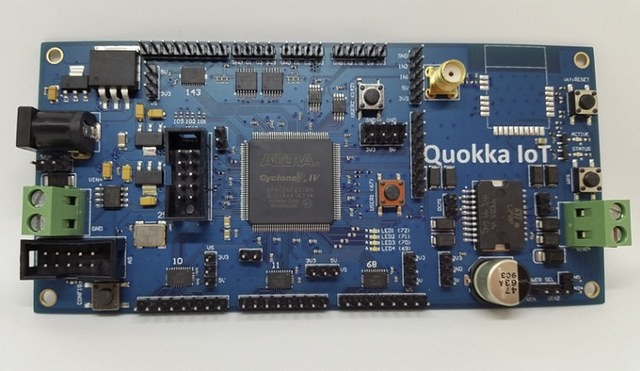
Quokka FPGA IoT Controller is a board based on Altera Cyclone IV FPGA with a WiPy module for connectivity, and various I/Os that allows you to make robotics projects for example. While you could program the FPGA using VHDL, the developer – Evgeny Muryshkin – also designed Quokka Development Toolkit (QDT), a cloud-based SaaS, allowing to program FPGA with a high-level programming language, currently C#, so that software people can more easily become involved in FPGA development. Quokka IoT (preliminary) hardware specifications: FPGA – Intel Altera Cyclone IV, 6K logic elements, EP4CE6E22C8 Clock – 50MHz Connectivity – WiFi via WiPy module Expansion 40x GPIO (3 banks by 8 pins, with direction and voltage (3.3V or 5V) configuration, 16 raw IO pins 3.3V) 2x Dual Channel 10 bit ADC (3.3V) 2x Dual Channel 10 bit DAC (3.3V) H-Bridge for DC motors with support for external power Power Supply – 5-24V DC input […]
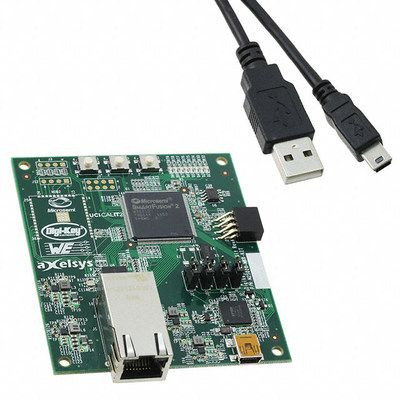
$34 SmartFusion2 Maker Board Arm Cortex-M3 + FPGA Board Supports ESP32 & ESP8266 Modules
Xilinx Zynq SoCs are probably the most well-known FPGAs with ARM cores, as their Cortex A9/A53 cores can run Linux, but they are not the only ones. Microsemi launched SmartFusion2 SoC comprised of FPGA fabric and an Arm Cortex-M3 core in 2013, as well as a $300 development kit. The company has now partnered with Digikey to launch SmartFusion2 Maker Board, a low-cost evaluation platform for the SoC that comes with Gigabit Ethernet, a USB port, a connector for ESP8266 module, PCB footprint for ESP32 module, among other features like a light sensor, LEDs, and buttons. SmartFusion2 maker board (M2S010-MKR-KIT) main features & specifications: SoC – Microsemi SmartFusion2 M2S010 SoC with: Arm Cortex-M3 @ 166 MHz, 6oKB+80KB eSRAM, 256KB eNVM FPGA with 12,084 logic element, 400 Kbits RAM Storage – 16 Mbit SPI Flash Connectivity Gigabit Ethernet via VSC8541 PHY, RJ45 connector Connector for ESP8266 (Sparkfun WRL-13678 – not included) […]
Apertus AXIOM Beta Open Source Professional Digital Cinema is Built around MicroZed Board
Apertus AXIOM Beta is a professional digital cinema camera built around FOSS (Free and Open Source Software) and open hardware licenses. The project started around year 2011 with AXIOM Alpha camera, and AXIOM Beta is the latest iteration powered by MicroZed development board based on Xilinx Zynq 7020 ARM + FPGA SoC, and running Arch Linux ARM. AXIOM Beta developer kit (planned) hardware specifications: “Linux” Board – Xilinx Zynq 7020 based MicroZed board Beta Main Board – Hosts two external medium-speed shield connectors and two high-speed plugin module slot connectors. Image Sensor – 12MP CMV12000 (Used for research and development) via CMV12K ZIF Sensor Board Lens Mount Passive E-mount Ports – USB / USB UART / JTAG / Gigabit Ethernet Modules and Shields Single HDMI Full HD (4:4:4) output at up to 60 FPS Dual 6G SDI output (in development) 3x PMOD debug module LED matrix debug module Genlock, Trigger, […]
Intel Stratix 10 MX FPGA Integrates High Bandwidth Memory DRAM (HBM2)
Intel started sampling (Altera) Stratix 10 ARM + FPGA SoC in late 2016, and now the company has announced the availability the new Stratix 10 MX FPGA family wih High Bandwidth Memory DRAM (HBM2). The latter allow Stratix 10 MX FPGAs to offer up to 10 times the memory bandwidth when compared with standalone DDR memory solutions. The higher bandwidth will be useful for multi-function accelerators for high-performance computing (HPC), data centers, network functions virtualization (NFV), and broadcast applications. Intel / Altera Stratix 10 MX SoC key features and specifications: Processor – Quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 MP Core up to 1.5 GHz Logic Density Range – 1.092M LE to 2.073M LE Embedded Memory 3.5 to 8GB HBM2 high-bandwidth DRAM memory 45 Mbit to 90 Mbit eSRAM memory 86 Mbit to 134 Mbit M20K memory 6 Mbit to 11 Mbit MLAB memory Up to 7,920 18 x 19 Multipliers Up to 72 […]
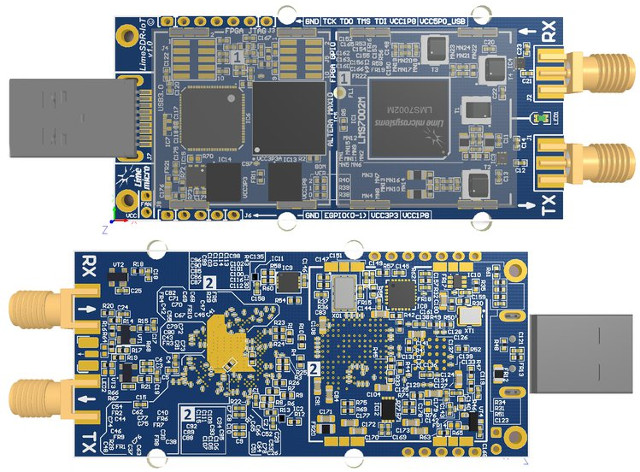
LimeSDR Mini is a $135 Open Source Hardware, Full Duplex USB SDR Board (Crowdfunding)
LimeSDR open source hardware software defined radio was launched last year with the promise of integration with Ubuntu Snap Store allowing to easily download and install various radio implementations such as LTE, WiFi, Bluetooth, LoRa, etc… It was offered for $200 and up as part of a crowdfunding campaign, but Lime Microsystems is back on CrowdSupply with a cheaper and low end version aptly called LimeSDR Mini.LimeSDR mini specifications: FPGA – Intel Altera Max 10 (10M16SAU169C8G) with 16K Logic gates, 549 KB M9K memory, 2,368 KB user flash memory Storage – 4 MB flash memory for data; 2x128KB EEPROM for RF transceiver MCU firmware and data RF Lime Microsystems LMS7002M RF transceiver Tx & Rx SMA connectors Frequency range – 10 MHz to 3.5 GHz RF bandwidth – 30.72 Mhz Sample Rate – 30.72 MSps with 12-bit sample depth Power Output (CW): up to 10 dBm USB – 1x USB […]
Embedded Linux Conference & Open Source Summit Europe 2017 Schedule
The Embedded Linux Conference & IoT summit 2017 took place in the US earlier this year in February, but there will soon be a similar event with the Embedded Linux Conference *& Open Source Summit Europe 2017 to take up in Europe on October 23 – 25 in Prague, Czech Republic, and the Linux Foundation has just published the schedule. It’s always useful to find out what is being discussed during such events, even if you are not going to attend, so I went through the different sessions, and compose my own virtual schedule with some of the ones I find the most interesting. Monday, October 23 11:15 – 11:55 – An Introduction to SPI-NOR Subsystem – Vignesh Raghavendra, Texas Instruments India Modern day embedded systems have dedicated SPI controllers to support NOR flashes. They have many hardware level features to increase the ease and efficiency of accessing SPI NOR […]
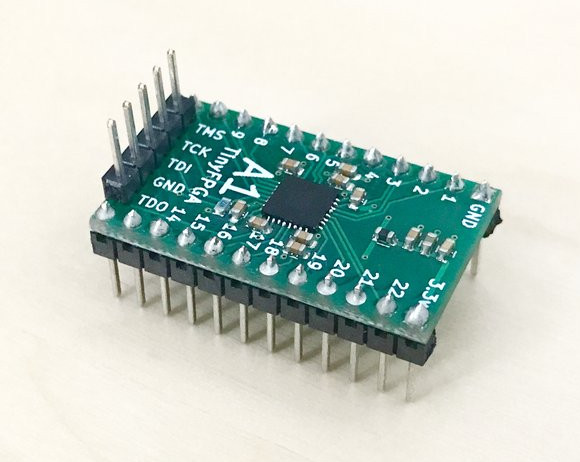
TinyFPGA is a Breakout Board for Lattice Semi MachXO2 FPGA
We’ve covered several low cost FPGA boards over the years, but if you want a platform with the bare minimum, you may be interested in tinyFPGA breakout board based on Lattice Semi MachXO2 FPGA board that comes with two flavors: A1 with MachXO2-256, and A2 with the more powerful MachXO2-1200 FPGA. TinyFPGA board specifications: FPGA A1 board – Lattice MachXO2-256 with 256 LUTs, 2 kbits distributed RAM A2 board – Lattice MachXO2-1200 with 1280 LUTs, 10 kbits distributed RAM, 64 kbits EBR SRAM, 64 kbits flash memory, and a PLL (See datasheet for MachXO2 family) Built-in flash configuration memory programmable via JTAG I/Os 18 user IOs (21 with JTAGEN) 1x SPI Hard-IP 2x I2C Hard-IPs A2 board only – 1x PLL Hard-IP Power Supply – 3.3V Dimensions – ~3.05 x 1.8 cm You’ll need a JTAG programmer for Lattice FPGA as well as Lattice Diamond software – available for Windows […]
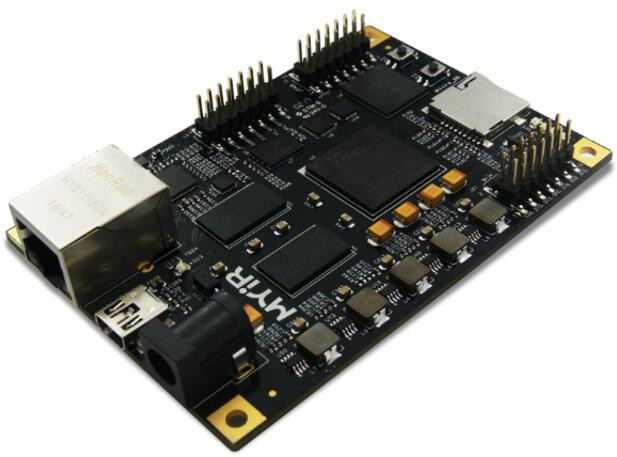
MYiR Introduces Z-Turn Lite Board Powered by Xilinx Zynq-7007S/Zynq-7010 SoC for $69 and Up
Xilinx launched a cost down version of their Zynq-7000 series with Zynq-7000S series SoC combining a single ARM Cortex A9 core with Artix FPGA fabric last year. We’ve already seen sub 100 Euros/Dollars board based on the new SoCs with ZynqBerry and MiniZed boards. MYiR Tech has now launched their own version, a cost-down version of their Z-Turn board, with Z-Turn Lite board featuring either the new cost-down Zynq-7007S or the “good old” Zynq-7010 SoC. Z-Turn Lite specifications: SoC Xilinx XC7Z007S-1CLG400C (Zynq-7007S) with a single ARM Cortex A9 core @ 667 MHz, Artix-7 FPGA fabric with with 23K logic cells, 14,400 LUTs, 66 DSP slices OR Xilinx XC7Z010-1CLG400C (Zynq-7010) with two ARM Cortex A9 cores @ 667 MHz, Artix-7 FPGA fabric with 28K logic cells, 17,600 LUTs, 80 DSP slices. System Memory – 512 MB DDR3 SDRAM (2 x 256MB, 32-bit) Storage – 4GB eMMC flash, 16MB QSPI flash, and […]