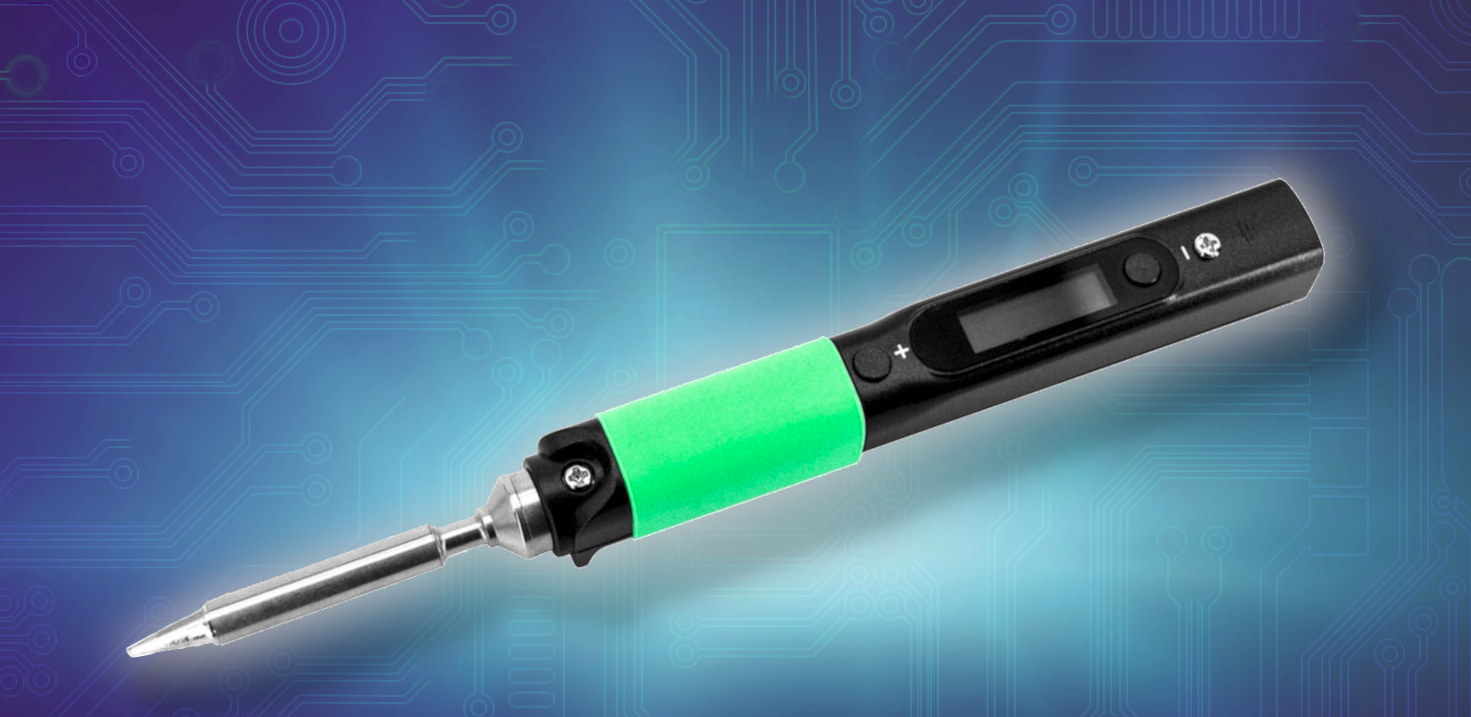
PINE64 is about to launch the second generation Pinecil RISC-V soldering iron with the Pinecil V2 featuring a new Bouffalo Lab BL706 RISC-V microcontroller with Bluetooth LE connectivity, optimizations for higher power levels, as well as tentative support for the new USB PD EPR standard (Extended Power Range) working at up to 28V. I don’t solder every day, but when I do, I use my Pinecil soldering iron, as it’s heating super fast and does the job, and in my case, works quite better than the TS100 soldering iron. So it should come as no surprise that the Pincel is the most popular consumer hardware from the PINE64 community (after SOPine modules), and the new Pinecil V2 is a welcome upgrading building on the same design but with Bluetooth LE connectivity and a lower tip resistance. Pinecil V2 preliminary specifications: MCU – Bouffalo Lab BL706 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller @ 144 […]
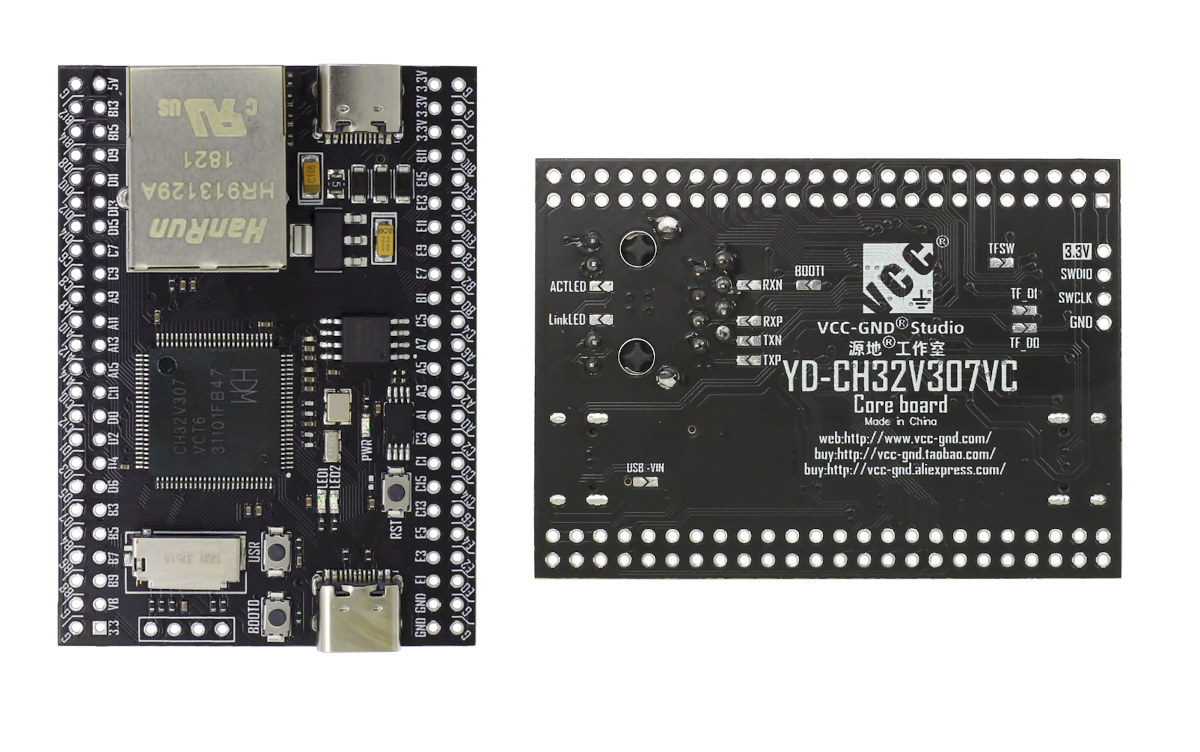
YD-CH32V307VCT6 RISC-V MCU board comes with Ethernet and plenty of I/Os
At the beginning of the year, we wrote about WCH CH32V307 RISC-V microcontroller and a development board with 8 UART ports controlled over Ethernet. I’ve now been informed of a similar, but much more compact by VCC-GND Studio named “YD-CH32V307VCT6”. Besides the 144 MHz RISC-V microcontroller, the board features a 10Mbps Ethernet port, two USB Type-C ports, SPI flash, EEPROM, a microSD card socket, and four rows of 24 pins each for a total of 96 pins exposing all pins out of the LQFP100 package. YD-CH32V307VCT6 board specifications: MCU – WCH CH32V307VCT6 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller @ 144 MHz with 256K Flash, 64K SRAM Storage – 32Mbit SPI NOR flash (W25Q32), 64kbit EEPROM (24C64), MicroSD card slot Networking – 10 Mbps Ethernet USB – 1x USB 2.0 Type-C port (High Speed: 480 Mbps), 1x USB 2.0 Type-C port (Full Speed: 12 Mbps) Expansion – 2x 48-pin headers with 2 x 12-bit […]
RISC-X? Top Chinese scientist discusses potential for RISC-V fork in extreme case
Is RISC-X next? Bao Yungang, a professor and scientist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the secretary-general of the China RISC-V Alliance, has suggested RISC-V related standard specifications can be bifurcated into a new RISC-X standard independently developed in China for the “Belt and Road” countries. [Update July 9, 2022: The title has been updated, as Bao Yungang only answered a hypothetical question, and the screenshot below from a slack (maybe internal) shows SCMP may have misunderstood his meaning, and China would have no need to fork RISC-V based on how licensing works. I’ve also been given the link to Bao Yungang’s Zhuhi account, and there’s no mention of “RISC-X”. I’ve left the rest of the post unchanged for reference and general discussion about the topic] The world has become more complicated with new sanctions imposed nearly every week, and those include not only primary sanctions but also secondary […]
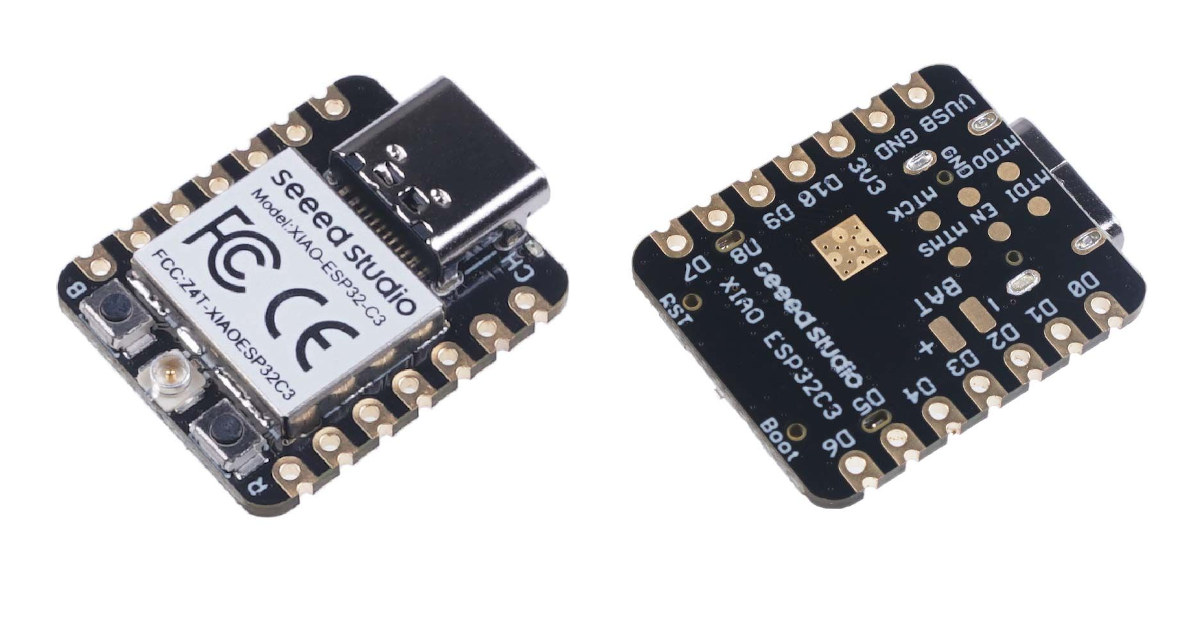
Seeed Studio outs $5 XIAO ESP32C3 board with WiFi and BLE, battery support
Seeed Studio’s XIAO family of tiny MCU boards expands with the XIAO ESP32C3 board equipped with ESP32-C3 WiFi and Bluetooth LE (BLE) microcontroller, support for LiPo batteries, and following the same 21 x 17.5mm form factor. If I’m counting right, this is the fifth member following the original XIAO based on Microchip SAMD21G18 Cortex-M0+ MCU, XIAO RP2040, and the nRF52840-based XIAO BLE and XIAO BLE Sense boards which I tested with Edge Impulse. XIAO ESP32C3 specifications: Wireless MCU – Espressif Systems ESP32-C3 single-core RISC-V microcontroller @ 160 MHz with 400KB SRAM, 384KB ROM, 4MB flash Wi-Fi 4 & Bluetooth LE 5.0 connectivity Antenna – External u.FL antenna USB – USB Type-C port for power and programming Expansion I/Os 2x 7-pin headers with 1x UART, 1x I2C, 1x SPI, 11x GPIO (PWM), 4x ADC, I2S 3.3V I/O voltage (not 5V tolerant) Debugging – JTAG pads Misc – Reset button, Boot button, […]
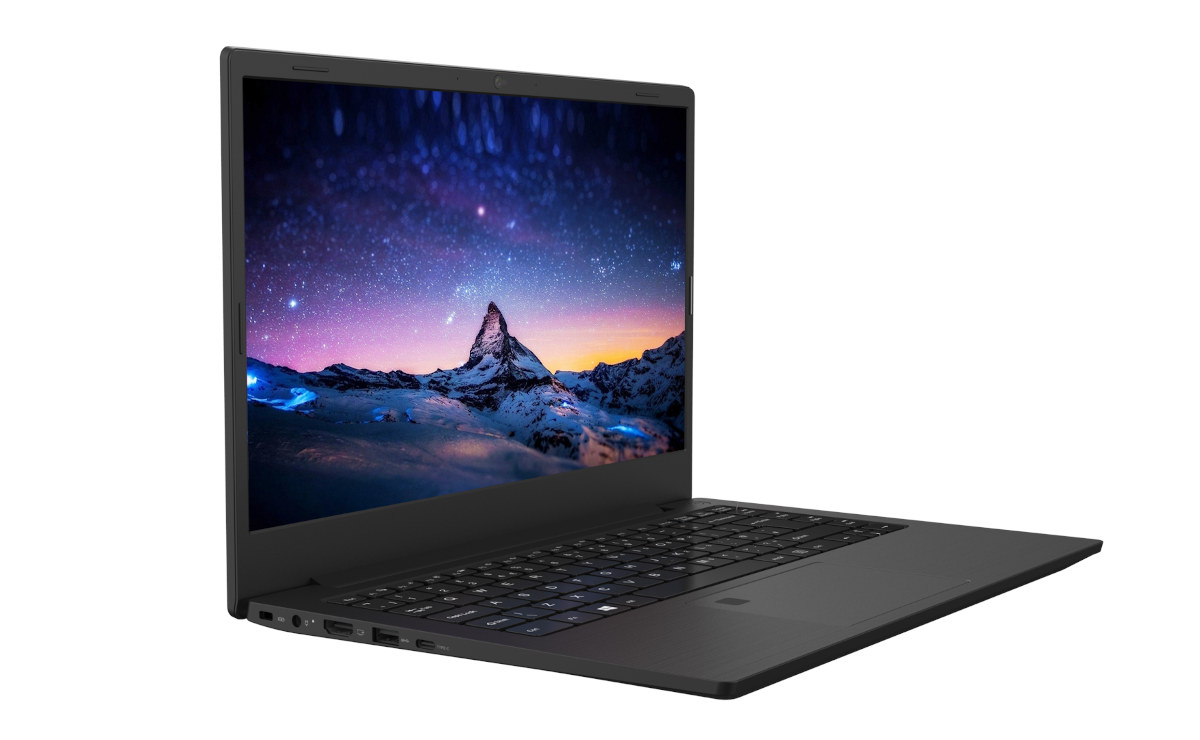
ROMA Linux laptop to feature quad-core RISC-V SoC, support Web3, NFT, cryptocurrencies, etc…
ROMA is an upcoming Linux laptop equipped with an unnamed quad-core RISC-V processor with GPU and NPU, up to 16GB RAM, 256GB storage, primarily aimed at software developers, and with Web3 technology integration. The ROMA laptop will be born out of the collaboration between DeepComputing working on engineering and Xcalibyte taking care of system tuning, plus PW (assembly), ECP (security), XC (crypto), Rexeen (voice), and the LatticeX Foundation (PoS blockchain, NFT). ROMA laptop preliminary specifications: SoC – Quad-core RISC-V CPU with GPU for graphics, NPU for AI (12nm chip for the Pro model, 28nm chip for the Standard model) System Memory – 16GB LPDDR4/LPDDR4X RAM Storage – 256GB eMMC flash Security – Arm SC300 security enclave processor Display, keyboard, touchpad I agree that’s a bit light on details. We’re told the laptop will support most Linux operating systems and the company will offer free SoC and SoM upgrades, as well […]
A RISC-V laptop or mini PC with Rockchip RK3588-class performance may be coming soon
Mark Himelstein, Chief Technology Officer, RISC-V International, and Dr. Philipp Tomsich, Chief Technologist & Founder, VRULL GmbH hinted that we may see a RISC-V laptop in 2022 in a presentation entitled “From Technology to Product – Maturing the RISC-V Ecosystem” with one of the slides showing what could be a RISC-V laptop prototype and The Register suspected it might come from the Institute of Software at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISCAS) since it was planning to build 2,000 RISC-V laptops by the end of 2022. But there’s at least one more potential RISC-V laptop project coming our way with StarFive asking users to fill out a survey about a laptop, mini PC, or development board/SBC based on a RISC-V SoC with performance comparable to Rockchip RK3588 or MediaTek MT8192 octa-core Cortex-A76/Cortex-A55 processors. The hardware and software specifications of the device will depend on the answers to the survey. First, it’s […]
Imagination unveils IMG RTXM-2200 32-bit RISC-V real-time “Catapult” CPU
Imagination IMG RTXM-2200 32-bit RISC-V real-time CPU core is the first member of the company’s Catapult family comprised of four distinct RISC-V families for dynamic microcontrollers, real-time embedded CPUs, high-performance application CPUs, and functionally safe automotive CPUs. The company says it’s a highly scalable real-time, deterministic, 32-bit embedded CPU, that is feature-rich and flexible in design for mainstream devices, but, excuse the pun, leaves most of the details to your imagination… The new core will mostly be used as a helper core (aka co-processor) in more complex SoCs for 5G modems, cellular base stations, networking solutions for data transfer, packet management, and storage controllers, but may also find its way into smart meters. In all fairness, we do have some limited technical details with L1 cache sizes up to 128KB, I/D TCM sizes up to 128KB, and PMA regions. The real-time core will also include optional features such as single-point […]
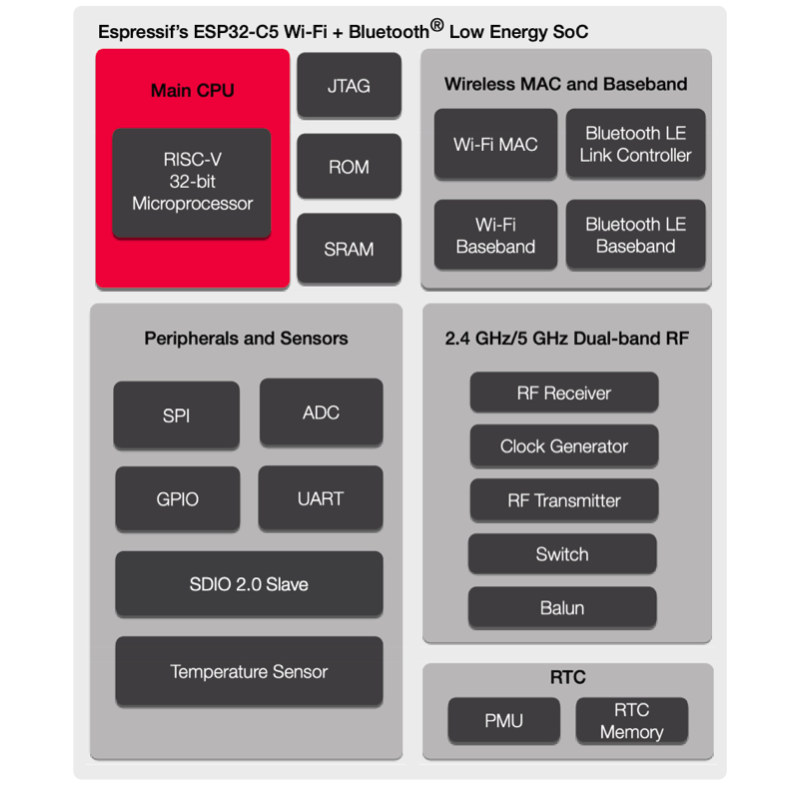
ESP32-C5 RISC-V IoT MCU supports dual-band WiFi 6, Bluetooth 5.0 LE
Espressif Systems ESP32-C5 is an upcoming wireless RISC-V microcontroller for IoT applications that supports dual-band (2.4 & 5.0 GHz) WiFi 6 connectivity as well as Bluetooth 5.0 LE. It is the first dual-band processor from Espressif, as while the Shanghai-based company previously announced the ESP32-C6 WiFi 6 and Bluetooth 5 LE RISC-V SoC last year, it only supports 2.4 GHz frequency. Note it’s not the first dual-band WiFi 6 IoT chip on the market as NXP introduced the IW612 Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.2, 802.15.4 tri-radio solution last January, but ESP32-C5 should target different use cases. ESP32-C5 preliminary specifications: CPU – Single-core 32-bit RISC-V processor @ up to 240 MHz Memory – 400KB SRAM on-chip Storage – 384KB of ROM on-chip, support for external flash Connectivity Dual-band 802.11ax WiFi 6 in the 2.4GHz and 5 GHz bands, with 802.11b/g/n WiFi 4 standard support for backward compatibility 20MHz bandwidth for the 802.11ax […]