
|
1 2 |
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade |
For new installation, browse the list of supported boards, select the Debian/Ubuntu image you’d […]
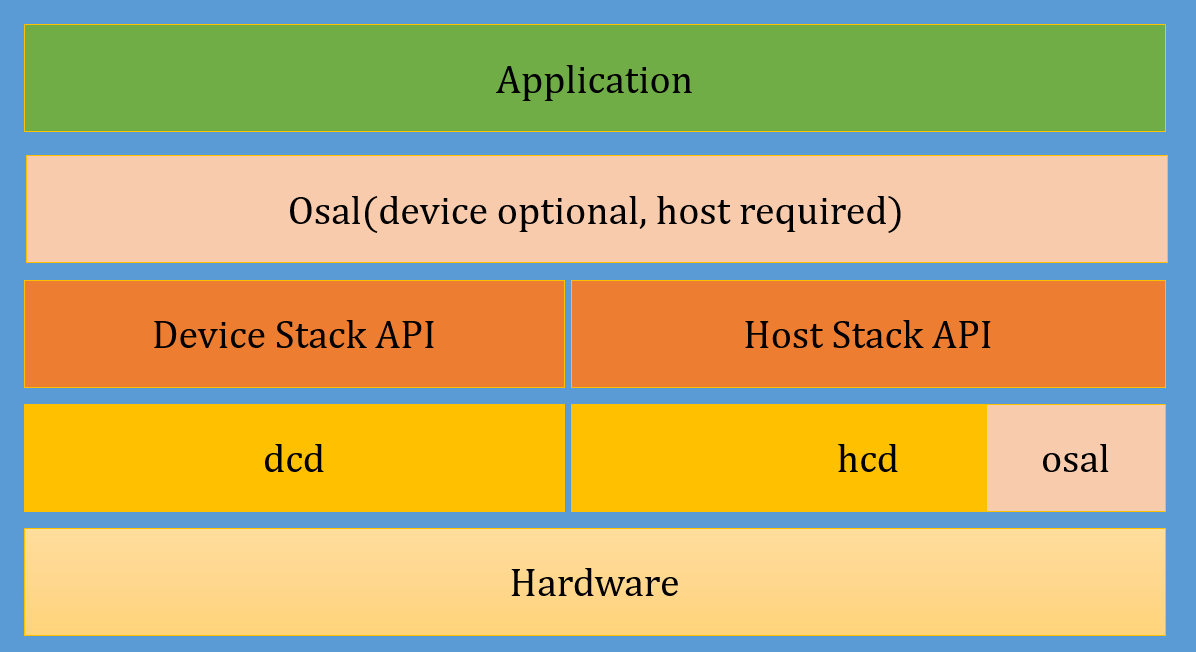
CherryUSB – A lightweight USB device/host stack for embedded systems
CherryUSB is a lightweight open-source USB device/host stack for embedded systems with one or more USB interfaces. The stack implements various class drivers such as CDC, HID, MSC, audio, video, and so on. It’s apparently part of Boufallo Lab SDK (e.g. for BL702 MCU), and has been ported and tested with WCH CH32V307 RISC-V MCU, STMicro STM32F4, and Nuvoton NUC442 Cortex-M4 microcontroller, as well as a two Arm Cortex-M3 microcontrollers I’ve never heard of: EastSoft ES32F3 and MindMotion MM32L3xx. CherryUSB device stack highlights: Support for USB2.0 full and high speed Endpoint irq callback USB classes support Composite Device Communication Device Class (CDC) Human Interface Device (HID) including “Custom HID” Mass Storage Class (MSC) USB VIDEO Class (UVC1.0,UVC1.5) USB AUDIO Class (UAC1.0, UAC2.0) Device Firmware Upgrade CLASS (DFU) MIDI CLASS (MIDI) Test and Measurement CLASS (TMC) Vendor class Remote NDIS (RNDIS) support Support WINUSB 1.0,WINUSB 2.0 with BOS (Binary Device Object […]
Linux 5.18 release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V, and MIPS architectures
Linux 5.18 is out! Linus Torvalds has just announced the release on lkml: No unexpected nasty surprises this last week, so here we go with the 5.18 release right on schedule. That obviously means that the merge window for 5.19 will open tomorrow, and I already have a few pull requests pending. Thank you everybody. I’d still like people to run boring old plain 5.18 just to check, before we start with the excitement of all the new features for the merge window. The full shortlog for the last week is below, and nothing really odd stands out. The diffstat looks a bit funny – unusually we have parsic architecture patches being a big part of it due to some last-minute cache flushing fixes, but that is probably more indicative of everything else being pretty small. So outside of the parisc fixes, there’s random driver updates (mellanox mlx5 stands out, […]
Embedded World 2022 – June 21-23 – Virtual Schedule
Embedded World 2020 was a lonely affair with many companies canceling attendance due to COVID-19, and Embedded World 2021 took place online only. But Embedded World is back to Nuremberg, Germany in 2022 albeit with the event moved from the traditional month of February to June 21-23. Embedded systems companies and those that service them will showcase their latest solution at their respective booths, and there will be a conference with talks and classes during the three-day event. The programme is up, so I made my own little Embedded World 2022 virtual schedule as there may be a few things to learn, even though I won’t be attending. Tuesday, June 21, 2022 10:00 – 13:00 – Rust, a Safe Language for Low-level Programming Rust is a relatively new language in the area of systems and low-level programming. Its main goals are performance, correctness, safety, and productivity. While still ~70% of […]
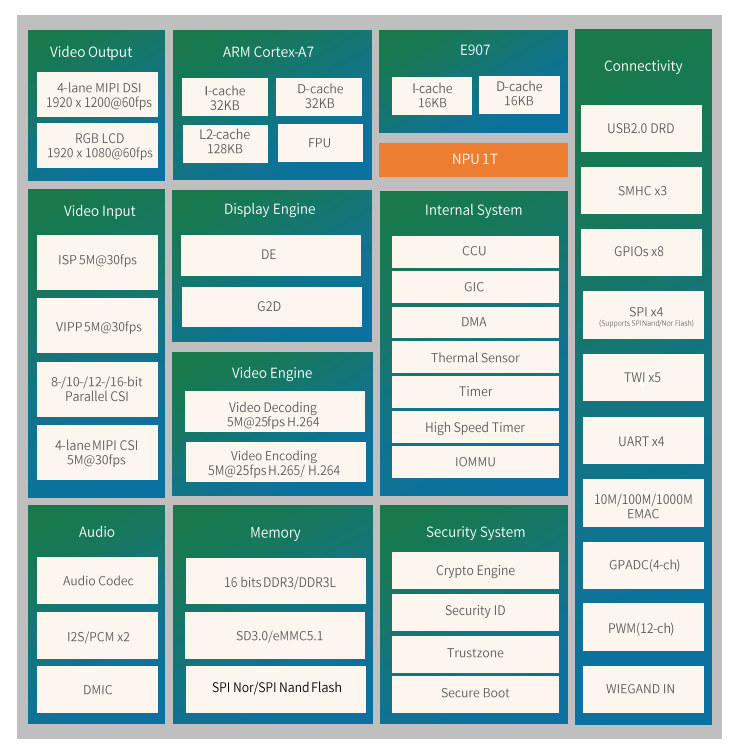
Allwinner V853 Arm Cortex-A7 + RISC-V SoC comes with 1 TOPS NPU for AI Vision applications
Allwinner V853 SoC combines an Arm Cortex-A7 core with a Xuantie E907 RISC-V core, and a 1 TOPS NPU for cost-sensitive AI Vision applications such as smart door locks, smart access control, AI webcams, tachographs, and smart desk lamps. Manufactured with a 22nm process, the SoC comes with an ISP image processor and Allwinner Smart video engine capable of up to 5M @ 30fps H.265/H.264 encoding and 5M @ 25fps H.264 decoding, offers parallel CSI and MIPI CSI camera interfaces, and well as MIPI DSI and RGB display interfaces. Allwinner V853 specifications: CPU Arm Cortex-A7 CPU core @ 1 GHz with 32 KB I-cache, 32 KB D-cache, and 128 KB L2 cache Alibaba Xuantie E907 RISC-V core with 16 KB I-cache and 16 KB D-cache NPU (Neural network Processing Unit) – Up to 1 TOPS for V853 and 0.8 TOPS for V853S, embedded 128KB internal buffer, support for TensorFlow, Caffe, […]
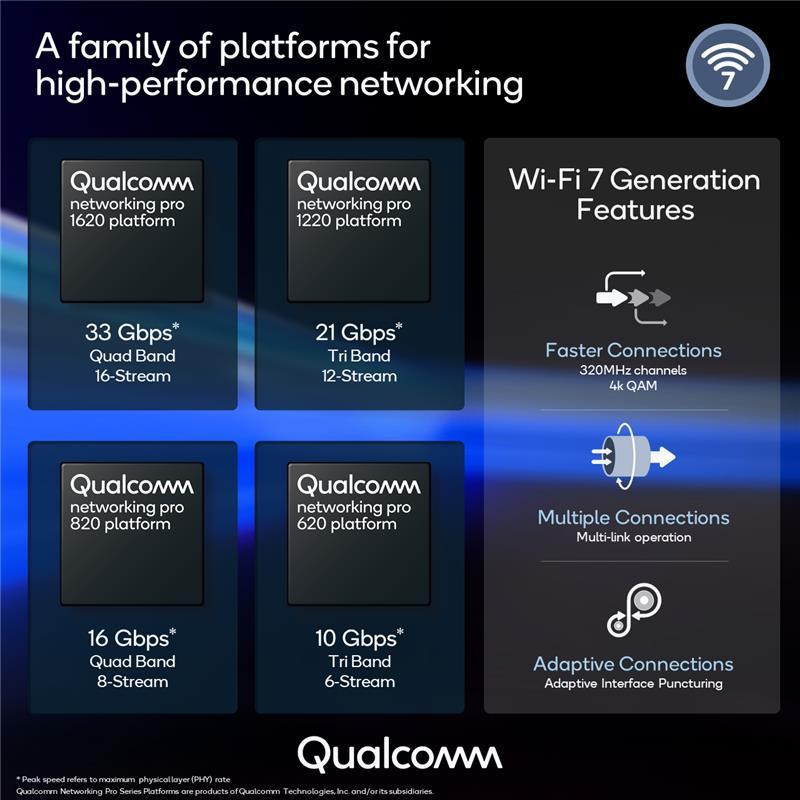
Qualcomm Wi-Fi 7 Networking Pro Series SoCs support up to 33 Gbps PHY rate, up to 2,000 clients
Qualcomm has announced the Wi-Fi 7 capable Qualcomm Networking Pro Series Gen 3 family designed for routers and access points with a PHY rate up to 33 Gbps with the quad-band 16-stream Networking Pro 1620 platform and offers some competition to the recently announced Broadcom WiFi 7 access point chips. The company will also offer the tri-band 12-stream Networking Pro 1220 with up to 21.6 Gbps aggregated link rate, the quad-band 8-stream Networking Pro 820 capable of 16.5 Gbps PHY rate, and at the low-end of the scale, the Networking Pro 620 limited to 10.8 Gbps with three bands and six streams. Qualcomm Networking Pro 1620 (IPQ9574) platform specifications: CPU – Quad-core Arm Cortex-A73 @ 2.2 GHz System Memory – DDR3L, DDR4 16/32-bit Storage – eMMC, NAND, Serial NOR, SD/eMMC Networking Wired – 6 Port Integrated Ethernet Switch 4 x 2.5 GbE + 5 GbE + 10 GbE Wireless Wi-Fi […]