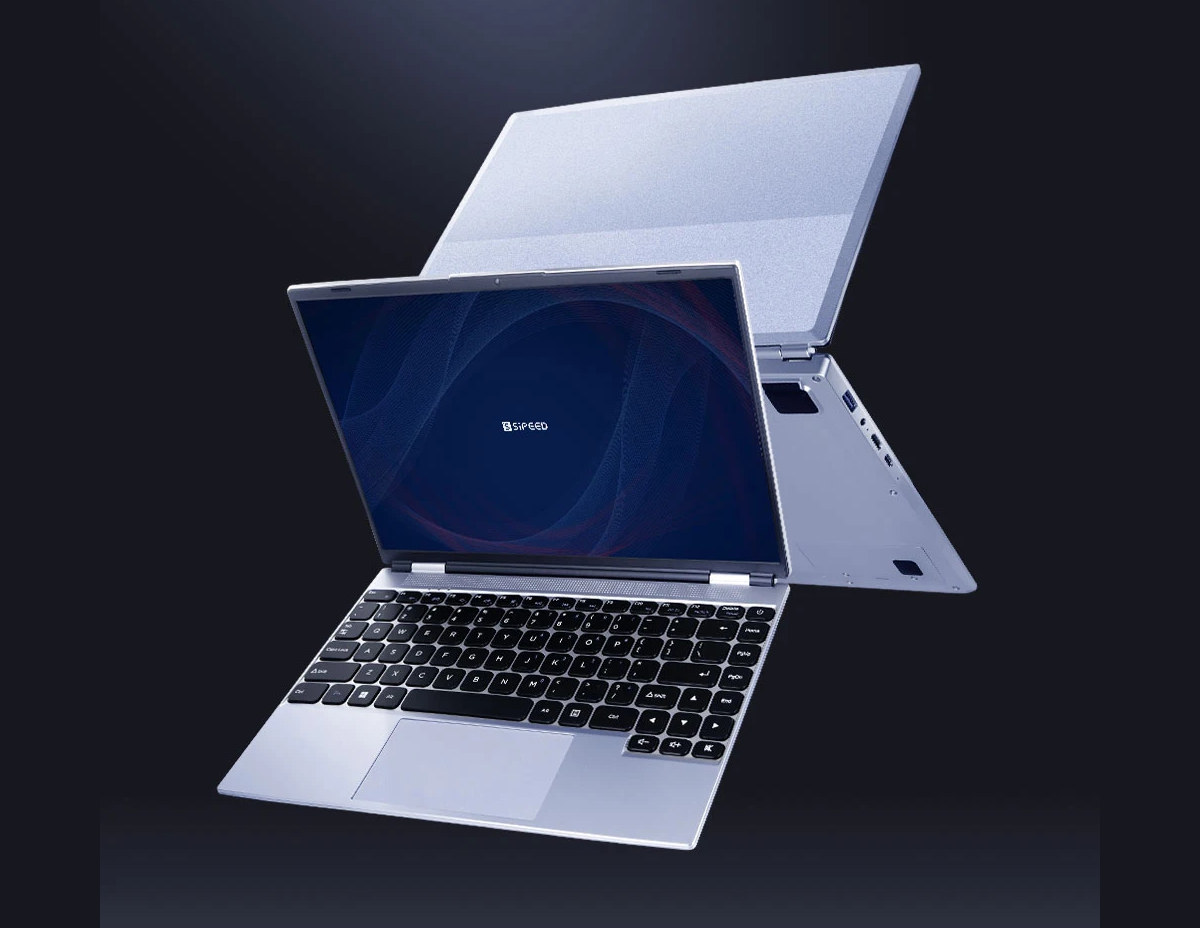
We’ve just written about Deep Computing’s DC-ROMA RISC-V Laptop II, but Sipeed has just launched the Lichee Book 4A modular RISC-V laptop based on the quad-core Alibaba T-head TH1520 processor and running Debian Linux. I was expecting the Lichee Book to launch with the SpacemIT K1 octa-core RISC-V processor, but Sipeed started with the time-tested TH1520 quad-core RISC-V processor coupled with up to 16GB RAM and 128GB eMMC flash and equipped with a 14-inch IPS display. In the future, we’ll get the Lichee Book 3A with the SpacemIT K1, and the Lichee Book 5A with an unnamed Cortex-A75-class RISC-V SoC with a 20 TOPS AI accelerator. Sipeed Lichee Book specifications: 260-pin SO-DIMM system-on-module (SoM) Sipeed LM3A – Upcoming module based on SpacemIT K1 octa-core RISC-V CPU (Cortex-A55 class) with 2 TOPS NPU Sipeed LM4A SoC – Alibaba T-Head TH1520 CPU Quad-core RISC-V Xuantie C910 (RV64GCV – RVV 0.7) processor @ […]
DC-ROMA RISC-V Laptop II with SpacemIT K1 octa-core SoC to run Ubuntu supported by Canonical
Deep Computing has announced the DC-ROMA RISC-V Laptop II powered by a 2.0 GHz SpacemIT K1 octa-core 64-bit RISC-V processor coupled with up to 16GB DDR4 and running Ubuntu with official support from Canonical. Deep Computing unveiled the first RISC-V laptop – named ROMA – in 2022 but it never really took off because of all the web3 and cryptocurrency features plus the ultra-high price. The new DC-ROMA RISC-V Laptop II does without those and features a 14-inch IPS display, a 1TB SSD, a WiFI 6 and Bluetooth 5.2 module, a webcam, several USB ports including a USB-C with DisplayPort Alr mode, and a “development interface” with a few GPIOs. DC-ROMA RISC-V Laptop II specifications: SoC – SpacemiT K1 CPU – 8-core X60 RISC-V processor @ up to 2.0 GHz; single-core performance equivalent to about 1.3x the performance of an Arm Cortex-A55 GPU – Imagination IMG BXE-2-32 with support for […]
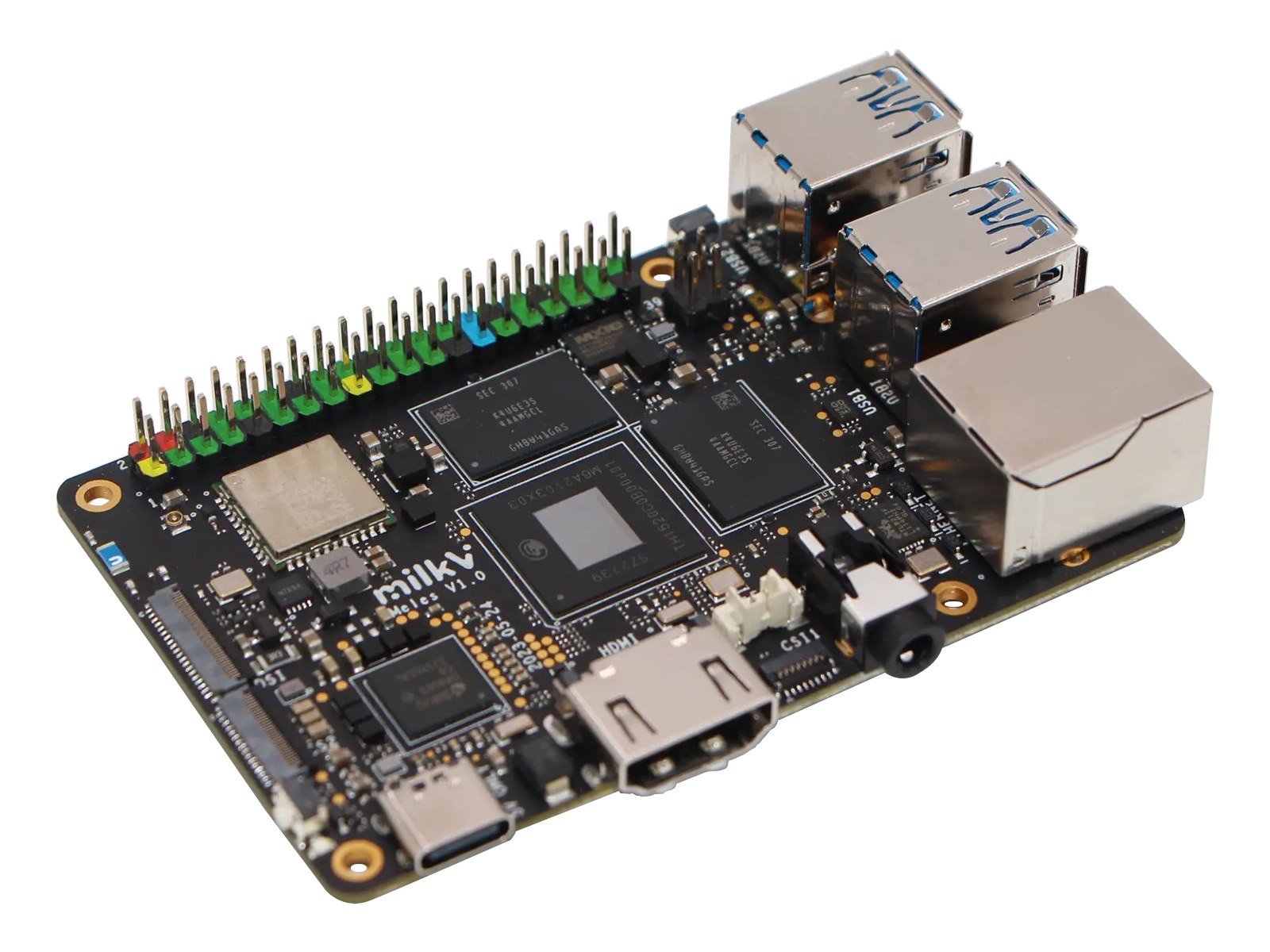
Meles RISC-V credit card-sized SBC is powered by T-Head TH1520 quad-core SoC
Shenzhen Milk-V Technology’s Meles SBC (single board computer) is powered by a T-Head TH1520 quad-core RISC-V processor and offered in a credit card form factor similar to the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B layout. The board is quite more powerful with a 2.0 GHz quad-core SoC equipped with a modern GPU, a 4K capable video encoder and decoder, and a 4 TOPS NPU. The board also features gigabit Ethernet, a WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 5.2 module, four USB 3.0 ports, HDMI 2.0 video output, MIPI CSI and DSI interfaces, and a 40-pin GPIO header. Meles specifications: SoC – Alibaba T-Head TH1520 CPU Quad-core RISC-V Xuantie C910 (RV64GCV – Vector Extension version 0.7) processor up to 2.0 GHz Low-power Xuantie E902 core GPU – Imagination BXM-4-64 GPU with support for OpenGL ES3.0/3.1/3.2, OpenCL 1.1/1.2/2.0, Vulkan 1.1/1.2; 50.7GFLOPS DSP – Xuantie C906 audio DSP @ 800 MHz VPU Video Decoder H.265, H.264, […]
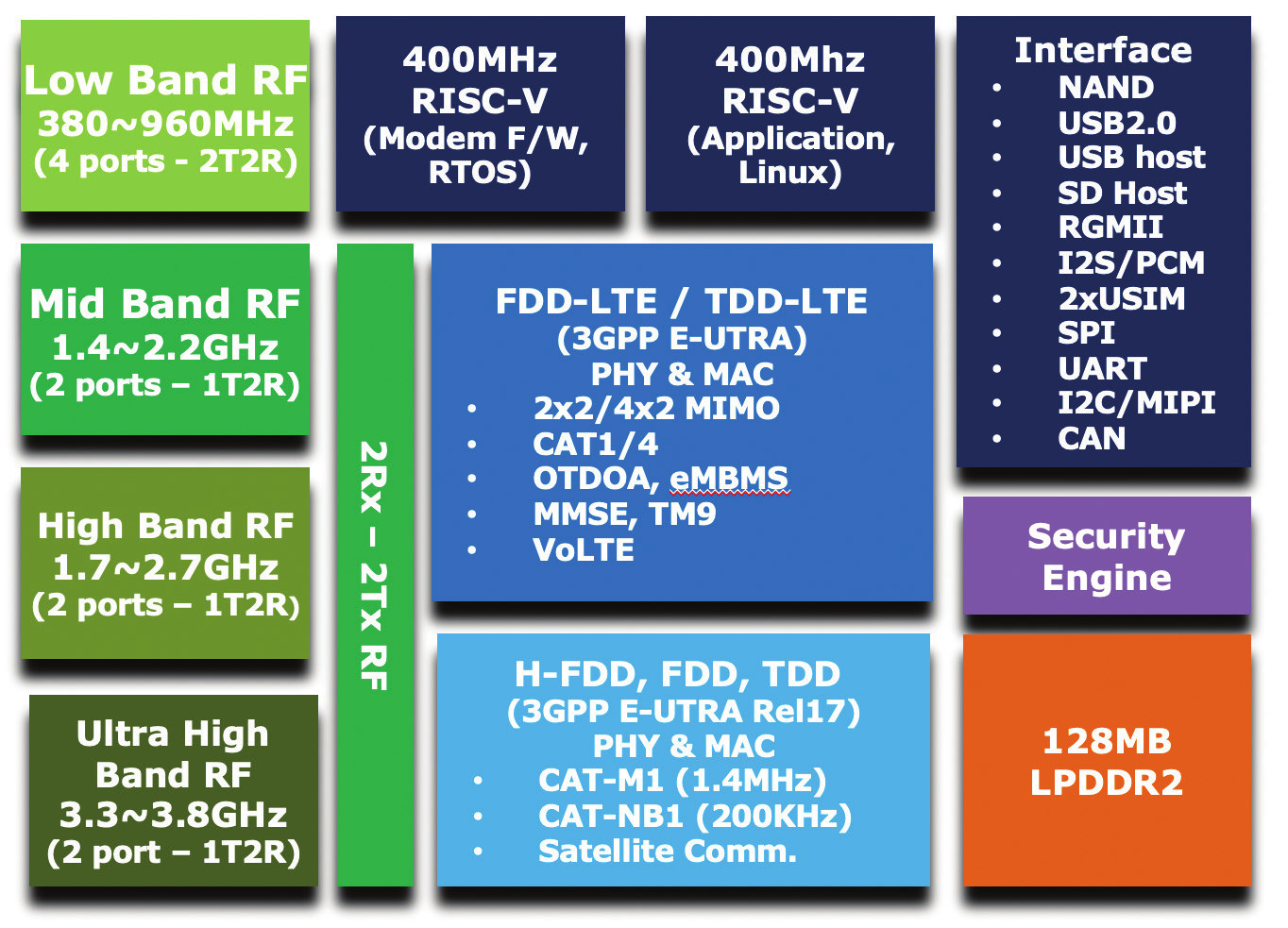
GCT GDM7243SL is a dual-core RISC-V 5G/4G LTE modem with support for NTN, NB-IoT, LTE Cat M, Cat1bis, Cat1 and/or Cat4
CT Semiconductor Holding GDM7243SL is a multi-mode 5G/4G LTE IoT modem with two 400 MHz RISC-V cores capable of operating in Cat 4, Cat 1bis, Cat M1, Cat NB1/NB2 (NB-IoT) and non-terrestrial networks (NTN) in order to work anywhere on earth. If I remember correctly, one of the first commercial RISC-V SoCs I saw was a storage controller from Western Digital introduced in 2019. But since then, we’ve seen more and more RISC-V chips come to market from entry-level microcontrollers up to Linux-capable application processors, and even chips for datacenters that are out of the scope of topics covered on CNX Software. But with GDM7243SL, I think it’s the first time I’ve encountered a RISC-V modem, so let’s have a closer look. There are two models, the GDM7243SL1 and GDM7243SL2, with different memory and storage options, and the L1 lacks support for LTE Cat 4. GDM7243SL key features: CPU 400 […]
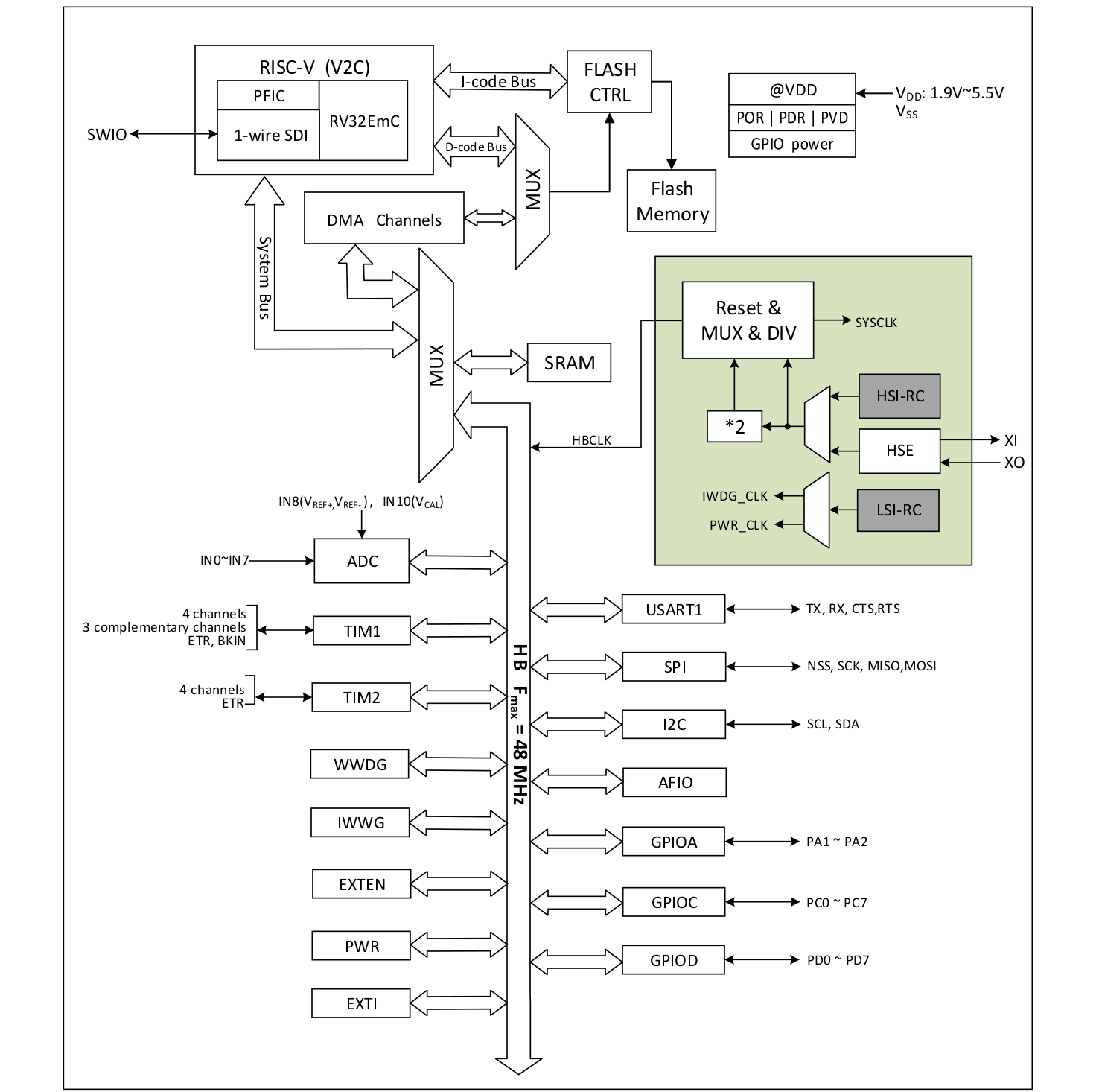
WCH CH32V002 32-bit RISC-V MCU comes with 4KB SRAM, supports 2V to 5V DC supply voltage
WCH CH32V002 is an industrial-grade general-purpose 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller that is pin-to-pin compatible with the popular CH32V003 MCU with 4KB SRAM instead of 2KB, a wider input voltage range from 2V to 5V, and other improvements. Earlier this month we wrote about the WCH CH32V006 RISC-V microcontroller that offers an upgrade to the CH32V003 with more I/Os, memory, and storage, requiring a new PCB layout. But now, the Chinese company has unveiled a pin-compatible alternative with the CH32V002 that adds more SRAM, uses the new V2C core with RV32EmC instruction set (also used in the CH32V006), offers a larger bootloader and configuration memories, upgrades the ADC to 12-bit, and adds support for 8-channel touch-key channel detection. WCH CH32V002 specifications (highlights in bold show differences against the CH32V003): CPU – 32-bit “RISC-V2C” core up to 48 MHz using RV32EmC instruction set Memory – 4KB SRAM Storage – 16KB flash, 3328 Bytes […]
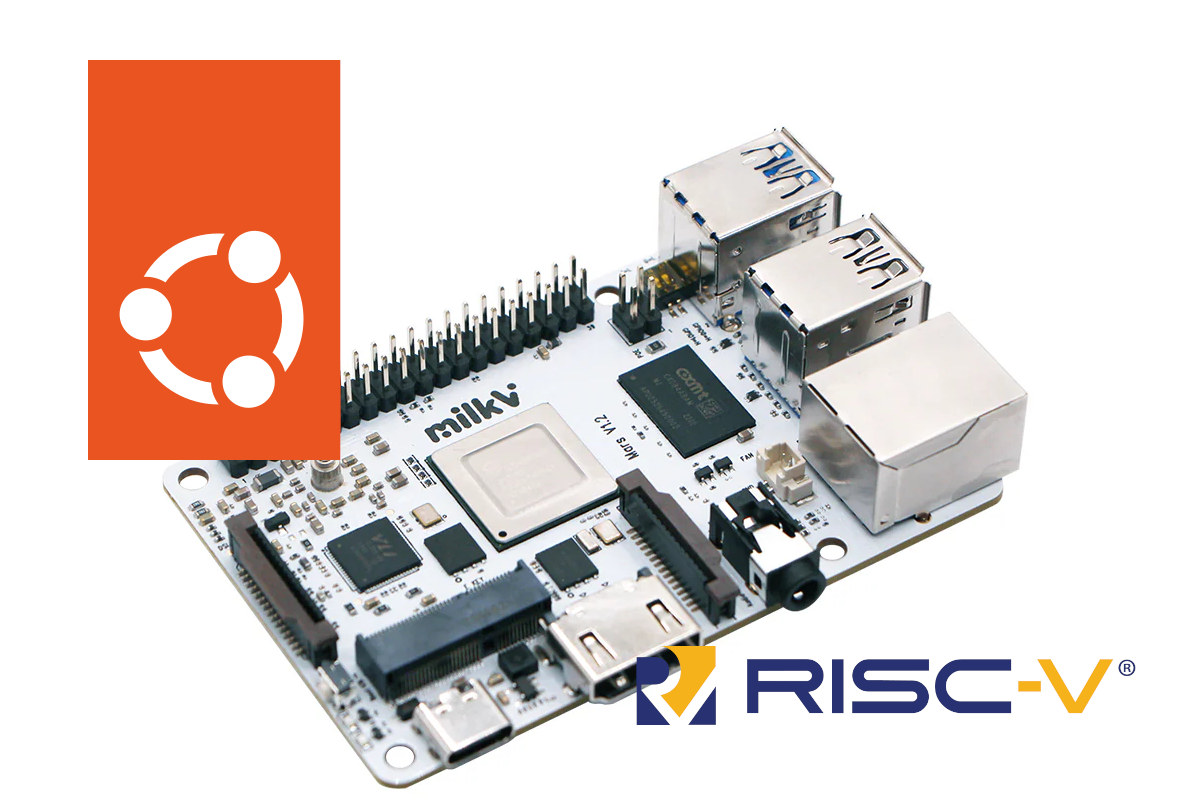
Canonical releases Ubuntu 24.04 Server image for Milk-V Mars RISC-V SBC
Canonical has been releasing Ubuntu RISC-V images for SBCs and QEMU at least since 2021. The latest addition is an Ubuntu 24.04 Server image for the Mars credit-card-size SBC powered by StarFive JH7110 quad-core RISC-V SoC and designed by Shenzhen Milk-V Technology. That means we now have Ubuntu Server images for the QEMU emulator, AllWinner Nezha SBC, Microchip Polarfire SoC FPGA Icicle Kit, SiFive Unmatched mini-ITX motherboard, Sipeed LicheeRV Dock, StarFive VisionFive 2 SBC, and the Mars SBC. You’ll note there aren’t any Ubuntu Desktop images for now, because the GPU (if any) in RISC-V SoCs is not yet fully supported. Mars SBC specifications: SoC – StarFive JH7110 CPU – Quad-core RISC-V processor (RV64GC) at up to 1.5GHz GPU – Imagination BXE-4-32 GPU with support for OpenCL 1.2, OpenGL ES 3.2, Vulkan 1.2 VPU H.264 & H.265 4Kp60 decoding H.265 1080p30 encoding JPEG encoder / decoder System Memory – 1GB, […]
Linux 6.9 release – Main changes, Arm, RISC-V, and MIPS architectures
Linus Torvalds has just announced the release of Linux 6.9 on LKML: So Thorsten is still reporting a few regression fixes that haven’t made it to me yet, but none of them look big or worrisome enough to delay the release for another week. We’ll have to backport them when they get resolved and hit upstream. So 6.9 is now out, and last week has looked quite stable (and the whole release has felt pretty normal). Below is the shortlog for the last week, with the changes mostly being dominated by some driver updates (gpu and networking being the big ones, but “big” is still pretty small, and there’s various other driver noise in there too). Outside of drivers, it’s some filesystem fixes (bcachefs still stands out, but ksmbd shows up too), some late selftest fixes, and some core networking fixes. And I now have a more powerful arm64 machine […]
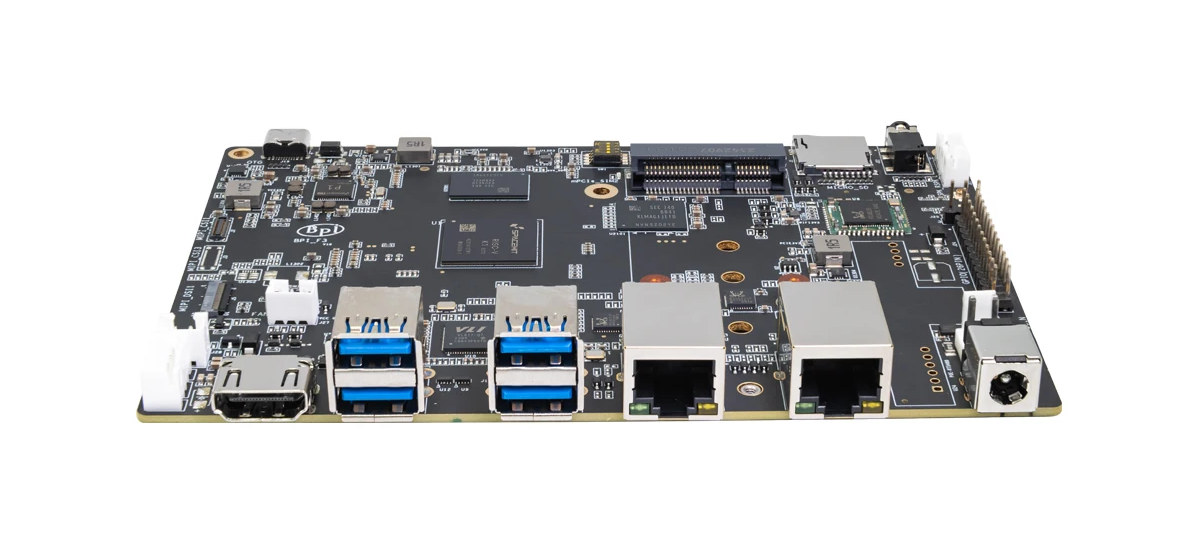
Banana Pi BPI-F3 SBC features SpacemIT K1 octa-core RISC-V AI SoC
Banana Pi BPI-F3 single board computer (SBC) is powered by the same SpacemiIT K1 octa-core 64-bit RISC-V SoC with 2TOP AI accelerator found in the upcoming Muse Book RISC-V laptop. The board comes with up to 4GB RAM and 16GB eMMC flash, supports NVMe or SATA storage via its M.2 socket, is equipped with HDMI and MIPI DSI display interfaces, two MPI CSI camera interfaces, two gigabit Ethernet ports, a WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 4.2 module, and can also take a PCIe module for 4G LTE cellular connectivity. Other features include four USB 3.0 Type-C ports, a microSD card slot, a 26-pin GPIO header, and optional support for PoE. Banana Pi BPI-F3 specifications: SoC – SpacemiT K1 CPU – 8-core X60 RISC-V processor with single-core performance equivalent to about 1.3x the performance of an Arm Cortex-A55 GPU – Imagination IMG BXE-2-32 with support for OpenCL 3.0, OpenGL ES3.2, Vulkan 1.2 […]